|
|
||
|
17 March 2024 |
||
|
- Collapse of the Gulf Stream System
- Sangam: Digital Twin Initiative
- EU’s Digital Services Act (DSA)
- Global Pulse Confederation (GPC) held in New Delhi
- INSAT-3DS launch
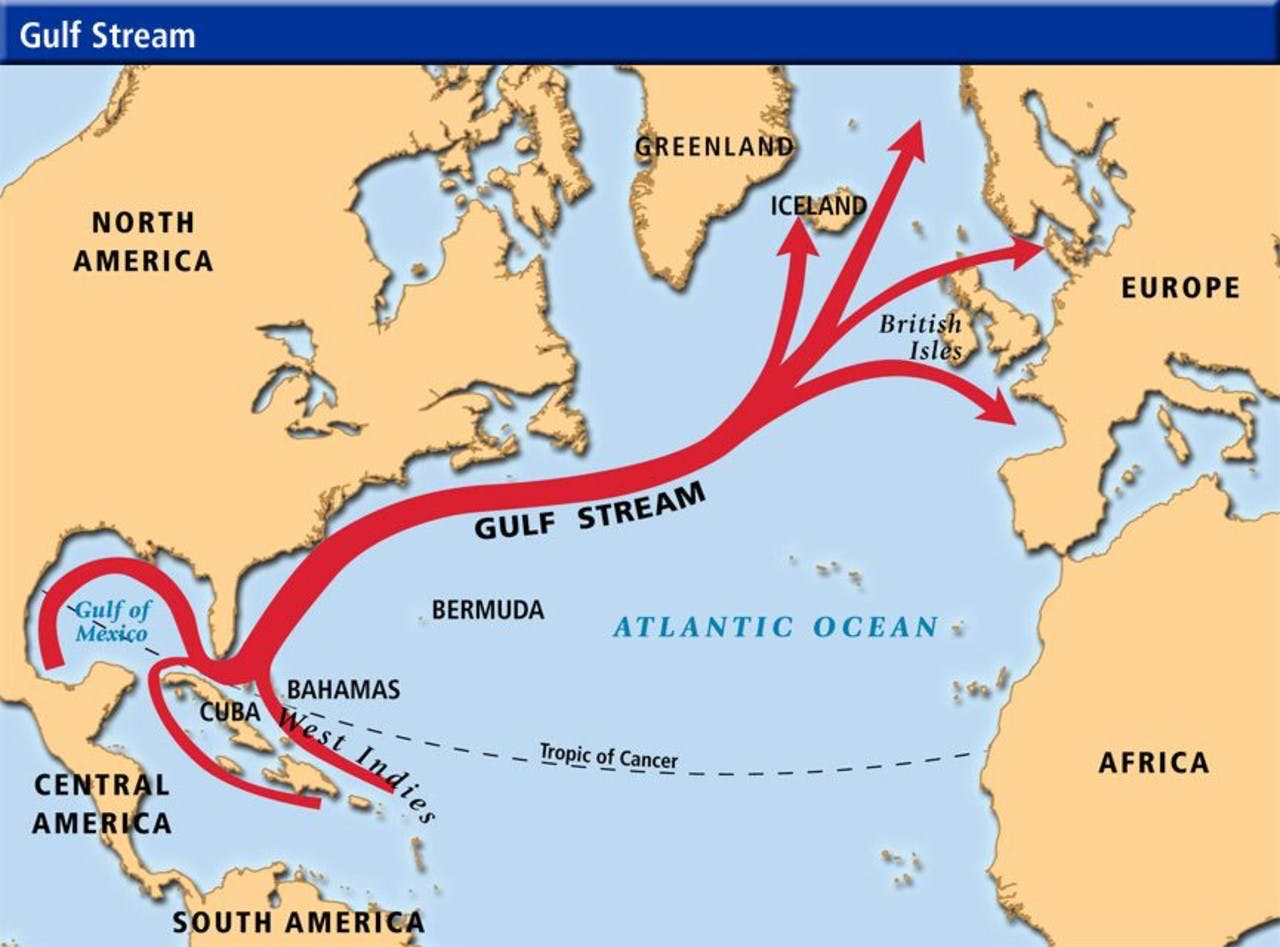
Collapse of the Gulf Stream System
Context:
Recent studies indicate that the Gulf Stream System, also known as the Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation (AMOC), is in danger of collapsing due to continuous global carbon emissions.
If no action is taken, this collapse could happen sometime between 2025 and 2095, with an estimated timeframe around 2050.
Description of the Gulf Stream System:
- Origin: It originates in the Gulf of Mexico, where warm waters from the Caribbean Sea and the Gulf of Mexico merge.
- Flow: It moves northward along the eastern coast of the United States.
- Current: It transports warm waters from the tropics towards higher latitudes.
- Speed and Volume: The Gulf Stream consists of swift ocean currents, moving at speeds of 2 to 5 miles per hour and carrying approximately 30 million cubic meters per second.
- Function: Its primary function is to distribute heat towards the North Atlantic region, influencing climate and weather patterns.
- Climate Impact: The Gulf Stream plays a crucial role in moderating the climate of Western Europe, keeping it relatively warmer than other regions at similar latitudes.
- Interaction with the Atmosphere: It releases heat and moisture, affecting weather and precipitation patterns.
- Importance for Marine Life: The Gulf Stream supports a diverse range of marine life and serves as a migratory route for fish and marine mammals.
Vulnerability of the Gulf Stream:
- The Gulf Stream is currently at its weakest point in 1,600 years, largely due to the effects of global warming.
- Signs of a tipping point were observed as early as 2021.
- Past collapses during ice ages have resulted in rapid temperature shifts of up to 10 degrees Celsius within a few decades, highlighting its significant impact on climate.
Implications of Collapse:
- The potential collapse of the Gulf Stream could have severe global consequences, including:
- Disrupted Rainfall Patterns: Regions like India, South America, and West Africa, which rely on these patterns for food production, would face food insecurity.
- Intensified Storms and Colder Temperatures: Europe would experience more frequent storms and colder temperatures.
- Rising Sea Levels: Coastal communities along the eastern coast of North America would be at risk of flooding due to rising sea levels.
- Endangered Ecosystems: The Amazon rainforest and Antarctic ice sheets could face serious threats to their survival.
- Sangam: Digital Twin Initiative
- Introduction :
- The Department of Telecommunications (DoT) has initiated the ‘Sangam: Digital Twin’ program, calling for Expressions of Interest (EoI) from various sectors including industry leaders, startups, MSMEs, academia, innovators, and forward-thinkers.
-
![pib] Sangam: Digital Twin Initiative - Civilsdaily](https://statecraft.in/wp-content/uploads/2024/04/pib-sangam-digital-twin-initiative-civilsdaily.jpeg)
- Understanding Digital Twin Technology
- Digital twin technology creates a virtual replica of a physical entity, be it an object, person, or process, embedded within a digital representation of its environment.
- This allows organizations to simulate real-world scenarios and predict outcomes, thereby facilitating informed decision-making.
- Overview of Sangam: Digital Twin Initiative
- In alignment with the technological advancements of recent years in communication, computation, and sensing, the initiative is geared towards realizing the vision for 2047.
- Proof of Concept (PoC) in Two Stages
- The initiative will unfold in two stages, to be held in a major Indian city:
- Exploratory Phase: This initial stage will focus on expanding horizons and fostering creative exploration to unlock potential.
- Demonstration Phase: Following the exploratory phase, the initiative will transition into practical demonstrations of specific use cases. This aims to create a blueprint for future collaboration and scalability in infrastructure projects.
- Objectives
- Showcase practical implementations of innovative infrastructure planning solutions.
- Develop a model framework to enhance collaboration efficiency.
- Provide a blueprint for scaling and replicating successful strategies in future infrastructure projects.
- Features
- Sangam: Digital Twin is a collaborative effort aimed at reshaping infrastructure planning and design. It incorporates advanced technologies such as 5G, IoT, AI, AR/VR, AI-native 6G, Digital Twin, and next-generation computational tools.
- By bringing together various stakeholders including public entities, infrastructure planners, technology companies, startups, and academic institutions, Sangam strives to translate innovative concepts into tangible solutions.
- Ultimately, it seeks to bridge the gap between ideation and realization, paving the way for transformative advancements in infrastructure.
- EU’s Digital Services Act (DSA)
Introduction
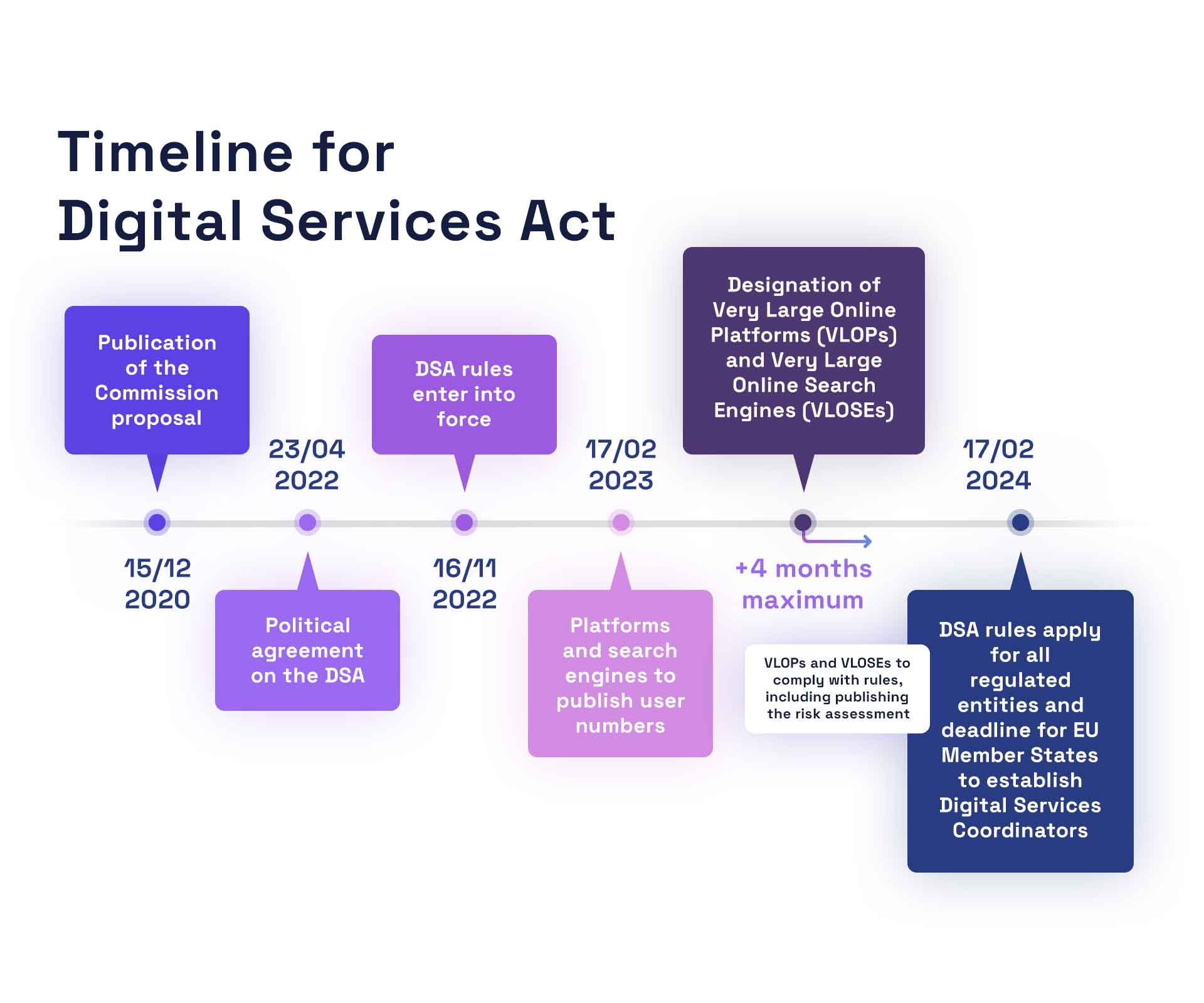
In July 2022, the European Parliament enacted the Digital Services Act (DSA) with the aim of bolstering online safety and transparency for users within the European Union (EU).
Initially focusing on major platforms like Facebook and TikTok, the DSA now applies its regulations to all platforms except the smallest ones.
Understanding the Digital Services Act (DSA)
Purpose: The DSA aims to foster a safer and more transparent online environment by regulating platforms that offer goods, services, or content to EU citizens.
Key Provisions:
1. Removal of Illegal Content: Platforms are mandated to prevent and take down illegal or harmful content, such as hate speech, terrorism, and child abuse.
2. User Reporting: Platforms must facilitate mechanisms for users to report illegal content.
3. Ad Targeting Restrictions: Targeted advertising based on criteria like sexual orientation or political beliefs is prohibited, with extra protections for children against inappropriate ads.
4. Algorithm Transparency: Platforms are required to disclose how their algorithms function and impact content display.
5. Stricter Regulations for Large Platforms: Platforms reaching more than 10% of the EU population face additional requirements, including data sharing, crisis response cooperation, and external audits.
Implications for Non-EU Regions
- Global Standard: Although enforced by the EU, the DSA seeks to establish a global benchmark for online intermediary liability and content regulation, potentially influencing policies worldwide.
- Consistency in Policies: Platforms may adopt DSA-compliant changes universally to streamline operations, leading to broader effects beyond the EU.
- Example of Impact: The DSA’s influence extends beyond the EU, evidenced by the standardization of features like USB Type-C ports on devices such as the upcoming iPhone 15 series.
Motivation behind DSA Implementation
- Addressing Evolving Platform Dynamics: The DSA replaces outdated regulations to adapt to the changing landscape of online platforms, emphasizing the necessity for enhanced consumer protection.
- Tackling Risks and Abuses: Major platforms now resemble quasi-public spaces, posing risks to user rights and public participation, necessitating stricter regulations.
- Fostering Innovation and Competitiveness: By establishing a better regulatory environment, the DSA aims to foster innovation, growth, and competitiveness while supporting smaller platforms and startups.
Affected Online Platforms and Compliance Measures
- Large Platforms: Notable platforms like Facebook, Google, and Amazon are obligated to adhere to DSA regulations.
Compliance Initiatives:
- Google: Enhancing transparency reporting and expanding data access for researchers.
- Meta: Expanding its Ad Library and offering users control over personalization.
- Snap: Providing opt-out options for personalized feeds and limiting personalized ads for younger users.
Enforcement and Penalties
- Non-compliant platforms may face penalties of up to 6% of their global revenue.
- The Digital Services Coordinator and the Commission possess the authority to demand immediate actions from non-compliant platforms.
- Repeat offenders could face temporary bans from operating within the EU.
Conclusion
The enactment of the Digital Services Act represents a significant stride toward improving online safety and transparency within the EU. While initially aimed at major platforms, its ramifications extend globally, establishing standards for intermediary liability and content regulation.
- Global Pulse Confederation (GPC) held in New Delhi

Introduction:
In New Delhi, India, the Global Pulse Confederation (GPC) has launched Pulses 24, a three-day convention.
About Global Pulse Confederation (GPC):
- The Global Pulse Confederation (GPC) emerged in 2016 from the merger of the Global Pulse Confederation (GPC) and the International Starch Institute (ISI).
- Based in Dubai, United Arab Emirates, its mission is to represent and promote sustainable growth within the global pulse industry.
- Its key focuses include advocating for supportive policies, providing resources to industry stakeholders, and fostering research and innovation in pulse production and utilization.
- Membership is open to various entities involved in the pulse industry, such as growers, processors, traders, and researchers.
India’s Involvement:
- India, a significant producer and consumer of pulses, actively engages with the GPC and holds membership status, aligning with the organization’s objectives.
Key Highlights from Pulses 24 Convention:
1. Production Growth: Over the past decade, India’s pulses production has surged by 60%, reaching 270 lakh tonnes in 2024 from 171 lakh tonnes in 2014.
2. Partnership Goals: Mr. Goyal underscored the partnership between NAFED and GPC, aiming to position pulses as a crucial dietary component not only domestically but also globally.
3. Minimum Support Price (MSP): The government ensures an MSP offering 50% over the actual production cost to farmers, resulting in attractive returns. Notable increases in MSP for various pulses were noted, particularly in masoor and moong, reaching as high as 117% and 90%, respectively, over the past decade.
4. Self-Sufficiency by 2027: India is progressing towards self-reliance in chickpeas and other pulses, targeting self-sufficiency in all pulses by 2027. Initiatives include the distribution of new seed varieties and the expansion of cultivation for tur and black gram.
5. Global Knowledge Sharing: The GPC president highlighted India’s potential to benefit from the convention by exchanging best practices and technological advancements in pulse cultivation from other countries.
6. Focus on Smallholding Farmers: Pulses offer soil benefits and nutritional value, particularly advantageous for smallholding farmers.
- INSAT-3DS launch: Naughty Boy of ISRO
Introduction
The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) is preparing to launch the INSAT-3DS meteorological satellite aboard the GSLV F14 spacecraft.

INSAT-3DS Mission Objectives
1. Continuity of Services: The mission aims to maintain and improve upon the services currently provided by operational satellites like INSAT-3D and INSAT-3DR.
2. Meteorological Observations: INSAT-3DS will enable advanced meteorological observations, monitoring of land and ocean surfaces, and improved weather forecasting.
3. Disaster Warning: It will play a crucial role in disaster warning systems, facilitating timely alerts and response efforts.
4. Satellite-aided Research and Rescue Services (SAR): Additionally, the satellite will support SAR operations, enhancing search and rescue capabilities.
Significance
- This launch signifies the 16th mission for the GSLV, showcasing India’s advancements in space technology.
- INSAT-3DS is set to be deployed into the Geosynchronous Transfer Orbit (GTO), funded entirely by the Ministry of Earth Sciences, marking a significant milestone in India’s space endeavors.
- Approximately 18 minutes after launch, the satellite will be placed into a 36,647 km x 170 km elliptical orbit.
Why called “Naughty Boy”?
- The GSLV F14 has faced challenges in previous missions, earning the nickname “naughty boy” within the Indian space program due to its history of encountering issues.
- With a failure rate of 40%, GSLV F14 has experienced problems in six out of its fifteen missions thus far.




