|
|
||
|
19 February 2024 |
||
|
- Approximately half of pregnancies in India are classified as high-risk.
- Exploring Ultradian Rhythms: Embracing Life’s Natural Cycle
- What is in IPCC’s Assessment Reports?
- Manganese Bismuth Sulfide (MnBi2S4): A Promising Multiferroic Compound for Sustainable Data Storage Applications
- Medaram Jatara: Asia’s Largest Tribal Festival

- Approximately half of pregnancies in India are classified as high-risk.
https://www.thehindu.com/sci-tech/nearly-50-of-pregnancies-in-india-are-high-risk/article67853989.ece
Introduction
- This report presents the results of a recent extensive investigation carried out by researchers at the ICMR’s National Institute for Research in Reproductive and Child Health (NIRRCH) in Mumbai.
- Drawing upon data collected from the National Family Health Survey-5 (2019-2021), the study provides a detailed analysis of the occurrence and causes of high-risk pregnancies among women in India.
Pregnancy Issues: Key Statistics
- The study analyzed data from approximately 24,000 pregnant women throughout India, revealing an alarming prevalence of high-risk pregnancies at 49.4%.
- Particularly high rates were observed in the Northeastern states, including Meghalaya (67.8%), Manipur (66.7%), and Mizoram (62.5%), as well as Telangana (60.3%).
- Meghalaya stood out with a notably high incidence of multiple high-risk factors at 33%.
- These findings underscore the urgent need for tailored interventions to effectively address regional disparities and local challenges.
Methodology
The study utilized unit-level data sourced from the Demographic Health Surveys (DHS) program to meticulously examine the prevalence of high-risk pregnancies among women aged 15-49.
Key risk factors identified include short birth spacing, adverse birth outcomes, and caesarean deliveries, all of which significantly contribute to the incidence of high-risk pregnancies.

Major Risks Identified
- Critical maternal factors such as age, height, body mass index (BMI), and gestational weight gain emerged as pivotal determinants of pregnancy-related risks.
- Additionally, lifestyle choices such as tobacco use, alcohol consumption, and previous birth outcomes were found to significantly influence the likelihood of high-risk pregnancies.
- Moreover, pregnant women with limited formal education exhibited disproportionately higher prevalence rates of multiple high-risk factors compared to their educated counterparts.
- The study also highlighted temporal patterns, indicating an escalation of high-risk factors during the third trimester, emphasizing the importance of vigilant monitoring and timely interventions.
Major Government Interventions
Several government initiatives have been implemented to address maternal and child health issues, including:
- Janani Shishu Suraksha Karyakram (JSSK) (2011)
- Pradhan Mantri Surakshit Matritva Abhiyan (PMSMA) (2016)
- LaQshya Initiative (2011)
- Pradhan Mantri Matru Vandana Yojana (PMMVY) (2016)
- Surakshit Matritva Aashwasan (SUMAN)
- Anaemia Mukt Bharat (2018)
Way Forward
To effectively mitigate the prevalence of high-risk pregnancies and promote equitable access to healthcare, the study recommends:
- Region-specific interventions targeting areas with high prevalence rates
- Strengthening antenatal care services, particularly for at-risk women
- Investing in healthcare professional training to identify and manage high-risk pregnancies
- Coordinating and integrating existing government initiatives for holistic maternal care.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the study advocates for a comprehensive approach to address the challenges posed by high-risk pregnancies, with a focus on safeguarding maternal and child health and ensuring equitable healthcare access across socio-economic strata.
- Exploring Ultradian Rhythms: Embracing Life’s Natural Cycle
Introduction
Life on Earth exhibits a series of recurring processes vital for sustaining and improving survival, with one such cornerstone process being ultradian rhythms.
Distinct from circadian rhythms, ultradian rhythms are biological cycles occurring more frequently than once every 24 hours, governing crucial physiological functions.
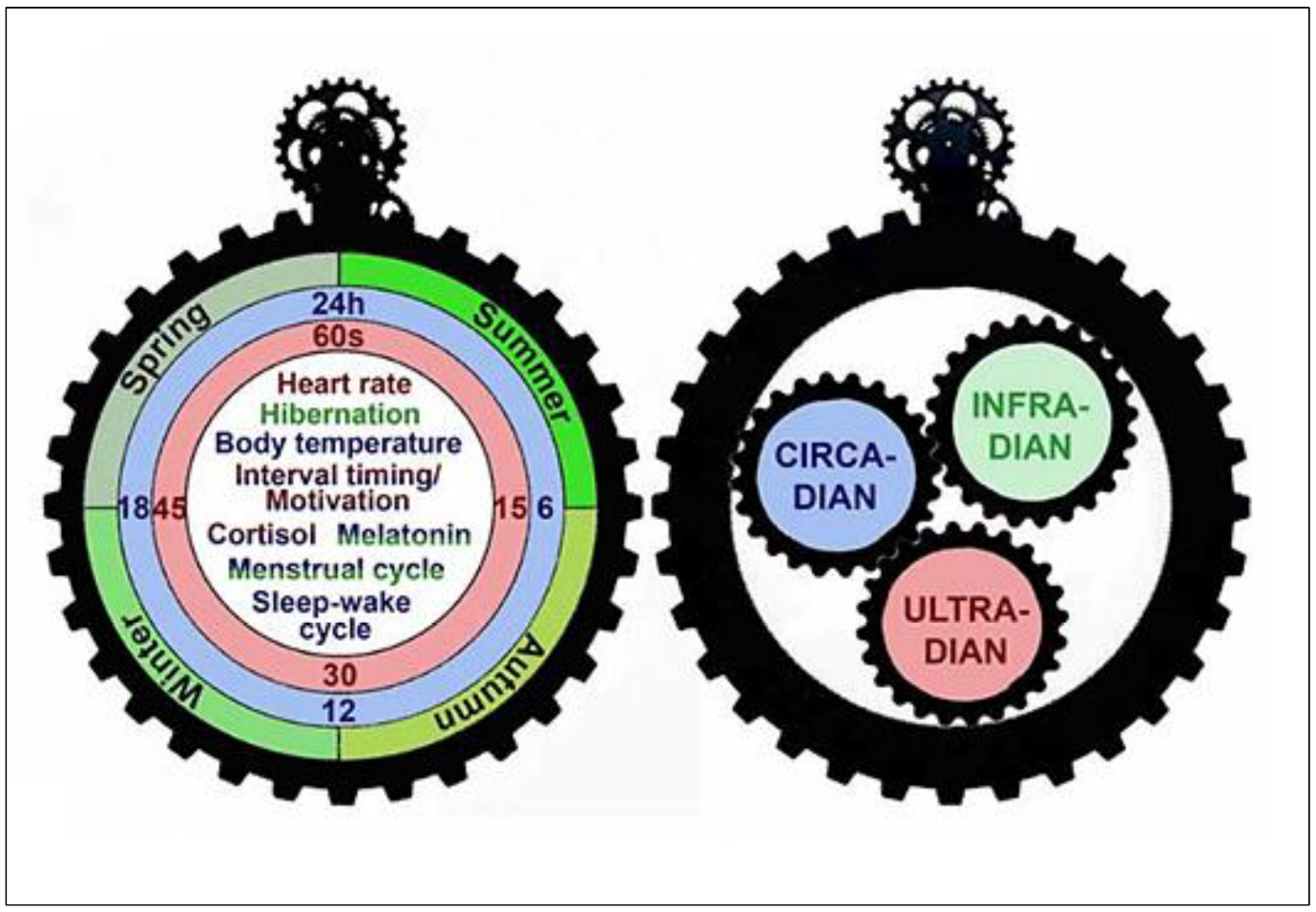
Key Characteristics of Ultradian Rhythms
1. Frequency: Ultradian rhythms recur more frequently than circadian rhythms, influencing various biological processes.
2. Physiological Patterns: These rhythms regulate heartbeat, breathing, hormonal release, and brain-wave activity, ensuring proper functioning of living organisms.
|
Feature |
Ultradian Rhythms |
Circadian Rhythms |
|
Definition |
Repeat at intervals of less than 24 hours. |
Repeat approximately every 24 hours. |
|
Duration |
Shorter cycles, typically minutes to a few hours. |
Longer cycles, around 24 hours. |
|
Examples |
Sleep cycles, heart rate variability, hormone release. |
Sleep-wake cycle, body temperature regulation. |
|
Influence |
Impact physiological processes within a single day. |
Regulate sleep-wake patterns, hormone release, etc. |
|
Importance |
Essential for various bodily functions and processes. |
Crucial for maintaining overall health and well-being. |
|
Disruption Effects |
Interruption can lead to fatigue or mood swings. |
Disruption can cause sleep disorders or mood disorders. |
Significance
- Sleep Cycle: An exemplary ultradian rhythm is the sleep cycle, comprising alternating periods of REM (Rapid Eye Movement) and non-REM sleep, typically lasting around 90 minutes each.
- REM and Non-REM Sleep: REM sleep involves dreaming, while non-REM sleep is vital for physical restoration and memory consolidation.
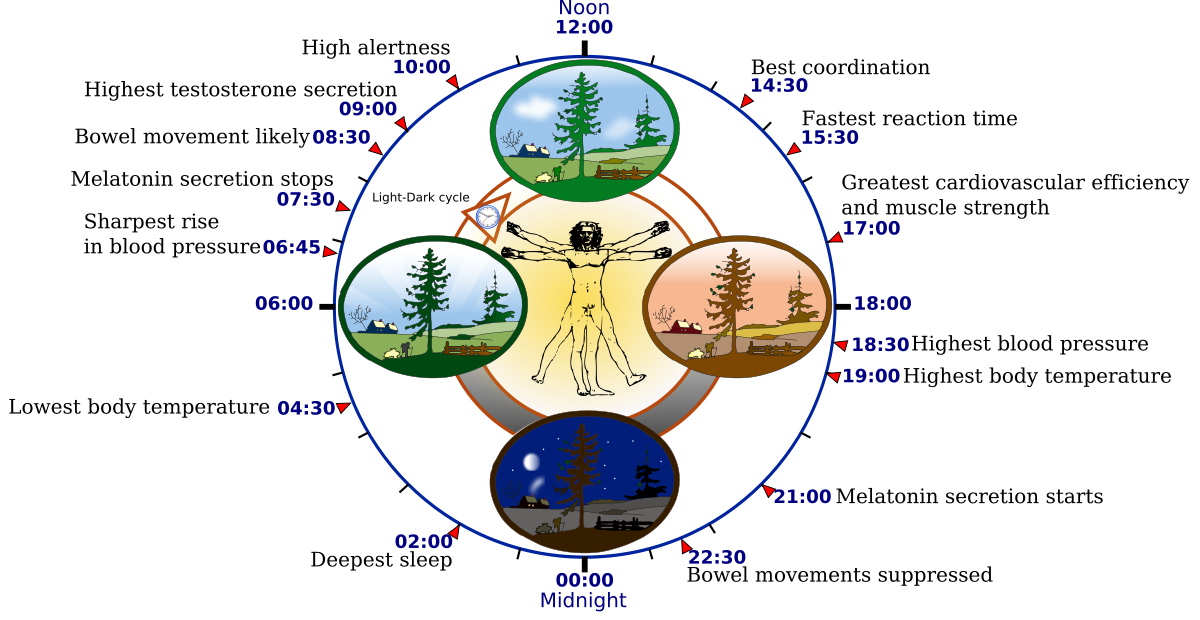
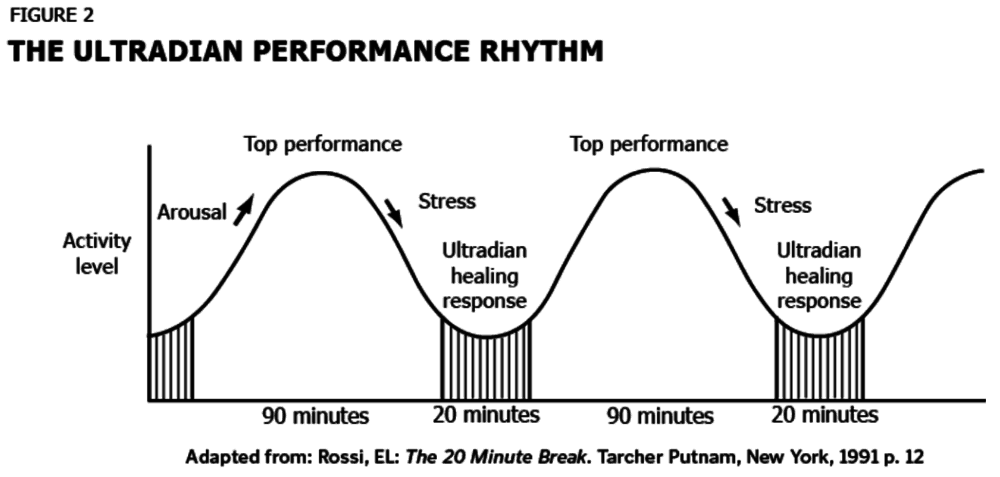
Role in Hormonal Regulation
1. Pulsatile Hormone Secretion: Ultradian rhythms affect the pulsatile secretion of hormones like growth hormone, cortisol, and insulin throughout the day.
2. Metabolism and Stress Response: These hormonal fluctuations play a crucial role in regulating metabolism, energy levels, and responses to stress, ensuring overall well-being.
- What is in IPCC’s Assessment Reports?
Introduction
Since its establishment in 1988, the UN Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) has played a central role in evaluating climate science and shaping worldwide responses to climate change through its assessment reports and special publications.
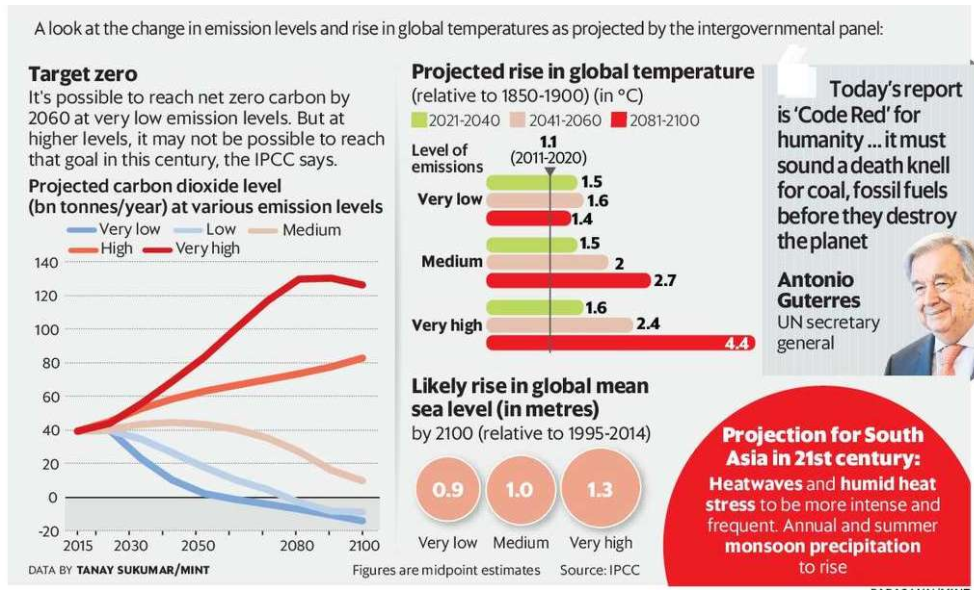
The recent Sixth Assessment Report (AR6) highlights the pressing need to restrict global warming to 1.5 degrees Celsius, reflecting the gravity of the situation.

Key Findings of AR6
- AR6 sends a clear and urgent warning that time is rapidly dwindling to limit global warming to 1.5 degrees Celsius.
- It emphasizes the imperative for immediate action to mitigate the adverse impacts of climate change.
- Additionally, the report highlights the considerable challenges associated with adapting to climate change and proposes strategies to bolster resilience in both natural and human-made systems.

Initiation of AR7 Cycle
- In January 2024, the IPCC launched its seventh assessment cycle (AR7) with a bureau meeting held in Turkey.
- This meeting focused on discussions regarding budget allocation, timelines, and the overall work program for the upcoming cycle.
- Insights gleaned from the AR6 cycle, coupled with contributions from member countries, informed deliberations on the structure and thematic focus of forthcoming reports.
Global Stocktake and IPCC’s Role
- The global stocktake (GST) serves as a crucial mechanism for evaluating progress toward the goals outlined in the Paris Agreement, with the IPCC playing a pivotal role by providing scientific input.
- Member countries have requested IPCC reports to align with the GST, facilitating comprehensive assessments of the effectiveness of climate action initiatives.

Scope and Timeline of AR7 Cycle
- The AR7 cycle will encompass a range of reports, including full assessment reports, synthesis reports, methodology reports, and a special report specifically addressing climate change and its impact on urban areas.
- Methodology reports will cover topics such as short-lived climate forcers and carbon removal, with technical guidelines on impacts and adaptation set to be updated.
- The publication timeline aims for special and methodology reports to be released by 2027, although timelines for assessment reports are subject to further discussion.
Challenges and Considerations
- One of the primary challenges facing the IPCC is balancing the imperative for timely reports with the rigorous review process and the evolving landscape of climate research.
- The shortened timelines may potentially compromise the scientific rigor and inclusivity of the reports.
- Additionally, limited timeframes may hinder effective engagement with marginalized communities and stakeholders, thereby impacting the overall quality of the reports.
Conclusion
- The commencement of the IPCC’s AR7 cycle represents a pivotal moment in global climate science, underscoring the urgent need for concerted action to address climate change.
- Despite the challenges ahead, the IPCC remains steadfast in its commitment to delivering comprehensive and scientifically robust assessments to inform climate action.
- Effective collaboration between scientists, policymakers, and stakeholders will be paramount in navigating the complexities of climate science and fostering sustainable solutions for a resilient future.
- Manganese Bismuth Sulfide (MnBi2S4): A Promising Multiferroic Compound for Sustainable Data Storage Applications

Introduction
Researchers have recently discovered an intriguing phenomenon involving electric polarization through magnetic ordering in a newly identified mineral called “MnBi2S4”, presenting potential applications in energy-efficient data storage.
About Magnetoelectric Multiferroics
Magnetoelectric multiferroics, a rare class of materials known for their unique properties encompassing both magnetism and ferroelectricity concurrently, serve various purposes in advanced technologies such as spintronics, electronic memory devices, actuators, and switches.
What is MnBi2S4?
- Also referred to as mineral gratianite, MnBi2S4 belongs to the ternary manganese chalcogenide family, boasting distinctive magnetic structures, including spin density wave, cycloidal, and helical spin structures.
- Notably, the latter two spin configurations induce ferroelectric behavior in the material.
- MnBi2S4, exhibiting centro-symmetric properties, undergoes magnetic ordering at relatively low temperatures (27, 23, and 21.5 Kelvins).
Significance of the Study
- This discovery highlights the profound interplay between magnetism and electric polarization, driven by magnetic frustration, representing a significant advancement in magnetoelectric coupling.
- If MnBi2S4 can exhibit similar phenomena at ambient temperatures, it holds the potential to transform data storage processes by minimizing energy consumption during write operations.
- Moreover, these findings could facilitate the development of a four-state logic memory system, offering enhanced device performance compared to existing binary logic systems.
- Medaram Jatara: Asia’s Largest Tribal Festival
Introduction
Preparations for Asia’s largest tribal festival, the Medaram Jatara, are ongoing as people flock to shop in anticipation.
The festival, centered around the veneration of the deities Sammakka and Saralamma, involves devotees offering jaggery equivalent to their own weight.

About Medaram Jatara
Description: Rooted in the legend of Sammakka and Sarakka, revered figures in the local tribal community, Medaram Jatara holds significant historical and cultural importance.
Origin:The festival’s origins lie in the story of Sammakka and Sarakka, a mother-daughter duo celebrated among the local tribal community.
Historical Significance: Medaram Jatara commemorates the 13th-century battle of Sammakka and Sarakka against the taxation imposed by the Kakatiya rulers on the Koya people.
Location: Situated in Mulugu, Telangana, India, Medaram Jatara draws devotees from diverse tribal and non-tribal communities.
Frequency: This biennial festival attracts approximately 1.5 crore devotees not only from Telangana and Andhra Pradesh but also from states like Madhya Pradesh, Jharkhand, Chhattisgarh, and Maharashtra.
Political & Social Impact: Recognized as a State Festival in 1996, Medaram Jatara receives active support from the Ministry of Tribal Affairs and the Telangana state government.
Infrastructure Development: Efforts are underway to develop community shelters and infrastructure in and around Medaram, with allocated funds for this purpose.
Ministry Support:The Ministry of Tribal Affairs and the Telangana state government actively participate in and financially support Medaram Jatara.
Tribal Circuit Development:The Ministry of Tourism sanctions funds for the integrated development of the tribal circuit, further enhancing the festival’s significance.


