 |
||
| 15 April 2024 | ||
|
- Population Crisis in Asian Nations
- Mahad Satyagraha: A Milestone in the Dalit Movement
- Global Trade Projection and Analysis
- Exploring Cryogenics
- Understanding the Precautionary Principle
- Easementary Rights
- Operation Meghdoot: Securing Siachen Glacier
- Understanding Shrinkflation
Population Crisis in Asian Nations
Context;
Fertility rates have fallen below replacement levels in numerous Asian nations, particularly in East and Southeast Asia, leading to a population crisis characterized by dwindling birth rates and record-low fertility rates. 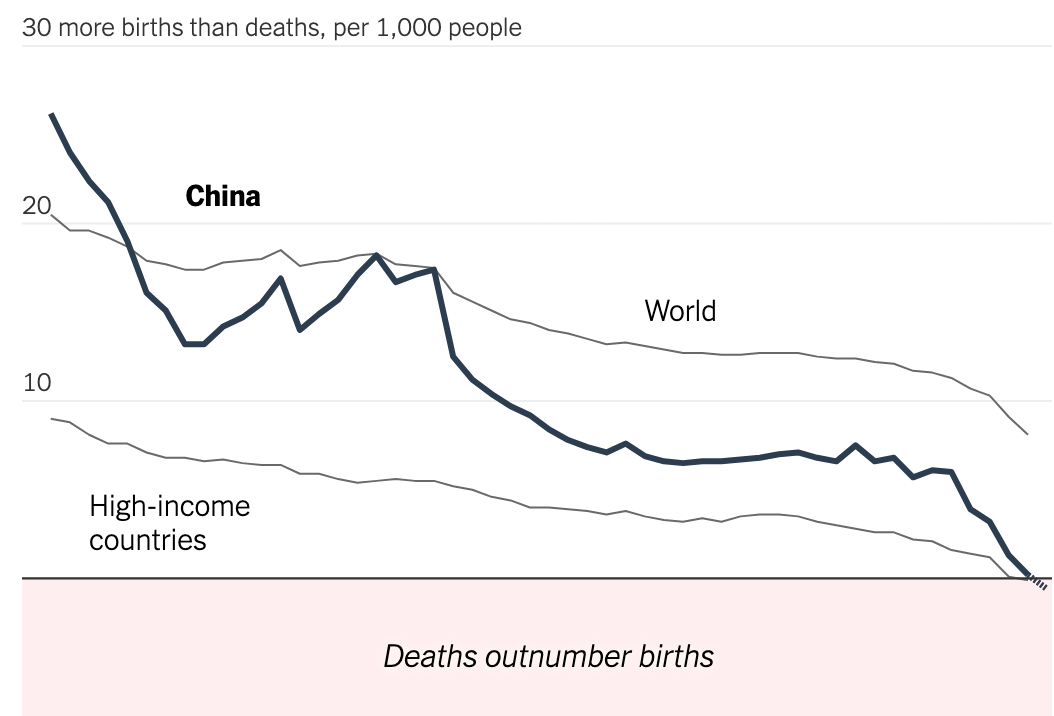
Decreased Demand for Newborn Delivery Service;
In March of this year, several hospitals in China ceased offering newborn delivery services due to decreased demand.
Factors Contributing to Declining Fertility Rates;
1. Family Planning Measures: Some countries, like South Korea and Singapore, have implemented strict family planning policies that encourage couples to limit the number of children they have. For instance, South Korea’s slogan from the 1980s, “Even two children per family are too many for our crowded country,” underscores the focus on population control.
2. Career Opportunities for Women: The availability of more career opportunities for women has led to a shift in priorities away from childbearing.
3. Declining Marriage Rates: Decreasing marriage rates also contribute to lower fertility rates, as marriage traditionally correlates with having children. As fewer people marry or delay marriage, the window for childbearing diminishes.
4. Cost of Raising Children: The rising expenses associated with raising children, including education, healthcare, and housing, serve as a deterrent to having larger families.
Ideal Fertility Rate and Its Importance
The ideal fertility rate for a population to maintain stability, without factoring in immigration or emigration, is 2.1 children per woman, known as the replacement rate. This rate ensures that each generation replaces itself.
Measures to Maintain Ideal Fertility Rate
1. Supporting Work-Life Balance: Implement policies such as flexible work schedules, parental leave, and affordable childcare to encourage individuals to have children while pursuing their careers.
2. Financial Incentives: Provide financial incentives or subsidies to families to ease the financial burden of raising children, thereby making it more feasible for individuals to start families.
3. Education and Awareness: Offer education and awareness programs highlighting the benefits of having children at a younger age and the importance of family planning to help individuals make informed decisions about their fertility.
4. Healthcare Support: Enhance healthcare services related to fertility, pregnancy, and childbirth to ensure a safe and supportive environment for individuals considering starting a family.
Conclusion;
the declining fertility rates in Asian nations stem from factors such as stringent family planning, increased career opportunities for women, declining marriage rates, and the high cost of raising children. Implementing measures such as promoting work-life balance, providing financial incentives, offering education and awareness, and improving healthcare can help maintain an ideal fertility rate.
Mahad Satyagraha: A Milestone in the Dalit Movement
Introduction;
The Mahad Satyagraha stands as a pivotal moment in the Dalit movement, symbolizing the community’s unified stand against the caste system and assertion of basic human rights.
Overview of Mahad Satyagraha
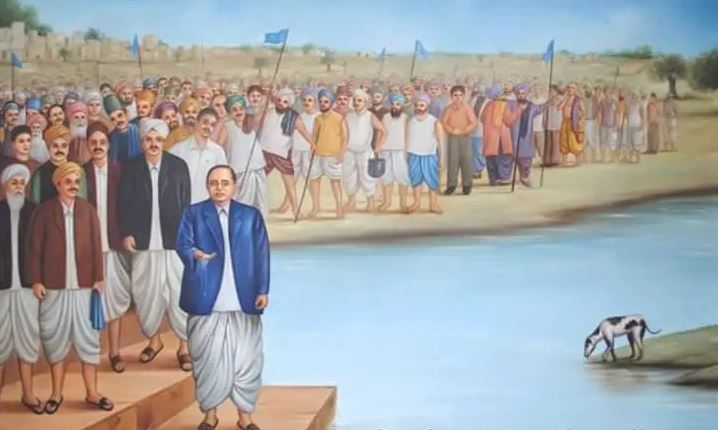
Conducted by B. R. Ambedkar on 20 March 1927 in Mahad, Raigad District of Maharashtra, the Mahad Satyagraha, also known as the Chavdar Tale (Lake) Satyagraha, aimed to secure the right of untouchables to access water from a public tank.

Historical Context;
- Untouchables (Dalits) faced segregation in Indian society, being prohibited from utilizing public water sources and thoroughfares frequented by other Hindu castes.
- Despite a resolution passed by the Bombay Legislative Council in August 1923 permitting depressed classes to access government-maintained areas, opposition from savarna Hindus persisted.
- Mahad attempted to enforce this resolution through its municipal council in January 1924 but encountered resistance, leading to protests.
The Satyagraha Movement;
- In 1927, Ambedkar initiated a satyagraha to assert the rights of untouchables to use public facilities. Mahad was chosen due to the support received from ‘caste Hindus.’
- Surendranath Tipnis, president of the Mahad municipality, extended an invitation to Ambedkar to convene a meeting there.
- Ambedkar’s symbolic act of drinking water from the tank, followed by thousands of untouchables, underscored the movement’s momentum.
- He also advocated for Dalit women to discard the practices of untouchability and adopt saris akin to those worn by high-caste women, a move embraced by the community.
Aftermath and Legal Battles;
- Rumors of Ambedkar’s intention to enter a Hindu temple sparked a riot, resulting in the purification of the tank with cow-urine and cow-dung.
- Despite facing legal hurdles, including a case filed by caste Hindus, Ambedkar planned a follow-up conference in Mahad in December 1927.
- The culmination of these efforts came on 25 December 1937, when the Bombay High Court decreed that untouchables possessed the right to access water from the tank.
Enduring Legacy;
On 19 March 1940, Ambedkar organized a rally in Mahad to commemorate the Satyagraha as “Empowerment Day,” highlighting its enduring significance in the struggle for Dalit rights and dignity.
Global Trade Projection and Analysis
Overview;
The World Trade Organization (WTO) forecasts a gradual recovery in global goods trade for the current year following a decline observed in 2023.

World Merchandise Trade Volume;
- Projections indicate a growth of 2.6% in world merchandise trade volume for 2024, followed by a further increase of 3.3% in 2025. This comes after a notable decline of -1.2% in 2023.
- In 2023, weak import demand in real terms was notable across most regions, particularly in Europe, North America, and Asia. However, the Middle East and the Commonwealth of Independent States (CIS) region witnessed notable increases.
World Real GDP Growth and Inflationary Pressures;
- World real GDP growth, measured at market exchange rates, decelerated from 3.1% in 2022 to 2.7% in 2023. It is expected to remain relatively stable at 2.6% in 2024 and 2.7% in 2025.
- The contrast between steady GDP growth and the slowdown in merchandise trade volume is attributed to inflationary pressures, impacting the consumption of trade-intensive goods, especially in major trading nations.
US Dollar Value of World Trade
- The US dollar value of world merchandise trade experienced a 5% decrease in 2023, totaling US$ 24.01 trillion. However, this decline was partially offset by a robust 9% increase in commercial services trade, amounting to US$ 7.54 trillion.
- Declines in merchandise exports were influenced by falling commodity prices, such as oil and gas, while commercial services trade benefited from recovering international travel and growing digitally delivered services.
Resilience of World Trade;
- Despite significant economic shocks, world trade demonstrated remarkable resilience in recent years.
- By the end of 2023, merchandise trade volume was up by 6.3% compared to 2019, and commercial services experienced a 21% increase in annual US dollar values between 2019 and 2023.
Outlook and Risks;
- The forecast for 2024 and 2025 anticipates a gradual abatement of inflation, leading to growth in real incomes in advanced economies and subsequent increased consumption of manufactured goods.
- Risks to the forecast include geopolitical tensions and policy uncertainty, with conflicts in the Middle East impacting sea shipments between Europe and Asia, potential trade fragmentation due to tensions elsewhere, and rising protectionism posing threats to trade recovery in 2024 and 2025.
Exploring Cryogenics
Understanding Cryogenics;
- Cryogenics is the branch of science dedicated to studying materials and their behaviors at temperatures below -153 degrees Celsius, where gases like hydrogen and nitrogen undergo a phase transition into liquids.

Primary Cryogenic Fluids;
- Helium and nitrogen are among the primary cryogenic fluids, each with distinct boiling points: helium boils at -269 degrees Celsius, while nitrogen boils at -196 degrees Celsius.
Applications in Rocketry;
- Cryogenic hydrogen and oxygen play pivotal roles as rocket propellants, driving the performance of advanced rockets such as ISRO’s LVM-3.
Cryogenic Hardening;
- Cryogenic hardening is a process used to strengthen materials like steel, enhancing their hardness and durability for various industrial applications.
Medical Diagnostic Applications;
- Cryogenic fluids are indispensable in medical diagnostics, particularly in Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) devices, where they facilitate accurate imaging.
Utilization of Refrigeration Technology;
- Refrigeration technology is essential for achieving and maintaining the ultra-low temperatures required for cryogenic applications across various industries.
Advancements in Space Exploration, Industry, and Medicine;
- Cryogenics plays a crucial role in enabling the use of materials and fuels in extreme conditions, thereby driving advancements in space exploration, industrial processes, and medical diagnostics.
Engineering Challenges;
- One significant challenge in cryogenics is the proper storage of cryogenic fluids in vacuum flasks to prevent leakage and minimize environmental damage, presenting complex engineering hurdles.
Understanding the Precautionary Principle
Context;
The precautionary principle, as articulated by British environmentalist Norman Myers, is increasingly recognized as a fundamental guideline for policymakers addressing environmental challenges.

Explanation of the Precautionary Principle;
- The precautionary principle represents an approach to policymaking that validates the implementation of preventive measures to mitigate potential risks to public health or the environment associated with specific activities or policies.
- It asserts that in situations where there are threats of serious or irreversible harm, the absence of complete scientific certainty should not hinder the adoption of cost-effective measures to prevent environmental degradation.
Application and Implications;
- This principle empowers decision-makers to take precautionary actions in instances where scientific evidence regarding environmental or human health risks is uncertain but the potential consequences are significant.
- Essentially, it advocates for proactive measures to avert any potential harm, even in cases where the likelihood of harm is uncertain, thus prioritizing caution.
Historical Context and Legal Recognition;
- The concept of the precautionary principle emerged in the 1970s and has since been codified in various international treaties and agreements concerning the environment.
- It was formally recognized in international law during the 1987 International Conference on the Protection of the North Sea and has since been incorporated into numerous international environmental conventions.
Incorporation into International Agreements
- The precautionary principle is entrenched in several international environmental agreements, including the 1992 Rio Declaration (Principle 15), the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change, and the Protocol on Substances that Deplete the Ozone Layer.
- Additionally, it has been integrated into criteria for the listing of endangered species by the Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species and adopted by the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations.
Role in European Union Environmental Law
Within the European Union (EU), the precautionary principle holds a central position in environmental law and has significantly influenced the EU’s stance on issues such as genetically modified organisms.
Conclusion;
The precautionary principle serves as a cornerstone of environmental governance, guiding policymakers in taking proactive measures to safeguard public health and the environment in the face of uncertainty.
Easementary Rights
Overview;
In a recent legal dispute concerning easementary rights over a 20 ft. wide road situated on a piece of land, the Supreme Court reiterated that a power of attorney holder is limited to providing testimony based only on their personal knowledge.

Definition of Easementary Right;
- The concept of easement is explicitly defined under Section 4 of the Indian Easements Act, 1882.
- According to this provision, an easementary right is a privilege granted to the owner or occupier of one piece of land (referred to as the dominant heritage) over another piece of land (known as the servient heritage) to facilitate the beneficial enjoyment of the former.
Purpose and Scope;
- Easementary rights are bestowed to ensure that the occupier or owner of a piece of land can fully enjoy their property.
- This includes the right to perform certain actions on or prevent certain actions from occurring on the servient heritage in connection with the dominant heritage.
Key Terminology;
- The owner or occupier benefiting from the easementary right is termed the Dominant Owner.
- The land benefiting from the easementary right is referred to as the Dominant Heritage.
- Conversely, the owner of the servient land, upon which the easementary right is imposed, is known as the Servient Owner.
- The land on which the easementary right imposes obligations is designated as the Servient Heritage.
Example and Illustration;
For instance, if ‘P’ owns a property adjacent to ‘Q’s house and has the right of way over ‘Q’s property to access the street, this is recognized as a right of easement.
Nature and Characteristics;
- It’s important to note that an easement does not involve the transfer of property.
- It can be created, modified, or relinquished, and it is typically documented in writing, except in cases where it has been exercised without interruption for an extended period.
- A written record of the easement allows either party to contest its validity in a court of law.
Operation Meghdoot: Securing Siachen Glacier
Introduction;
The Indian Army recently marked the 40th anniversary of ‘Operation Meghdoot,’ a significant military endeavor that led to the securing of the Siachen Glacier.
Overview of Operation Meghdoot;
- Operation Meghdoot was the codename given to the Indian Armed Forces’ operation aimed at capturing the strategically vital Siachen Glacier, which dominates the Northern Ladakh region.
- The Siachen area has been a point of contention between India and Pakistan since the Karachi Agreement of 1949, which left the area undivided due to its hostile terrain and extreme weather conditions.

Objectives and Execution;
- The operation was India’s decisive response to what it termed Pakistan’s “cartographic aggression” in the Ladakh region, particularly north of map reference NJ9842, where the Line of Control (LoC) had been agreed upon.
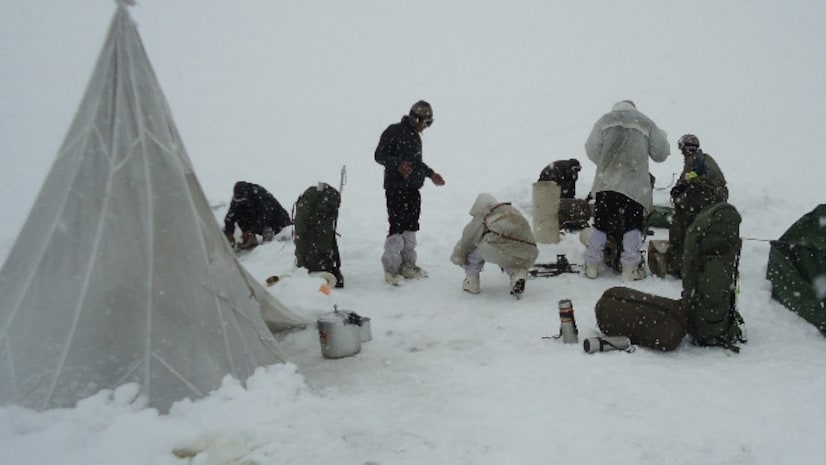
- Intelligence reports indicating potential Pakistani military actions prompted India to secure strategic heights on the Siachen Glacier, utilizing airlifts and air-dropping supplies to high-altitude airfields.
- The primary aim was to prevent the Pakistan Army from seizing the Sia La and Bilafond La passes.
Launch and Leadership;
- Launched on April 13, 1984, Operation Meghdoot made history as the first assault on the world’s highest battlefield.
- It was conducted under the leadership of Lieutenant General Manohar Lal Chibber, Lieutenant General PN Hoon, and Major General Shiv Sharma.
- The operation exemplified remarkable coordination and synergy between the Indian Army and the Air Force.
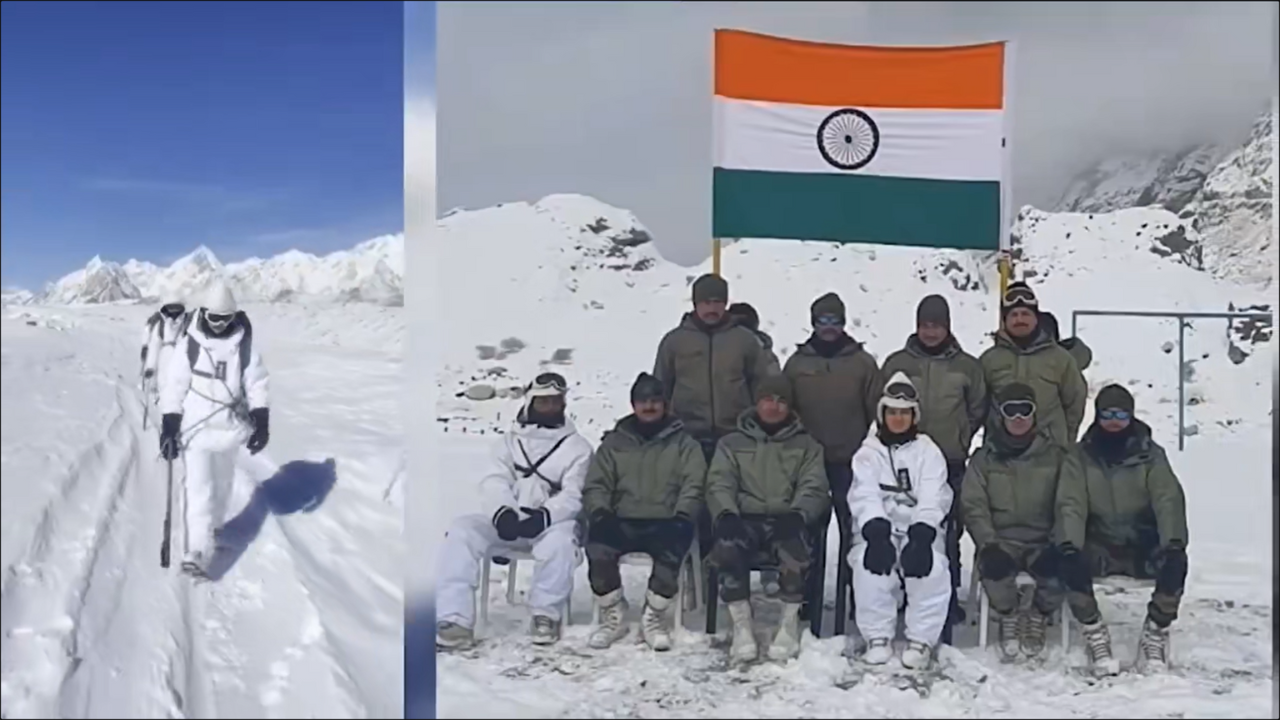
Achievements and Strategic Significance;
- Operation Meghdoot culminated in Indian forces gaining control over the entire Siachen Glacier, consolidating India’s strategic position in the region.
- The Siachen Glacier, situated at an altitude of approximately 20,000 feet in the Karakoram Mountain range, holds immense strategic importance.
- It dominates various key areas, including the Shaksgam Valley, routes from Gilgit Baltistan to Leh, and the ancient Karakoram Pass. Additionally, it provides crucial surveillance over Gilgit Baltistan, an Indian territory occupied by Pakistan since 1948.

Conclusion;
The 40th anniversary of Operation Meghdoot serves as a reminder of India’s bold and successful military operation to safeguard its territorial integrity in one of the world’s most challenging terrains.
Understanding Shrinkflation
Introduction;
With input prices transitioning from benign to inflationary in recent quarters, the concept of shrinkflation is gaining prominence, particularly within the fast-moving consumer goods (FMCG) sector.
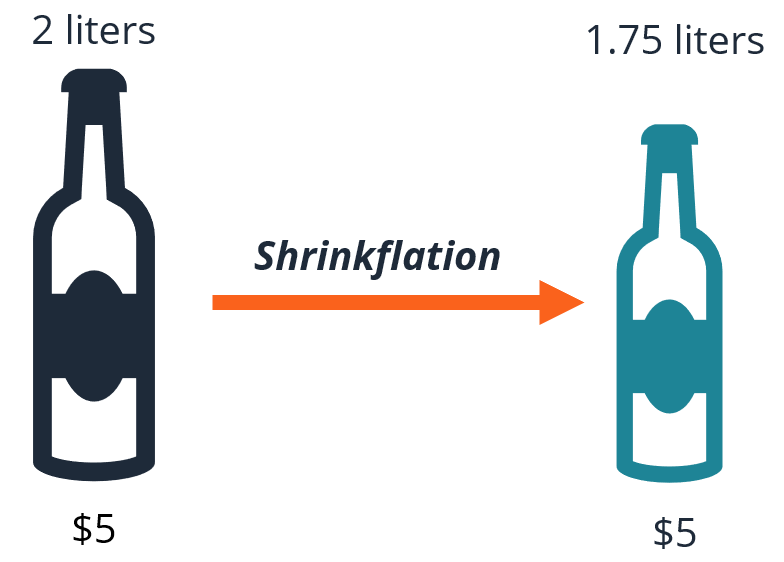
Explaining Shrinkflation;
- Shrinkflation occurs when the size of goods decreases while consumers continue to pay the same price.
- This phenomenon arises when manufacturers reduce the size of products to offset escalating production costs while keeping retail prices unchanged.
- Essentially, shrinkflation represents a form of hidden inflation, where the price per unit remains constant, but the quantity or volume of the product diminishes.
Mechanism and Impact;
- Rather than directly raising prices, producers opt to shrink product sizes to mitigate rising costs, leading to an apparent stagnation in the absolute price of the product.
- However, the price per unit of weight or volume effectively increases, impacting consumers’ purchasing power.1
Factors Driving Shrinkflation;
Shrinkflation is primarily driven by escalating production costs and intense market competition, compelling manufacturers to seek alternative strategies to maintain profitability without overtly increasing prices
Implications
- The impact of shrinkflation is particularly pronounced in the FMCG industry, characterized by high-volume sales, rapid inventory turnover, and a diverse range of products catering to consumer needs.
- Everyday essentials such as food and beverages, toiletries, cleaning supplies, and various low-cost household items are often subject to shrinkflation practices.
Conclusion;
As input costs continue to rise and market dynamics evolve, shrinkflation remains a significant concern for both manufacturers and consumers within the FMCG sector. Recognizing and understanding this phenomenon is crucial for navigating the changing landscape of consumer goods markets.

