 |
||
| 17 April 2024 | ||
|
- UN Permanent Forum on Indigenous Issues (UNPFII)
- Growth in Ashwagandha Exports
- Land Use and Land Cover Atlas of India (LULC Atlas)
- Armenia’s Accusations and Regional Dynamics”
- IMD Forecasts “Above Normal” Monsoon for India in 2024
- Kerogen
- Lake Kariba
- Imported Inflation: Understanding the Concept
- Athletics Federation of India (AFI)
UN Permanent Forum on Indigenous Issues (UNPFII)
Introduction:
The 23rd session of the UN Permanent Forum on Indigenous Issues commenced on April 15 in New York, focusing on expediting the recognition and protection of Indigenous Territories (ITs) globally.

Overview of UN Permanent Forum on Indigenous Issues (UNPFII):
- Establishment: July 28, 2000
- Headquarters: New York, USA
- Parent Organization: United Nations Economic and Social Council (ECOSOC)
Membership:
- Consists of 16 independent experts serving three-year terms.
- Eight experts nominated by member governments, while the remaining eight directly nominated by indigenous organizations.
- Member countries include Finland, Nepal, Chad, Australia, Colombia, Bolivia, United States, Russia, China, Ecuador, Burundi, Denmark, Mexico, Namibia, Estonia, and an additional rotating seat.
Mandate:
- Provide expert advice and recommendations on indigenous issues to the Council, UN programs, funds, and agencies through ECOSOC.
- Raise awareness and advocate for the integration of indigenous concerns within the UN system.
- Compile and disseminate information related to indigenous issues.
Secretariat:
- Established by the General Assembly in 2002.
- Located in New York within the Division for Inclusive Social Development (DISD) of the UN Department of Economic and Social Affairs (DESA).
Growth in Ashwagandha Exports
Context;
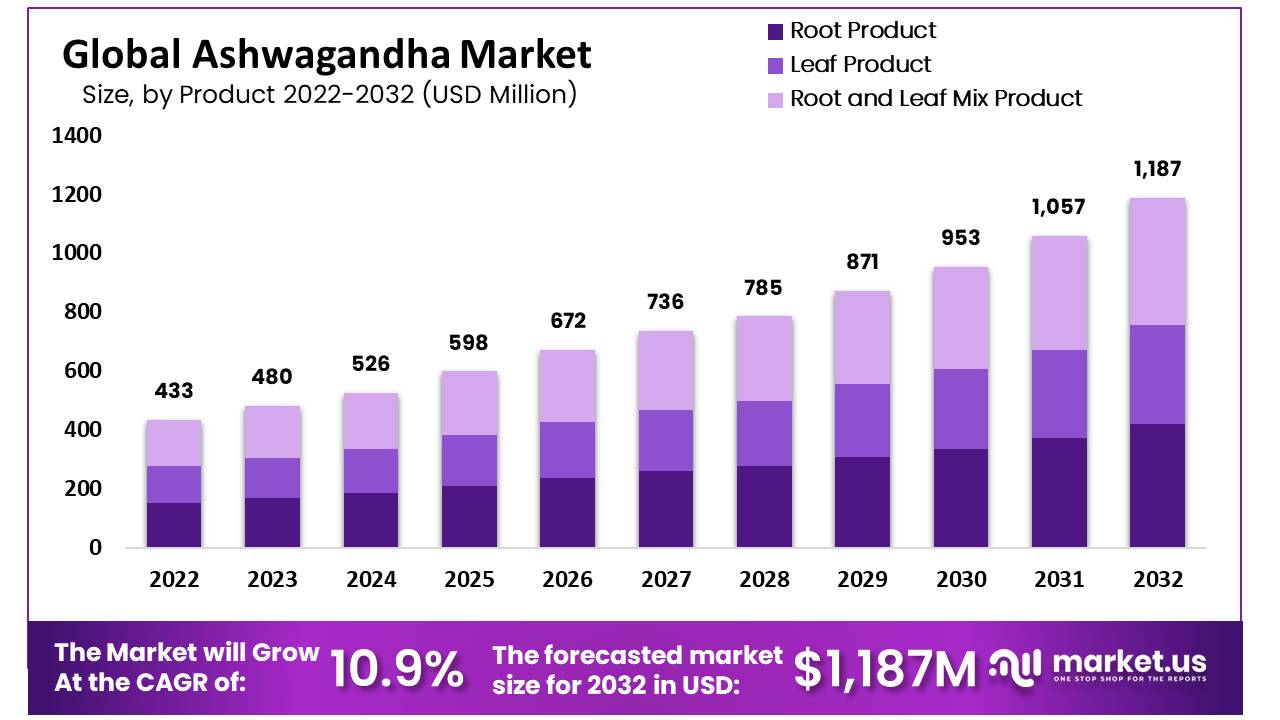
Over the past six years, Ashwagandha exports have witnessed an exceptional surge, increasing by a factor of 8 and penetrating markets like the United States, Czech Republic, and Canada.
1.Ayurvedic Industry Expansion:
The Ayurvedic industry in India has experienced substantial growth, boasting a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 17%. Its size has expanded from $3 billion in 2014 to $24 billion presently.
2.Regional Manufacturing Landscape:
Gujarat, with approximately 850 Ayurvedic manufacturing units, holds the fourth position in India’s Ayurvedic industry, following Uttar Pradesh, Kerala, and Maharashtra.
3.India’s Leadership in Production and Export:
India leads globally in the production and export of Ashwagandha, with states like Rajasthan and Madhya Pradesh emerging as key contributors.
4.Identification and Properties:
Ashwagandha, also known as Indian Ginseng or Withania somnifera, belongs to a group of herbs called ‘adaptogens,’ known for their rejuvenating properties.
5.Forms and Market Reach:
Available in various forms such as extracts, powder, and raw herbs, Ashwagandha caters to both domestic and international markets
6.Medicinal Applications:
Ashwagandha finds medicinal use in treating rheumatic pain, joint inflammation, nervous disorders, epilepsy, and serves as a tonic for various ailments.
7.Growing Regions:
Ashwagandha cultivation is prevalent in states like Rajasthan, Punjab, Haryana, Uttar Pradesh, Gujarat, Maharashtra, and Madhya Pradesh.
8.Optimal Conditions:
Thriving in arid conditions, Ashwagandha is cultivated as a late rainy season (kharif) crop at altitudes ranging from 600 to 1200 meters.
9.Soil and pH Preferences:
The crop prefers sandy loam or light red soil with a pH level between 7.5 and 8.0, with good drainage being essential for successful cultivation.
Land Use and Land Cover Atlas of India (LULC Atlas)
Context:
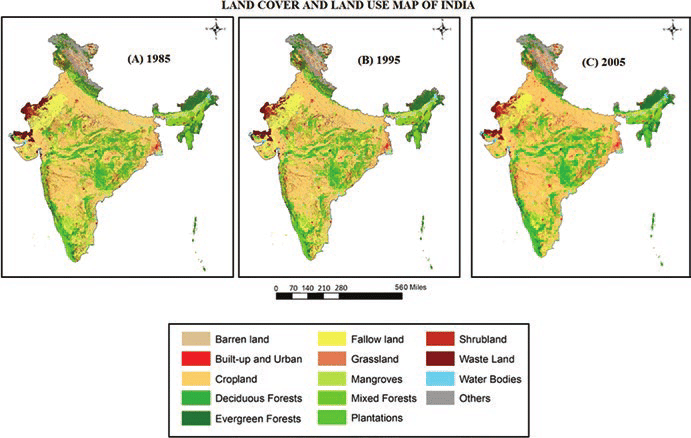
The Land Use and Land Cover Atlas of India (LULC Atlas) has been released by the National Remote Sensing Centre (NRSC) to provide comprehensive insights into the changing landscape of India. Leveraging remote sensing technology, the atlas offers detailed information on land use patterns and their evolution over time, aiming to support informed decision-making in various sectors such as agriculture, urban planning, and environmental conservation.
Issued by: National Remote Sensing Centre (NRSC)
Objective: The objective is to systematically analyze land utilization patterns, providing valuable insights into the evolving dynamics of our environment.
Key Highlights:
1. Cropland Expansion:
- Over the past 17 years, Kharif cropland has expanded by 46.06%, and Rabi cropland by 35.23%, while fallow land decreased by 45.19%.
2. Cropping Patterns:
- Areas for double/triple/annual cropping have seen an increase of 82.22%.
- Double/triple crop lands refer to areas where crops are sown and harvested twice/thrice in one crop year, while annual crops are perennial and grow throughout the year, such as sugarcane.
3. Shifting Cultivation Trends:
- Shifting cultivation increased until 2016-17, after which it declined.
4. Water Body Surfaces:
- Minimum water body surfaces have increased by 146% since 2005.
5. Built-up Land Growth:
- There has been an overall growth of 30.77% in built-up land since 2005.
- Built-up areas encompass regions with buildings, paved surfaces, commercial and industrial sites, and urban green areas.
Armenia’s Accusations and Regional Dynamics”
Context:
In the aftermath of the conflict in Nagorno-Karabakh, tensions between Armenia and Azerbaijan remain high. The region, which has a complex history of ethnic and territorial disputes, saw renewed violence in 2020, resulting in significant casualties and displacement of civilians. Against this backdrop, Armenia has accused Azerbaijan of committing “ethnic cleansing” in Nagorno-Karabakh, alleging widespread atrocities against the Armenian population.
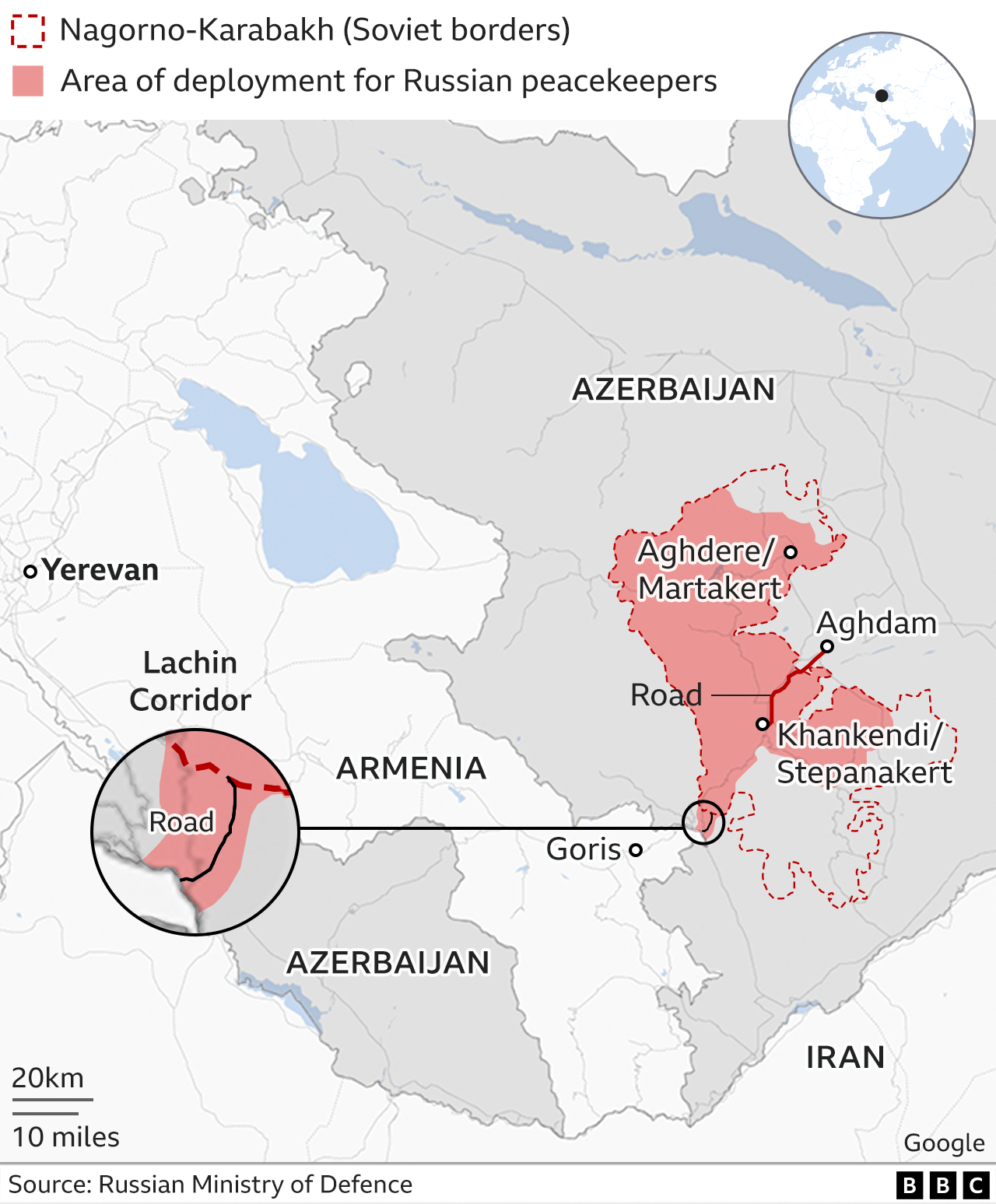
Recent Developments:
- Armenia’s accusations against Azerbaijan have escalated to the international stage, with Yerevan bringing the issue before the United Nations top court.
- Armenia claims that Azerbaijan’s actions amount to “completed ethnic cleansing” in Nagorno-Karabakh, a charge vehemently denied by Baku.
- Azerbaijan has dismissed Armenia’s allegations as “cherry-picking” and contends that they are part of Armenia’s broader strategy to discredit Azerbaijan in the ongoing legal battle at the International Court of Justice.
Location:
Armenia, a landlocked country in the Armenian Highlands of West Asia, finds itself at the center of geopolitical tensions in the region.
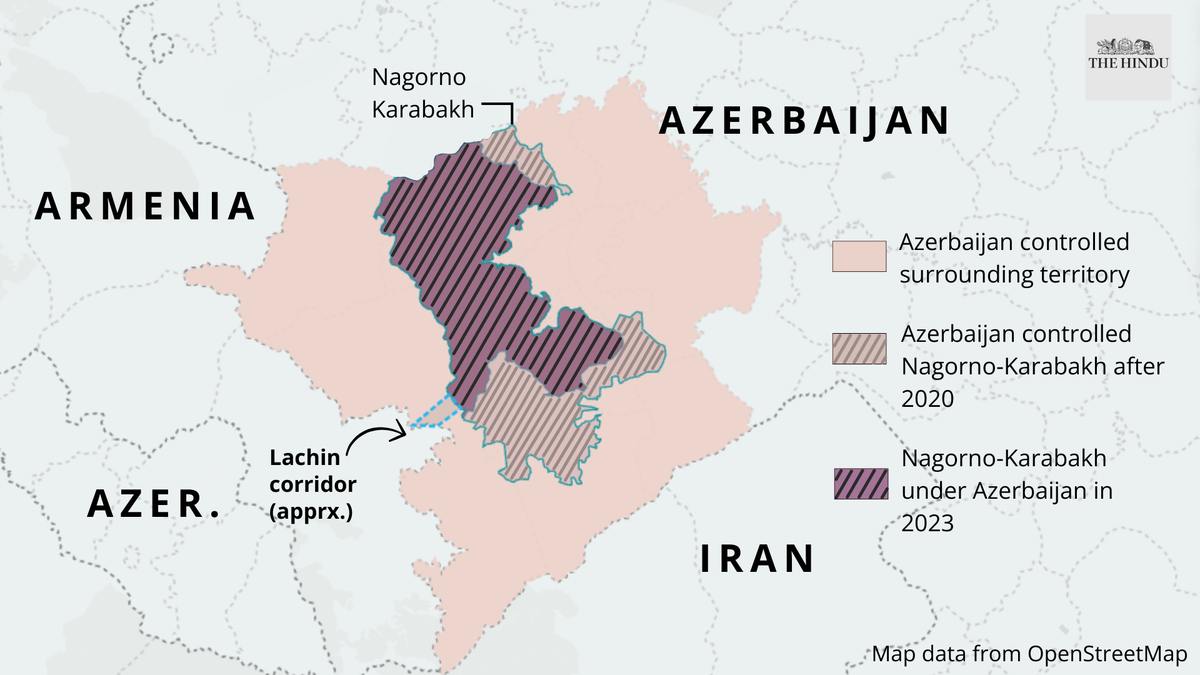
Political Boundaries:
The nation shares borders with Azerbaijan to the East, Turkey to the West, Georgia to the North, and Iran, along with the Azerbaijani exclave of Nakhchivan, to the South.
Physical Features:
- Mount Aragats stands as the highest peak in Armenia.
- The country is traversed by several significant rivers, including the Aras, Debed, Hrazdan, and Vorotan, which play crucial roles in Armenia’s geography and water resources.
- Armenia’s mineral wealth includes resources such as copper, molybdenum, and gold.
Membership:
Armenia maintains membership in various international organizations, including the United Nations, the Commonwealth of Independent States (CIS), and the Collective Security Treaty Organization (CSTO), reflecting its engagement on the global stage amidst ongoing regional challenges.
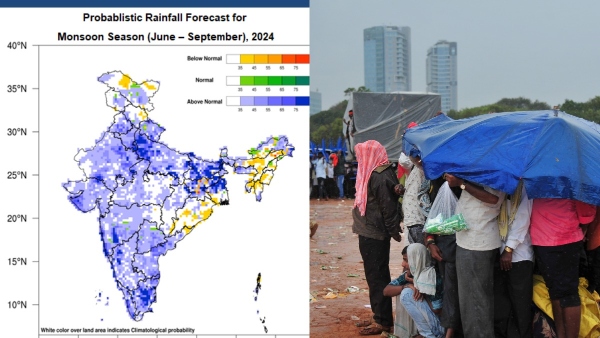
IMD Forecasts “Above Normal” Monsoon for India in 2024
Context
- The India Meteorological Department (IMD) has predicted an “above normal” monsoon rainfall for India between June and September this year.
- Remarkably, this is the first time in a decade that the IMD has forecasted “above normal” rainfall at the initial stage, nearly 45 days ahead of the onset of the four-month monsoon season.
- This early prediction provides valuable insights for farmers, policymakers, and the general public, allowing them to better prepare for the anticipated weather conditions and potentially benefiting agricultural productivity and water resources management across the country.
Dimensions Covered in the Article:
- IMD’s Rainfall Prediction for 2024
- Overall Rainfall Prediction: The country is expected to receive 106% of the long period average (LPA) rainfall.
- Long Period Average (LPA): LPA is the average rainfall received over the past 50 years, specifically the average from 1971-2020.
- Classification of Rainfall: Normal, Deficient, Below Normal, Above Normal.
- Regional Distribution: Except for some regions in the northwest, east, and northeast, nearly the entire country is likely to receive good rainfall.
- India’s Normal Rainfall: India typically receives 870 mm of rainfall during the monsoon season.
2.Factors Indicating Above Normal Rainfall;
- El Niño and La Niña: Weakening of El Niño and Development of La Niña.
- Indian Ocean Dipole (IOD): Positive IOD indicating above normal rainfall for the season.
3. Indian Ocean Dipole (IOD);
- Explanation of Negative and Positive IOD and their impacts.
- This comprehensive overview sheds light on the IMD’s forecast for the monsoon in India for the year 2024, providing crucial information for
various stakeholders to prepare and adapt to potential weather-related challenges.
Kerogen
Overview;
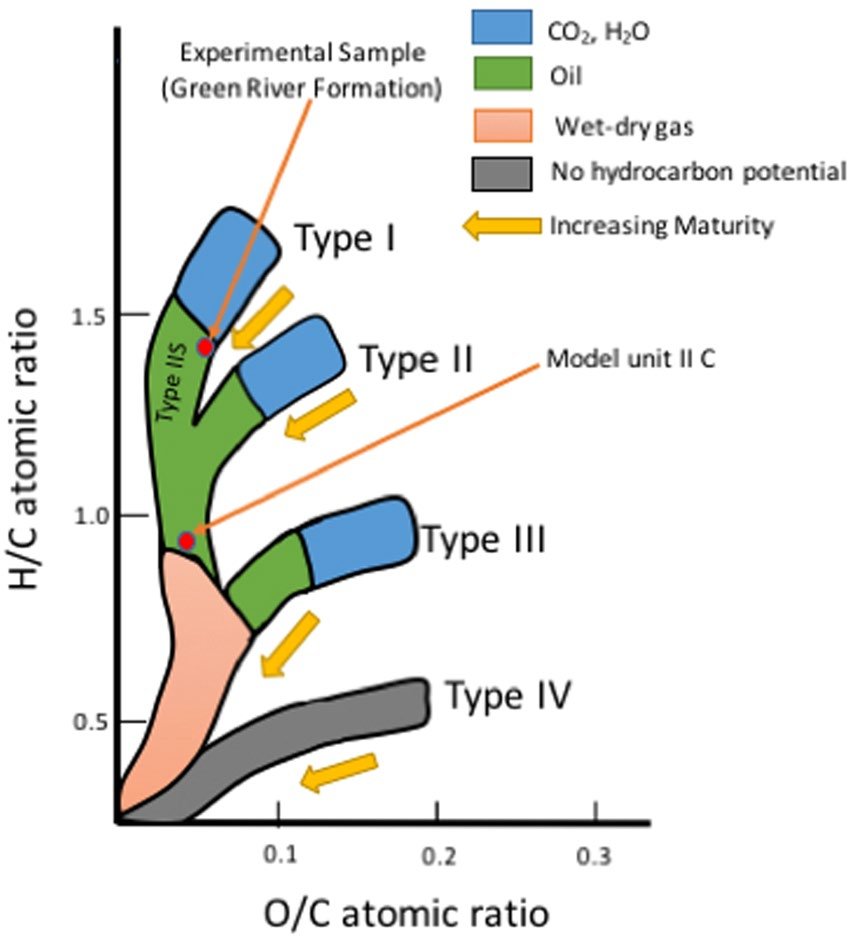
Kerogen, constituting the primary origin of hydrocarbons in subterranean formations, comprises lumps of organic matter insoluble in organic solvents. It constitutes approximately 90% of the organic carbon within sedimentary deposits.
Occurrence and Properties:
- Kerogen is predominantly found in source rocks and possesses the capacity to release hydrocarbons through thermal cracking.
- Common organic constituents include algae and woody plant material, encompassing both lighter and heavier hydrocarbons.
Role in Hydrocarbon Formation:
- Kerogen serves as a precursor to oil and natural gas formation, characterized by a higher molecular weight compared to bitumen or soluble organic matter.
- Bitumen originates from kerogen during the process of petroleum generation.
Types of Kerogens:
Type I: Primarily comprising algal and amorphous kerogen,demonstrates a high potential for oil generation.
Type II: Featuring a blend of terrestrial and marine source material, kerogen can yield waxy oil.
Type III: Derived from woody terrestrial source material, kerogen typically generates gas.
Impact on Hydrocarbon Generation:
- The variation in kerogen types significantly influences the composition of hydrocarbons within rocks.
- Diverse kerogen types exhibit distinct hydrogen-to-carbon ratios, determining the ratio of oil to gas produced during primary hydrocarbon-generating reactions.
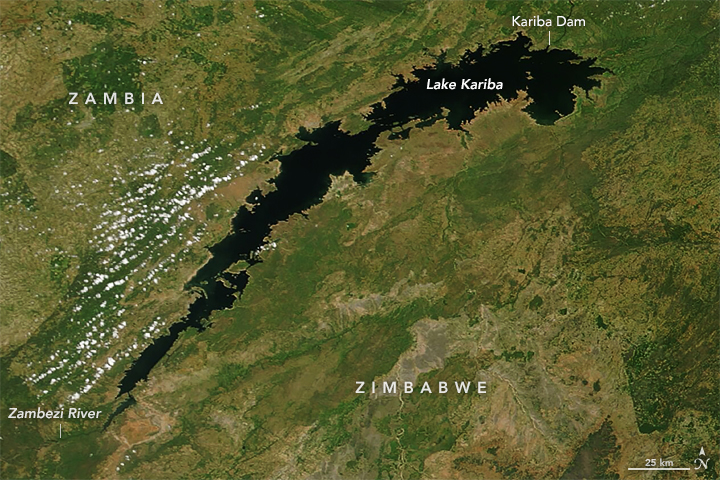
Lake Kariba
Context;
Lake Kariba stands as the world’s largest man-made lake and reservoir by volume, stretching approximately 280 kilometers in length and 40 kilometers in width, covering nearly 6,000 square kilometers.
Location:
Located around 1300 kilometers upstream from the Indian Ocean, Lake Kariba straddles the border between Zambia and Zimbabwe, approximately 200 kilometers downstream of Victoria Falls.
Formation:
The lake was formed upon the completion of the Kariba Dam wall at its northeastern end, which flooded the Kariba Gorge on the Zambezi River.
Kariba Dam:
The Kariba Dam features a double-arch wall with the following dimensions:
– Height: 128 meters
– Length: 617 meters
– Width (top): 13 meters
– Width (base): 24 meters
Construction:
Construction of the dam commenced on 6th November 1956 and was completed in 1959, spanning up to three years.
Significance:
Lake Kariba plays a crucial role in providing substantial electric power to both Zambia and Zimbabwe. Additionally, it supports a thriving commercial fishing industry.
Geographical Features:
Positioned across the Kariba gorge, Lake Kariba serves as a border crossing between Zambia and Zimbabwe.
Imported Inflation: Understanding the Concept
Overview:
The Asian Development Bank recently issued a warning about the potential for imported inflation in India, attributing it to the possible depreciation of the rupee amid increasing interest rates in Western economies.
About Imported Inflation:
- Imported inflation denotes a general and sustained increase in prices stemming from elevated costs of imported goods.
- This phenomenon encompasses the escalation in prices of raw materials and all imported products or services utilized by companies within a nation.
- It is often interchangeably referred to as cost inflation.
Factors Influencing Imported Inflation:
1. Exchange Rates: Fluctuations in exchange rates serve as the primary driver of imported inflation. A depreciating currency on the foreign exchange market translates to higher prices of imports, necessitating more significant expenditure to procure goods and services from abroad.
2. Commodity Prices: Many nations, particularly smaller economies, heavily rely on imported commodities such as oil, metals, and agricultural products. Global increases in commodity prices directly impact import costs, thereby contributing to inflationary pressures domestically.
3. Trade Policies and Global Supply Chains: Alterations in trade policies, including tariffs and quotas, can influence the pricing of imported goods.
4. Transportation Costs: Variations in transportation expenses, influenced by factors like fuel prices and logistical complexities, can impact the ultimate cost of imported merchandise.
Effect:
Imported inflation results in heightened production costs for companies, which often necessitate adjustments in the selling prices of goods and services. Consequently, domestic prices experience an upward trajectory due to these inflationary pressures.
Gaia-BH3: Unveiling the Most Massive Stellar Black Hole
Overview:
A groundbreaking discovery by astronomers has unveiled the most massive stellar black hole ever observed within the Milky Way galaxy, named Gaia-BH3.

About Gaia-BH3:
- Gaia-BH3 represents the most massive stellar black hole discovered within the Milky Way galaxy.
- Its identification stemmed from data collected by the European Space Agency’s Gaia mission, revealing peculiar motion patterns exerted on its companion star during orbit.
- The researchers employed the European Southern Observatory’s Very Large Telescope in Chile’s Atacama Desert and other ground-based observatories to confirm Gaia-BH3’s mass.
- Located approximately 1,926 light-years away in the Aquila constellation, Gaia-BH3 boasts a mass nearly 33 times that of our sun, marking it as the second-closest known black hole to Earth.
- In comparison, the nearest black hole, Gaia BH1, resides roughly 1,500 light-years away and possesses a mass nearly 10 times that of our sun.
Distinguishing Stellar Black Holes from Supermassive Black Holes:
1.Stellar Black Holes:
- Stellar-mass black holes originate from the gravitational collapse of a single star or the merger of two neutron stars.
- Consequently, their masses align closely with those of stars, ranging from about 3 times to 50 times the mass of our sun.
2.Supermassive Black Holes:
- In contrast, supermassive black holes exhibit masses exceeding 50,000 times that of our sun, extending to millions or billions of solar masses.
- These colossal entities, ubiquitous at the centers of galaxies, are far too massive to have formed through the gravitational collapse of a single star.
- While the exact formation mechanism of supermassive black holes remains elusive, their presence in virtually all galaxies suggests a fundamental association with galactic evolution processes.
Athletics Federation of India (AFI)
Overview:
In a landmark decision, the Athletics Federation of India has disaffiliated 16 district associations nationwide due to their failure to participate in the recent National inter-district junior athletics meet.

About Athletics Federation of India (AFI):
1. Governance and Affiliations:
– The AFI serves as the premier governing body responsible for the regulation of athletics in India.
– It operates as an independent and non-profit organization and holds affiliations with World Athletics, the Asian Athletics Association (AAA), and the Indian Olympic Association.
– Originally known as the Amateur Athletic Federation of India (AAFI), the federation oversees 32 affiliated state units and institutional units.
2. Establishment and Functions:
– Established in 1946, the AFI plays a central role in organizing National Championships, training Indian Athletics National Campers, and selecting teams for various international competitions.
– It manages the participation of Indian athletes in events such as the Olympics, Asian Games, Commonwealth Games, World Championships, and Asian Championships.
– The federation conducts National Championships across different age categories and organizes international and national championships to promote the sport and attract commercial interest.
3. Developmental Initiatives:
– AFI supervises and supports its state units, facilitates specialized coaching camps, and provides training for coaches.
– It initiates and implements development programs to promote grassroots athletics across India, aiming to nurture talent from a young age and foster the sport’s growth nationwide.

