Topics:
1. Hybrid Nanoparticles by IISC Bengaluru to detect and kill Cancer Cells
2. Picoflare Jets
3. Gresham’s Law
4. Matsaya 6000 – India’s deep sea submersible
5. Tribal Artisanal in G-20
6. Falling Cotton Production in India
Hybrid Nanoparticles by IISC Bengaluru to detect and kill Cancer Cells
Central Idea:
- Researchers at the Indian Institute of Science (IISc) have introduced an innovative approach with the potential to identify and eradicate cancer cells, particularly those that form solid tumor masses.
Gold and Copper Sulfide Nanoparticles:
- In a groundbreaking development, scientists at IISc have designed hybrid nanoparticles by combining gold and copper sulfide.
- These nanoparticles possess multiple functions that hold significant promise for cancer detection and treatment.
Photothermal and Oxidative Properties:
- These nanoparticles display remarkable photothermal capabilities, absorbing light and converting it into heat to effectively eliminate cancer cells.
- Additionally, they generate singlet oxygen atoms, further enhancing their toxic effects on cancer cells.
Utilizing Dual Mechanisms:
The nanoparticles utilize both photothermal and oxidative mechanisms to efficiently target and eliminate cancer cells.
Revolutionizing Cancer Diagnosis:
- Beyond their potential in cancer treatment, these hybrid nanoparticles offer considerable promise in cancer diagnosis.
- They leverage their photoacoustic property to absorb light and generate ultrasound waves.
Enhanced Detection:
The ultrasound waves significantly enhance the contrast for detecting cancer cells once the nanoparticles reach them, providing superior image resolution compared to conventional CT and MRI scans.
Improved Clarity and Oxygen Saturation Measurement:
Scans produced through ultrasound waves offer enhanced clarity and the capability to measure oxygen saturation within tumors, thereby improving the accuracy of cancer detection.
Seamless Integration with Existing Systems:
- The nanoparticles can seamlessly integrate with current detection and treatment systems.
- For instance, they can be employed alongside endoscopes used for cancer screening to induce localized heat generation with focused light.
Overcoming Size Limitations:
The hybrid nanoparticles, measuring less than 8 nm in size, possess a crucial advantage in terms of their mobility within tissues and their ability to reach tumors.
Potential for Safe Elimination:
- Due to their diminutive size, researchers anticipate that these nanoparticles may naturally exit the human body without accumulating.
- Nonetheless, extensive safety studies are imperative to confirm their suitability for internal use.
Successful Lab Testing:
In laboratory experiments, the researchers conducted effective tests using these nanoparticles on lung and cervical cancer cell lines, illustrating their considerable potential.
Progress Toward Clinical Development:
The promising outcomes from this study propel these nanoparticles closer to the prospect of clinical development.
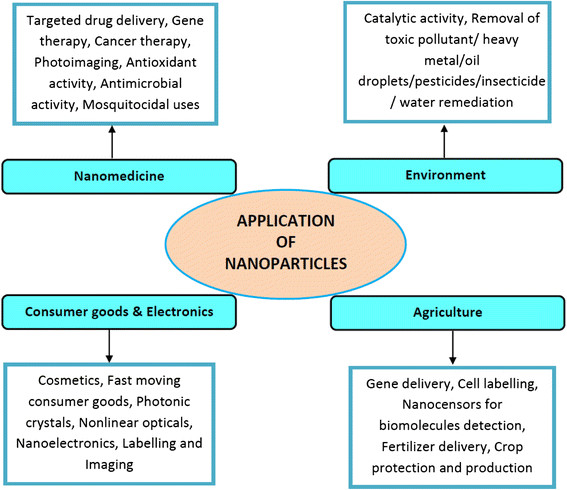
Basics
Nanoparticle: A nanoparticle is an extremely small, solid particle with dimensions typically ranging from 1 to 100 nanometers, possessing unique properties and behaviors due to its minuscule size.
Picoflare Jets
Introduction:
- In a recent breakthrough facilitated by the Solar Orbiter Aircraft, a collaborative initiative between the European Space Agency and NASA, the enigmatic Picoflare jets emerging from the sun’s outer atmosphere have been brought into the spotlight.
- These extraordinary jets, characterized by their supersonic emergence and brief durations lasting between 20 to 100 seconds, have captured the fascination of scientists and space enthusiasts alike.
Understanding Picoflare Jets:
- Picoflare jets, observed within the emissions emanating from the coronal hole, may be diminutive in scale, but their impact is far from trivial.
- Despite their fleeting existence, these jets play a significant role in energizing solar winds.
- Their name, “picoflare jets,” stems from their energy levels, which hover at an astonishing one-trillionth of the energy potential exhibited by solar flares.
- Solar winds, propelled by these strong gusts, not only contribute to the formation of auroras in Polar Regions but also have the potential to disrupt Earth’s magnetic field and pose risks to electronic systems on satellites and terrestrial circuits.
The Solar Orbiter Aircraft:
- Launched in 2020, the Solar Orbiter Aircraft embarks on an ambitious mission to capture unprecedented images of the Sun, venturing closer to it than any previous spacecraft.
- This remarkable endeavor is equipped with six remote-sensing instruments and four sets of in situ instruments, making it ideally suited for comprehensive solar exploration.
Mission Objectives:
- The Solar Orbiter Aircraft is driven by two primary mission objectives.
- Firstly, it seeks to meticulously scrutinize the Sun’s 11-year cycle of magnetic activity, unraveling its ebbs and flows.
Secondly, it endeavors to delve into the mysteries shrouding the solar corona, the uppermost layer of the Sun’s atmosphere, shedding light on hitherto unexplored facets of our celestial neighbor.
GRESHAM’S LAW
Context:
- In the informal economy of India, the concept of Gresham’s Law holds relevance due to the coexistence of counterfeit currency and substandard coins alongside genuine money, which has an impact on the overall value of the currency in circulation.
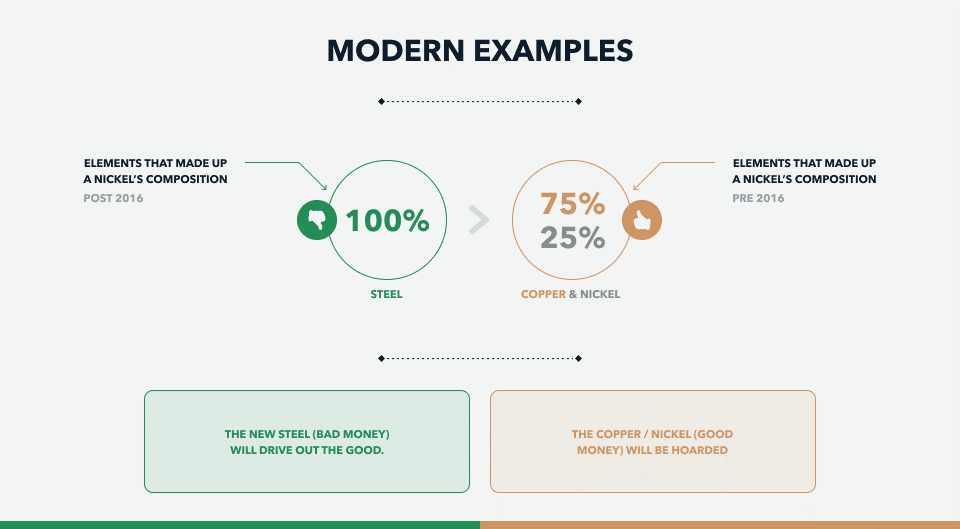
- Gresham’s Law, succinctly stated as “bad money drives out good,” comes into play when a government fixes the exchange rate between two currencies at a ratio different from the market exchange rate.
- This government-imposed price fixing results in the undervalued currency, the one pegged below the market rate, being phased out of circulation.
- Conversely, the overvalued currency continues to circulate but encounters difficulty finding buyers. The law takes its name from the English financial expert, Thomas Gresham, who provided counsel on financial matters to the English monarchy.
- It is important to note that the market exchange rate represents an equilibrium price where the currency supply matches its demand.
- The supply of a currency increases as its price rises and decreases as its price falls. Conversely, the demand for a currency decreases as its price rises and increases as its price falls.
- Therefore, when a government fixes a currency’s price below the market exchange rate, the supply of that currency decreases while its demand surges. Consequently, price controls can result in a scarcity of the currency, with demand outpacing supply.
- A recent instance of Gresham’s Law in action occurred during the economic crisis in Sri Lanka last year when the Central Bank of Sri Lanka pegged the exchange rate between the Sri Lankan rupee and the U.S. dollar.
Example:
In India, both one-rupee notes and one-rupee coins are considered legitimate forms of currency.
However, at times, the public exhibits a preference for one form of a particular denomination over another, such as favoring the paper note over the coin.
When such a preference arises for one form of currency over another, it serves as an illustration of Gresham’s Law in operation.
MATSAYA 6000 – INDIA’S DEEP SEA SUBMERSIBLE
Context: The government recently released images of India’s Matsya 6000 submersible on various social media platforms.
About Matsya 6000:
- Cutting-Edge Submersible Technology
- The Matsya 6000 stands as a remarkable underwater vessel, capable of accommodating three individuals and delving to depths of up to 6,000 meters beneath the ocean’s surface.
- The name “Matsya” finds its origin in Hindi, signifying ‘fish,’ and this impressive submersible is currently in development under the auspices of Chennai’s National Institute of Ocean Technology (NIOT).
- Key Features:
- Constructed from an 80mm-thick titanium alloy, the Matsya 6000 exhibits remarkable resilience, withstanding pressures equivalent to 600 times that of sea level.
- It’s worth noting that the use of titanium is a universal practice in all global research missions conducted in aquatic environments.
- Endurance and Precision:
- Operating continuously for an impressive duration of 12 to 16 hours, this submersible is also equipped with a 96-hour oxygen supply.
- Furthermore, it incorporates an advanced ultra short baseline acoustic positioning system (USBL), enabling communication between the submersible and its mothership, which carries the transponder.
- This feature facilitates precise tracking and positioning of the submersible, providing critical information to the mothership.
- Upcoming Trials:
- In the near future, the Matsya 6000 is slated to undergo trials in the Bay of Bengal, with the year 2024 earmarked for these crucial tests.
- This venture is part of India’s ambitious Samudrayaan project, designed to explore the mysteries of the deep sea.
- It’s essential to note that the Samudrayaan project is a component of India’s Deep Ocean Mission, which boasts a substantial budget of Rs 4,077 crores.
- Global Significance:
It’s worth highlighting that only a select group of nations—namely France, the United States, China, Russia, and Japan—have thus far succeeded in developing manned submersibles of this caliber.
Tribal Artisanal in G-20
Context:
- TRIFED, an integral part of the Ministry of Tribal Affairs, proudly presented India’s rich tribal heritage at the G20 Summit.
- The showcase included a diverse array of traditional crafts and cultural expressions, each representing the unique artistic traditions and skills of various tribal communities from across the country.
Highlights from the exhibition:
1.Longpi Pottery:
- Origin: Hailing from the village of Longpi in Manipur.
- Artisan Group: Crafted by the skilled Tangkhul Naga tribes.
- Technique: Notably, this pottery does not rely on a potter’s wheel; instead, artisans skillfully shape the clay by hand and molds.
- Products: Longpi Pottery is famous for its distinctive gray-black cooking pots, kettles, bowls, mugs, and nut trays.
- Innovation: The artisans are continuously exploring new design elements to expand their product range.
2. Chhattisgarh Wind Flutes
- Curated by: The Gond Tribe of Bastar in Chhattisgarh.
- Unique Feature: These wind flutes feature the ‘Sulur’ bamboo wind flute, known for its unique one-handed twirl that produces melodious tunes.
- Craftsmanship: Meticulous bamboo selection, hole drilling, and surface etching go into creating these beautiful musical instruments.
- Utility: These wind flutes serve utilitarian purposes, including animal control and cattle guidance.
3. Gond Paintings
- Artistic Expression: Reflecting the artistic brilliance of the Gond tribe, these paintings depict intricate stories connected to nature and tradition.
- Innovation: Gond artists have adapted their traditional art to contemporary mediums while retaining their signature dot-based techniques and vibrant color palette.
- Cultural Reflection: The paintings offer a glimpse into the tribe’s social milieu and their deep connection with their surroundings.
4. Gujarat Hangings:
- Curated by: The Bhil & Patelia Tribe in Dahod, Gujarat.
- Heritage: Stemming from an ancient Gujarat art form, these hangings originally featured dolls and cradle birds.
- Contemporary Touch: Today, they incorporate cotton cloth, recycled materials, mirror work, zari, stones, and beads, blending tradition with contemporary fashion.
5. Sheep Wool Stoles
- Crafted by: Tribes including Bodh, Bhutia, and Gujjar Bakarwal from Himachal Pradesh and Jammu & Kashmir.
- Design Evolution: These stoles have evolved from monochromatic to dual-colored designs, showcasing the artistry of the tribes.
- Techniques: The weaving process involves hand-operated looms with four pedals and stitching machines, resulting in intricate diamond, plain, and herringbone patterns.
- Labor-Intensive: Crafting these stoles is a labor-intensive process that exemplifies the skill and dedication of the tribal artisans.
6. Araku Valley Coffee:
- Origin: Hailing from the picturesque Araku Valley in Andhra Pradesh.
- Distinctive Qualities: This coffee is renowned for its unique flavors and sustainable cultivation practices.
- Sustainability: It is organically produced with meticulous oversight, from cultivation and harvesting to pulping and roasting, ensuring premium quality.
- Taste and Aroma: Araku Valley Coffee is celebrated for its rich flavor, invigorating aroma, and purity.
7. Rajasthan Artistry Unveiled (Mosaic Lamps, Ambabari Metalwork, and Meenakari Crafts):
- Heritage: Originating from Rajasthan, these art forms reflect the rich tribal heritage of the region.
- Glass Mosaic Pottery: These creations illuminate spaces with a kaleidoscope of colors, serving both aesthetic and functional purposes.
- Meenakari Crafts: Adorning metal surfaces with vibrant mineral substances, Meenakari showcases the intricate craftsmanship of Rajasthan.
- Metal Ambabari Craft: Extending beyond gold to silver and copper, this craft exhibits intricate enameling and celebrates Rajasthan’s cultural legacy.
8. Maheshwari Silk Sarees:
- Origin: These exquisite silk sarees hail from the town of Maheshwar in Madhya Pradesh, India.
- Distinctive Features: Renowned for their elegant and lightweight silk fabric, Maheshwari sarees typically feature distinctive motifs, zari work, and unique pallus.
- Blend of Tradition and Modernity: These sarees beautifully blend traditional craftsmanship with modern design, making them a timeless fashion statement.
- In presenting these treasures of tribal artistry and culture, TRIFED at the G20 Summit celebrated India’s diverse and vibrant tribal heritage while also promoting the livelihoods of these talented tribal artisans.
FALLING COTTON PRODUCTION IN INDIA
Introduction
In the realm of cotton farming in India, the pink bollworm (PWB) has emerged as a formidable adversary, posing significant challenges to cotton crops. Nevertheless, there is optimism surrounding the potential of innovative “mating disruption” technologies aimed at curbing this pest.
Understanding Mating Disruption Technology
Mating Disruption Strategy
Mating disruption is an inventive strategy that capitalizes on the utilization of sex pheromones to disrupt the mating process of male insects. These pheromones are natural chemical compounds emitted by insects to communicate with others of the same species.
Cotton Farming in India: Overview and Significance
Cotton’s Economic Role: Cotton cultivation in India plays a pivotal economic role, with a primary emphasis on the production of lint. In recent years, there has been a surge in the commercial importance of cottonseed and its by-products.
Cotton Composition: The composition of cotton encompasses lint or fiber (35-45%), seed (55-65%), seed oil (10-12%), and meal and hull (35-40%).
Climatic and Cultivation Factors
- Cotton is inherently a tropical and subtropical crop, with a growth cycle spanning 4-5 months.
- It thrives in temperatures ranging from 21°C to 28°C, and moderate rainfall between 50-75 cm is vital for its growth.
- Sunlight is particularly crucial during flowering and maturity stages.
- Black soil, known as Regur Soil, is the preferred soil type for cotton cultivation, and it is primarily grown during the Kharif season.
The Role of Bt Cotton in Modern Agriculture
- Genetically-Modified Cotton: Bt cotton stands as a prominent example of genetically-modified (GM) crops in India’s agricultural landscape. This variety of cotton is created by incorporating genes sourced from the soil bacterium Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt).
Combatting the American Bollworm: The Bt genes within this cotton variety code for proteins that are toxic to the deadly Helicoverpa armigera, also known as the American bollworm insect pest.
The Bt Cotton Revolution in India
Impressive Growth: Between the years 2000-01 and 2013-14, India witnessed an astounding growth in cotton production, specifically in terms of lint. Production figures nearly tripled, soaring from 140 lakh bales to an impressive 398 lakh bales.
Widespread Adoption: Presently, Bt cotton has secured its position in 95% of cotton-cultivated areas in India. Moreover, the average lint yields per hectare more than doubled from 278 kg in 2000-01 to a commendable 566 kg in 2013-14.
Recent Challenges and Decline in Cotton Production
Diminishing Returns: However, the subsequent years following the peak of Bt cotton’s success have witnessed a disheartening decline in both cotton production and yields. By 2022-23, cotton production had dwindled to 343.5 lakh bales, and lint yields per hectare had fallen to a mere 447 kg, raising concerns within the cotton farming community.