 |
||
| 20 April 2024 | ||
|
- World Future Energy Summit 2024: Spotlight
- Analyzing the Downturn in Private Investments: Insights and Implications
- Introducing the SPACE Testing & Evaluation Hub for Sonar Systems
- Mount Ruang Eruption in Indonesia:
- Exploring the Clouded Tiger Cat
- Unveiling Gross Fixed Capital Formation (GFCF)
- The Global Alliance for Incinerator Alternatives (GAIA)
- GPS Spoofing
- The Lakshmana Tirtha River
- DURGA-2: Directionally Unrestricted Ray Gun Array System
- Understanding the Hubble Tension
- Dragonfly Mission
World Future Energy Summit 2024: Spotlight
Context;
Panel Discussion on Future Growth Opportunities for Long Duration Energy Storage.The World Future Energy Summit 2024 recently made headlines with its engaging panel discussion in Abu Dhabi, focusing on the future prospects of long duration energy storage.

About World Future Energy Summit (WFES);
1.Origins and Purpose
The World Future Energy Summit (WFES) is an annual event held in Abu Dhabi, hosted by the United Arab Emirates, aimed at advancing future energy, energy efficiency, and clean technologies.
2.Inception and Leadership
Founded in 2008 under the patronage of Sheikh Mohammed Bin Zayed Al Nahyan, Crown Prince of Abu Dhabi, the summit was established with assistance from Edelman, a public relations firm, to enhance the UAE’s environmental reputation.
3.Mission and Vision
The WFES serves as a crucial platform to address the escalating demand for renewable energy solutions and sustainable development in response to global energy challenges.
Key Initiative: Young Future Energy Leaders (YFEL)
Engaging the Next Generation
The Young Future Energy Leaders (YFEL) program is an integral component of the annual World Future Energy Summit (WFES), designed to raise awareness and engage students and young professionals in renewable energy and sustainability efforts.
Affiliation and Commitment;
As a program affiliated with the Masdar Institute, YFEL is committed to nurturing future leaders in renewable energy and sustainability, fostering innovation and collaboration among youth worldwide.
Analyzing the Downturn in Private Investments: Insights and Implications
Context:
- The Indian economy has been grappling with a sluggish pace of private investment, as evidenced by the tepid growth in private GFCF relative to GDP.
- This trend has raised concerns among policymakers and economists alike, prompting a deeper examination of its underlying causes and potential remedies.

Deciphering GFCF:
- GFCF serves as a barometer of the expansion of fixed capital within an economy, encompassing investments in tangible assets like buildings and machinery.
- It offers insights into the willingness of the private sector to invest, thereby influencing overall economic growth trajectories.
Significance of GFCF:
- The vitality of GFCF lies in its role in driving productivity enhancements, ultimately translating into improved living standards for the populace.
- As fixed capital forms the backbone of economic output, any fluctuations in GFCF can have far-reaching implications for the economy at large.
Historical Trends in Private Investment:
- A historical overview reveals distinct phases in private investment patterns. Pre-liberalization, private investment maintained relative stability, with public investment overshadowing its growth.
- However, the liberalization era witnessed a surge in private investment, fueled by economic reforms that bolstered confidence.
- Yet, post the global financial crisis, private investment began faltering, with a noticeable decline observed in recent years.
Determinants of the Decline:
- Several factors contribute to the subdued nature of private investment.
- Some economists point to the sluggish pace of private consumption expenditure, emphasizing the pivotal role of robust consumer demand in stimulating investment decisions.
- Conversely, others highlight structural impediments and policy uncertainties as primary deterrents to private investment, citing unfavorable government policies and regulatory ambiguity.
Implications and the Way Forward:
- Addressing the decline in private investment necessitates a multifaceted approach.
- Policymakers must prioritize initiatives aimed at fostering consumer confidence while ensuring a conducive business environment characterized by policy stability.
- Balancing pro-growth fiscal measures with structural reforms is imperative to reigniting investment momentum, thereby fueling sustained economic growth and prosperity.
Conclusion;
In sum, comprehending the intricacies of private investment trends, as exemplified by GFCF dynamics, is crucial for devising targeted policy interventions that can rejuvenate investment sentiment and propel India towards a path of sustainable economic development.
Introducing the SPACE Testing & Evaluation Hub for Sonar Systems
Context;
- DRDO recently inaugurated a cutting-edge testing and evaluation hub for sonar systems tailored for the Indian Navy.
- Located at the Underwater Acoustic Research Facility in Kulamavu, Idukki, Kerala, SPACE is a project spearheaded by the Naval Physical & Oceanographic Laboratory of DRDO.
- It aims to emerge as the premier testing and evaluation center for sonar systems deployed across various Indian Navy platforms, encompassing ships, submarines, and helicopters.

Key Features of SPACE:
- SPACE consists of two integral components: a Floating Platform situated on the water surface and a Submersible Platform capable of descending to depths of up to 100 meters via winch systems.
- This setup allows for efficient resource utilization, as the submersible platform can be easily winched up and docked with the floating platform post operations.
Functions and Capabilities:
- SPACE primarily serves as a venue for the comprehensive evaluation of sonar systems, facilitating swift deployment and retrieval of scientific equipment such as sensors and transducers.
- Additionally, it is equipped for surveying, sampling, and data collection pertaining to air, surface, mid-water, and reservoir floor parameters, leveraging modern scientific instrumentation.
- SPACE is poised to meet the data processing and sample analysis needs, heralding a new era in Anti-Submarine Warfare research capabilities.
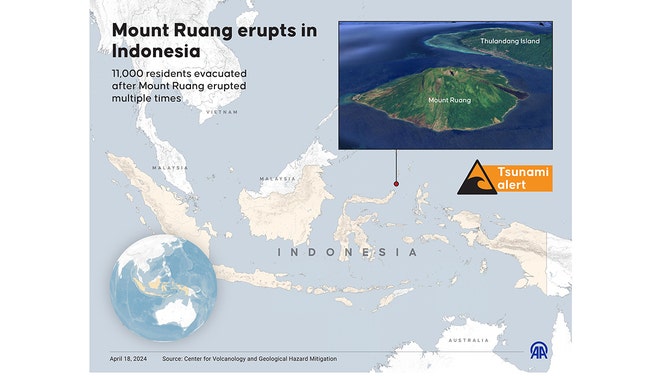
Mount Ruang Eruption in Indonesia:
Context;
- Mount Ruang is located within the Sangihe Islands arc in North Sulawesi, Indonesia.
- It is characterized by an island measuring 4 by 5 kilometers wide, featuring a partial lava dome at its summit towering to an altitude of 725 meters (2,379 ft).
- Notable peaks such as Klabat, Siau, and Ternate are visible from the volcano’s summit. Historical records indicate its first eruption occurred in 1808.
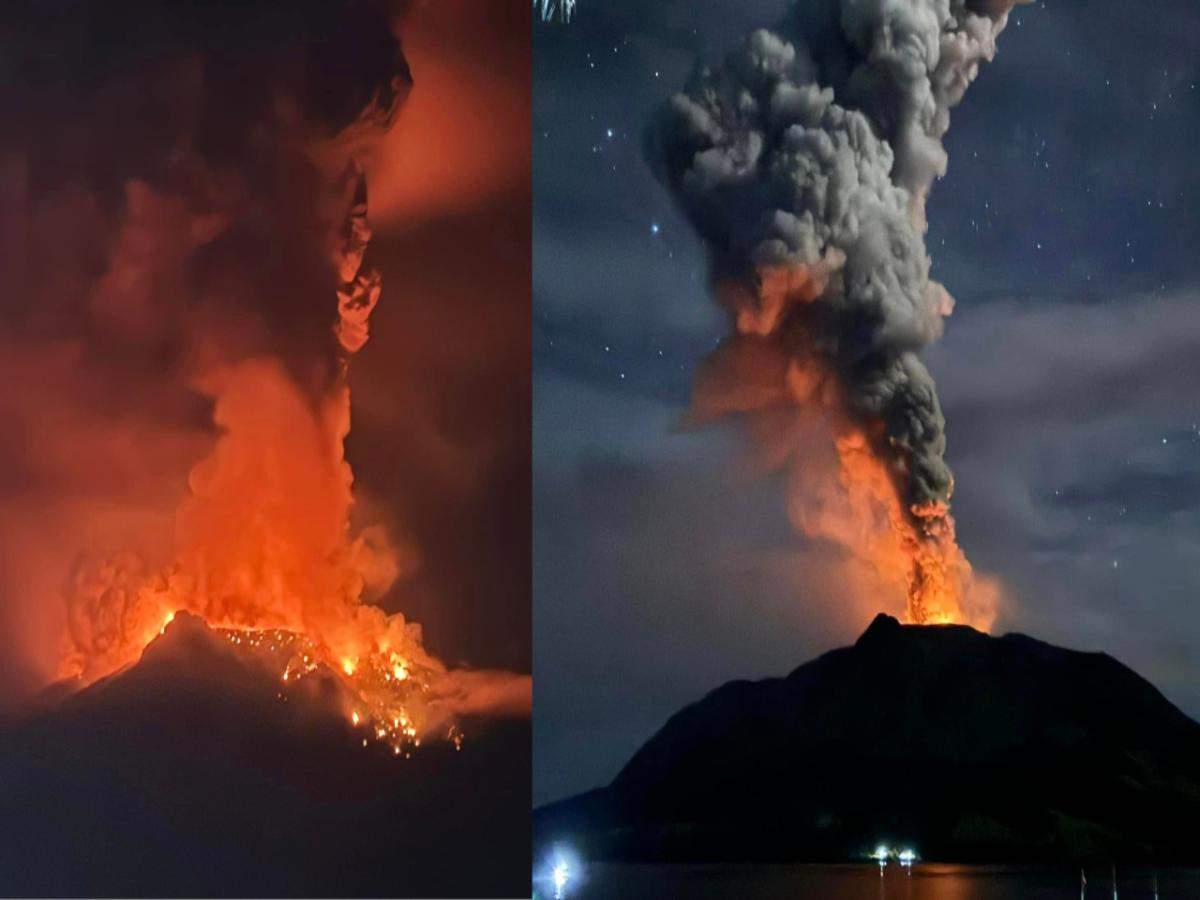

Understanding the Surge in Volcanic Activity in Indonesia:
- Indonesia, home to approximately 270 million people, boasts a landscape dotted with 120 active volcanoes.
- The nation’s susceptibility to volcanic eruptions is attributed to its geographical location along the “Ring of Fire,” an expansive belt of seismic fault lines encircling the Pacific Ocean.
Exploring the Pacific ‘Ring of Fire’:

- The Pacific ‘Ring of Fire,’ also referred to as the Pacific Rim or the Circum-Pacific Belt, encompasses a region characterized by active volcanoes and frequent seismic activity.
- This zone is delineated by volcanic arcs and oceanic trenches encircling the Pacific Basin, hosting a significant portion of the world’s volcanoes and earthquakes.
Geographic Spread and Seismic Activity:
- Stretching over 40,000 kilometers, the Ring of Fire traces a nearly circular arc encompassing regions from New Zealand to Indonesia, the Philippines, Japan, and along the western coasts of North and South America.
- This area experiences substantial seismic activity due to interactions between multiple tectonic plates, including the Pacific, Philippine, Juan de Fuca, Cocos, Nazca, and North American plates.
- The resultant movements generate earthquakes and tsunamis annually, particularly in subduction zones where tectonic plates converge.
Exploring the Clouded Tiger Cat
Introduction:
Recently unearthed in Brazil, the clouded tiger cat emerges as a newly discovered species facing imminent threats from deforestation and unlawful hunting.

Understanding Tiger Cats:
- Tiger cats, also identified as oncillas, are diminutive spotted felines endemic to Central and South America.
- Their adeptness in tree-climbing and hunting small prey showcases their remarkable adaptability to their surroundings.
Characteristics of Tiger Cats:
- These elusive creatures, among the smallest wild cats in the Americas, typically weigh between 1.5 to 3 kilograms (3.3 to 6.6 pounds).
- Previously classified into two species and various subspecies, recent research has revealed a third species: the clouded tiger cat (Leopardus pardinoides).
Discovering the Clouded Tiger Cat:
The clouded tiger cat represents a novel addition to the feline family, thriving in forested habitats.
Scientific Name: Leopardus pardinoides
Geographic Distribution:
Found within the cloud forests stretching across the southern Central American and Andean Mountain chains, their habitat spans from Costa Rica through Panama, Colombia, Peru, Bolivia, to Argentina.
Distinctive Features:
- With its lengthy tail, short-rounded ears, and an average weight of 2.27 kg, the clouded tiger cat exhibits a unique appearance.
- Noteworthy for its margay-like head, its fur showcases a rich reddish/orangish/grayish-yellow hue adorned with irregularly shaped medium-large ‘cloudy’ rosettes, distinctively marked and often blending together.
- Remarkably, this species possesses only one pair of mammae/teats, setting it apart from other feline species.
Unveiling Gross Fixed Capital Formation (GFCF)
Overview;
The Indian economy grapples with the sluggishness in private investment, evident in private Gross Fixed Capital Formation (GFCF) as a percentage of GDP at current prices.

Understanding the Challenge:
The stagnation in private investment, exemplified by private Gross Fixed Capital Formation (GFCF) as a percentage of GDP at current prices, presents a significant hurdle for the Indian economy.
Delving into Gross Fixed Capital Formation (GFCF):
GFCF denotes the expansion in the size of fixed capital within an economy, encompassing tangible or intangible assets produced as outputs from production processes utilized repeatedly for over a year.
Components of GFCF:
GFCF comprises investments made by resident producers in fixed assets during a specified period, subtracting disposals. Additionally, it includes increments to the value of non-produced assets realized by producers or institutional units.
Significance of GFCF:
- GFCF serves as an indicator of the private sector’s investment inclination within an economy.
- Fixed capital plays a pivotal role in enhancing production capacity, thereby fostering economic growth and improving living standards.
Impact of Fixed Capital:
- Fixed capital predominantly influences the overall output of an economy, thereby shaping consumer purchasing power in the market.
- Disparities in fixed capital exist between developed and developing economies, with developed nations exhibiting higher fixed capital per capita.
Analyzing Statistical Trends:
In the Indian context, GFCF witnessed a notable surge from INR 32.78 lakh crore in 2014-15 to INR 54.35 lakh crore in 2022-2023. This upswing mirrors substantial investments in infrastructure, industrial sectors, and public goods.
The Global Alliance for Incinerator Alternatives (GAIA)
Introduction;
- The Global Alliance for Incinerator Alternatives (GAIA) Asia Pacific, in collaboration with other environmental organizations, has urged ASEAN to take decisive action in response to plastic pollution.
- GAIA is a worldwide coalition comprising over 1,000 grassroots groups, non-governmental organizations (NGOs), and individuals in more than 90 countries.

Mission and Vision of GAIA;
- GAIA aims to facilitate a transition away from the current linear and extractive economy towards a circular system that upholds people’s right to a safe and healthy environment.
- The organization envisions a just, zero-waste world built on respect for ecological limits and community rights, where individuals are free from the burden of toxic pollution and resources are sustainably conserved, rather than being burned or dumped.
Approaches and Initiatives of GAIA;
- GAIA’s efforts involve fighting pollution and promoting regenerative solutions in cities through local campaigns, policy and financial adjustments, research and communication initiatives, and movement building.
- The organization focuses on four primary areas of intervention: incineration, zero waste, plastic, and climate.
Understanding Incineration;
- Incineration is the process of burning hazardous materials at high temperatures to destroy contaminants.
- It is typically carried out in specialized furnaces known as incinerators, designed for burning hazardous substances in a controlled environment.
Materials Treated by Incineration;
- Incineration can treat various hazardous materials, including soil, sludge, liquids, and gases.
- While it effectively destroys many harmful chemicals such as solvents, PCBs, and pesticides, it does not eliminate metals such as lead and chromium.
Modern Incinerators and Pollution Control;
Modern incinerators are equipped with air pollution control equipment, such as fabric filters, scrubbers, and electrostatic precipitators, to remove fly ash and gaseous contaminants from the emissions.
GPS Spoofing
Overview;
Reports suggest that Israel employed GPS spoofing tactics against Iran’s missile targeting teams by disrupting Global Positioning System (GPS) navigation signals.
![On GPS spoofing of aerial platforms: a review of threats, challenges, methodologies, and future research directions [PeerJ]](https://statecraft.in/wp-content/uploads/2024/04/on-gps-spoofing-of-aerial-platforms-a-review-of-t.jpeg)
Understanding GPS Spoofing;
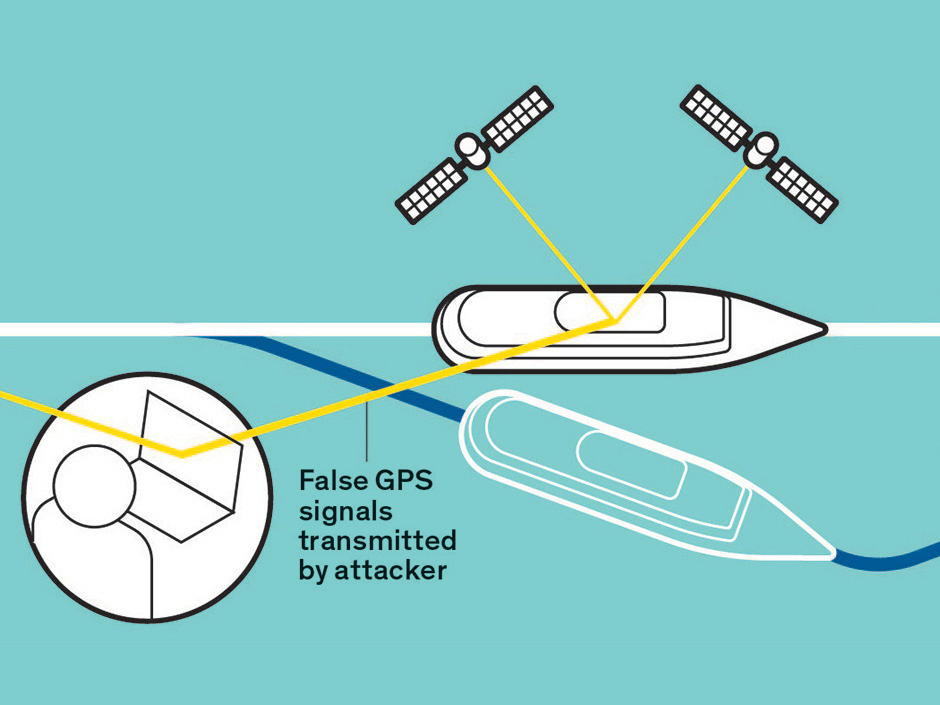
- GPS spoofing, also termed GPS simulation, involves the manipulation or deception of a GPS receiver through the transmission of false GPS signals.
- This deceptive practice misleads the GPS receiver into believing it is located in a different position, resulting in the provision of inaccurate location data.
Evolution of GPS Spoofing;
Originally considered a theoretical threat, GPS spoofing has evolved into a practical concern due to the availability of affordable software and hardware capable of generating fake GPS signals.
Differentiating Spoofing from Jamming;
- Spoofing and jamming are distinct concepts. While jamming involves the deliberate disruption of GPS signals, spoofing entails a more sophisticated form of deception.
- Incidents like those observed in the mentioned context involving aircraft are unprecedented, unlike routine jamming experienced by planes and other airborne vehicles.
How GPS Spoofing Works;
- GPS spoofing exploits the inherent vulnerabilities in the GPS infrastructure, particularly the relatively weak signal strength of GPS satellites.
- The system operates by transmitting signals from satellites to GPS receivers on Earth, which calculate their location based on the time taken for these signals to reach them.
- However, counterfeit signals can easily overwhelm the weak GPS signals, leading to inaccurate positioning data.
Potential Impacts of GPS Spoofing;
GPS spoofing can have severe consequences, especially in navigation scenarios. It has the potential to significantly impact various industries, including logistics, telecommunications, energy, and defense, potentially resulting in catastrophic outcomes.
The Lakshmana Tirtha River
Context;
- The Lakshmana Tirtha River has completely dried up due to severe drought conditions and intense heat.
- Situated in Karnataka, the Lakshmana Tirtha River serves as a tributary to the Kaveri River.
- Originating in the Brahmagiri hills of the Kodagu or Coorg District, Karnataka, the river flows eastward before merging with the Kaveri River in the Krishna Raja Sagara Lake.
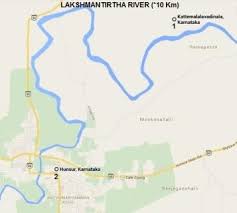
Significant Landmarks:
Notable attractions along the river include the Lakshmanatirtha Falls, also known as the Irupu Falls, located near the Kerala border on the way to Nagerhole National Park.
Sacred Status:
The Kaveri River, also revered as the Cauvery River, holds profound religious significance among Hindus in southern India.
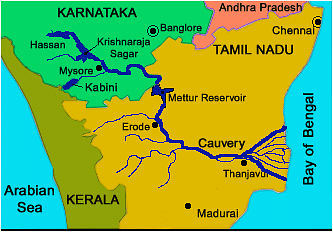
Course:
Originating at an elevation of 1,341 m in Talakaveri, Karnataka, the river flows until it meets the Bay of Bengal at Poompuhar, Tamil Nadu.
Cauvery Basin:
- Encompassing Tamil Nadu, Karnataka, Kerala, and the Union Territory of Puducherry, the river basin is bordered by the Western Ghats to the west and the Eastern Ghats to the east and south.
- It is also defined by ridges separating it from the Krishna basin and Pennar basin to the north.
Major Tributaries:
The Kaveri River is nourished by significant left bank tributaries such as Harangi, Hemavati, Shimsha, and Arkavati, as well as major right bank tributaries including Lakshmantirtha, Kabbani, Suvarnavati, Bhavani, Noyil, and Amaravati.
DURGA-2: Directionally Unrestricted Ray Gun Array System
Introduction:
Reports indicate that the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) is currently conducting tests on a prototype of the DURGA-2 (Directionally Unrestricted Ray Gun Array) system.

Functionality:
The DURGA-2 system is engineered to incapacitate or eliminate targets by emitting focused energy beams, including lasers, microwaves, or particle beams.
Advantages:
These cutting-edge weapons offer several advantages over conventional munitions:
- Speed: They deliver lethal force at the speed of light, approximately 300,000 kilometers per second.
- Resistance: Their beams remain unaffected by gravity or atmospheric resistance.
- Precision: They boast exceptional precision, allowing for accurate targeting.
4. Customization: The effects of these weapons can be finely tuned by adjusting the type and intensity of energy directed toward the target.
Impact on Warfare:
The development of DURGA-2 has profound implications for the aerospace industry, potentially transforming the dynamics of warfare.
Future Applications:
This advancement opens doors to the creation of advanced platforms, weaponry, sensors, and networks essential for achieving success in future conflicts.
Understanding the Hubble Tension
Overview:
Recent studies have drawn attention to the Hubble tension, a discrepancy in the measurement of the universe’s rate of expansion.
Defining Hubble Tension:
The Hubble tension arises from the disagreement between two equally valid methods used to measure the rate of the universe’s expansion.
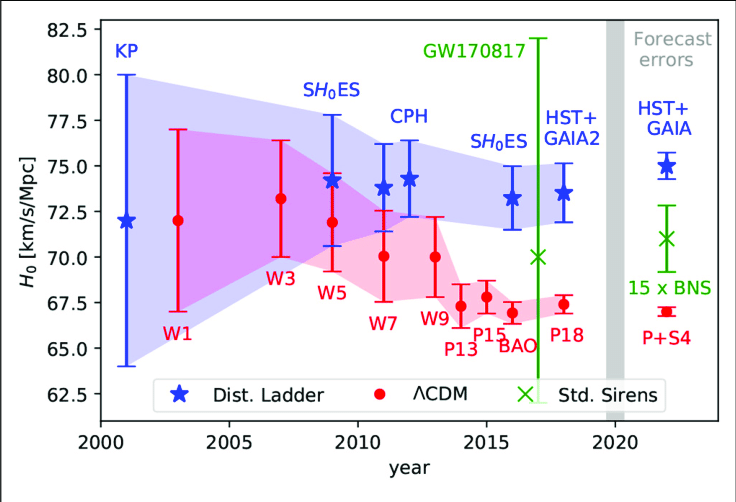
Measurement of Universe’s Expansion
The Hubble Constant:
The rate of the universe’s expansion is quantified by a parameter known as the Hubble Constant.
Methods of Measurement:
1. Cosmic Microwave Background (CMB):
This method relies on observations of the cosmic microwave background radiation, which is a remnant of the early universe. By analyzing the patterns in this radiation, scientists can derive an estimate of the Hubble Constant.
2. Cosmic Distance Ladder:
The cosmic distance ladder is a series of techniques used to determine the distances to celestial objects at varying distances from Earth. This method employs measurements of objects at different cosmic distances, including nearby galaxies, distant supernovae, and extremely remote quasars.
Key Differences and Challenges:
Cosmic Microwave Background (CMB):
- This method relies on observations of the afterglow of the Big Bang, providing a snapshot of the early universe.
- It offers a direct measurement of the universe’s expansion rate at early cosmic times.
Cosmic Distance Ladder:
- Utilizes various astronomical phenomena, such as the brightness of standard candles like Type Ia supernovae and the properties of variable stars like Cepheid variables.
- Provides a more direct measurement of the present-day expansion rate based on observations of nearby galaxies and stellar objects.
Implications and Future Directions:
- The unresolved Hubble tension has significant implications for our understanding of the cosmos.
- Scientists are actively seeking new models or theories to reconcile the discrepancies between these two methods and achieve a more accurate determination of the Hubble Constant.
- Resolving the Hubble tension is crucial for advancing our understanding of cosmology and the fundamental properties of the universe.
Dragonfly Mission
Context;
NASA has greenlit the Dragonfly mission, slated to embark on a journey to Saturn’s largest moon, Titan, with a budget of $3.35 billion and a scheduled launch in July 2028.Dragonfly is a groundbreaking NASA spacecraft mission aiming to deploy a robotic rotorcraft to explore Titan, Saturn’s largest moon.

Key Highlights:
- Scheduled to launch in July 2028, Dragonfly anticipates arriving at Titan by 2034.
- This mission marks the pioneering exploration of Titan’s atmosphere with a focus on investigating prebiotic chemistry and extraterrestrial habitability.
Significance of Titan:
Titan’s rich carbon chemistry and evidence of water-ice surfaces make it a prime target for astrobiology and the study of life’s origins.
Mission History:
- Proposed to NASA’s New Frontiers program in April 2017 by the Johns Hopkins Applied Physics Laboratory (APL).
- Selected as one of two finalists from twelve proposals in December 2017 and officially designated as the fourth mission in the New Frontiers program on June 27, 2019.
- Faced funding uncertainties resulting in a launch delay to July 2028 after undergoing a preliminary design review in March 2023.
Mission Design and Construction:
- Dragonfly is crafted as a rotorcraft lander, resembling an octocopter equipped with a Multi-Mission Radioisotope Thermoelectric Generator (MMRTG) for power generation.
- Equipped with scientific instruments including DraMS (Mass Spectrometer) and DragonCam (Camera Suite) to analyze Titan’s surface composition and microbial habitability.
Scientific Objectives:
- Dragonfly aims to investigate various locations on Titan’s surface to evaluate its habitability and explore prebiotic chemistry.
- It will explore regions where extraterrestrial liquid water and organic compounds may coexist, shedding light on the potential origins of life.
Trajectory and Landing Site:
- The mission’s journey will span approximately seven years, with Dragonfly undergoing entry and descent using an aeroshell and parachutes.
- Initial landing is planned in dunes southeast of the Selk impact structure, with subsequent exploration of the Selk impact crater to study geological features and potential cryovolcanism.

