 |
||
| 25 April 2024 | ||
|
- A Critical Examination of the PMAY-U Scheme
- India’s Strategy for Enhancing EV Production
- ISRO’s Study on Glacial Lake Dynamics in the Himalayas
- Pink Hydrogen: Leveraging Nuclear Energy for Sustainable Production
- Golden Trevally Fish: Successful Captive Breeding Achievement
- Voyager 1 and Voyager 2: Pioneering Space Probes
- Crystal Maze 2: Advancing Air-to-Surface Capabilities
- Indian Telecom Services Performance Indicator Report
- Europe’s Accelerated Warming
- NABARD’s Climate Strategy for 2030
- Asia’s Predicament: Insights from WMO’s Report
A Critical Examination of the PMAY-U Scheme
Context;
- Brief overview of the PMAY-U scheme initiated by the current Union government.
- Objectives of the Housing For All (HfA) program by 2022 under the PMAY scheme.
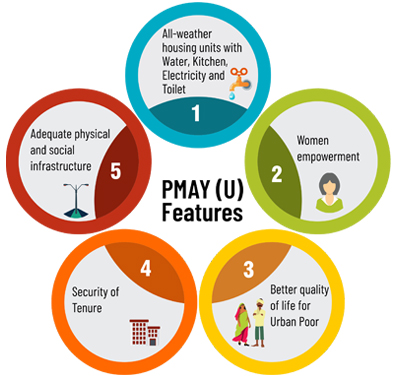
Highlights of the PMAY Scheme;
- Goals of the PMAY scheme, including slum rehabilitation, affordable housing promotion, and subsidies for construction.
Challenges Faced by the PMAY Scheme;
- Criticism surrounding the performance of PMAY-U, citing data indicating a shortfall in completed houses.
- Ineffectiveness of the in-situ slum redevelopment (ISSR) component and its low output compared to expectations.
- Discrepancy between achieved housing targets and actual housing needs, despite substantial investment.
Reasons Behind the PMAY Scheme’s Failure;
- Issues encountered in slum rehabilitation projects, such as vertical expansion and land acquisition difficulties.
- Neglect of social housing needs and community involvement in city development plans.
- Limited contribution from the central government and its minimal role in housing provision.
Proposed Solutions;
- Reevaluation of funding allocation, suggesting an increase in the central government’s share.
- Enhanced focus on slum rehabilitation through improved planning and community engagement.
- Emphasis on community participation and needs assessment in housing project implementation
Conclusion:
The Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana – Urban (PMAY-U) scheme stands at a critical juncture, grappling with significant challenges despite its ambitious objectives. The scheme, initiated by the current Union government, aimed to address the pressing issue of housing for all by 2022, particularly in urban areas. However, its performance has fallen short on multiple fronts, including slum rehabilitation, affordable housing promotion, and subsidy disbursement.
India’s Strategy for Enhancing EV Production
Introduction;
The Union government has greenlit a strategy aimed at positioning India as a prominent manufacturing hub for Electric Vehicles (EVs).
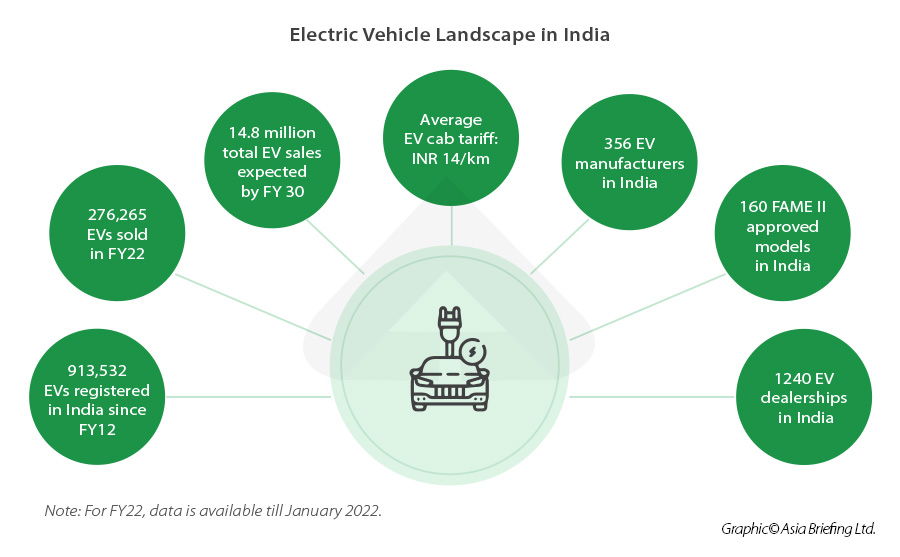
Key Components of the Electric Vehicles Policy:
- Reduction of Import Duty: Import duties on EVs brought in as Completely Built Units (CBUs) with a minimum CIF value of $35,000 will see a decrease from 70%-100% to 15% over a span of five years.
- Duty Waiver: Within a five-year period, a maximum of 40,000 EV imports will be permitted, with a duty waiver amounting to ₹6,484 crore or in proportion to the investment (whichever is lower), contingent upon a minimum investment of $800 million.
- Localization Targets: Manufacturers are mandated to establish manufacturing units in India within three years. They are required to achieve 25% localization by the third year and 50% localization by the fifth year of incentivized operation.
- Incentives for Establishing Manufacturing Facilities: The policy offers incentives to manufacturers for setting up manufacturing plants in India, including reduced import duties and waivers, provided they meet specified investment and localization criteria.
- Promotion of Global EV Manufacturers: The policy seeks to attract international EV giants like Tesla and Chinese EV manufacturer BYD to the Indian market by creating favorable conditions for establishing manufacturing facilities and importing EVs.
Concerns Raised by Private Market Players:
- Impact on Domestic Industry: Tata Motors has expressed reservations about the reduction of import duties, fearing adverse effects on the domestic industry. They argue that lowering duties might dampen the investment climate.
- Competitive Disadvantage: Domestic players are apprehensive that the policy primarily benefits higher-end Original Equipment Manufacturers (OEMs), potentially placing them at a competitive disadvantage in segments below ₹29 lakh.
- Favoritism towards Global Players: The policy seems to tilt in favor of global EV players and Indian ventures with such players, potentially complicating matters for purely domestic players to compete effectively.
Conclusion:
Engagement in constructive dialogue with stakeholders, including domestic players like Tata Motors, is imperative for addressing their concerns and soliciting their input in shaping the policy framework. Furthermore, there is a need to implement measures supporting domestic players, including offering incentives and backing for technology development, innovation, and capacity building.
ISRO’s Study on Glacial Lake Dynamics in the Himalayas
Introduction;
- Overview of ISRO’s satellite findings revealing changes in Gepang Gath Lake amid climate change concerns.
- Description of Gepang Gath Lake’s location and significance in the Western Indian Himalaya.
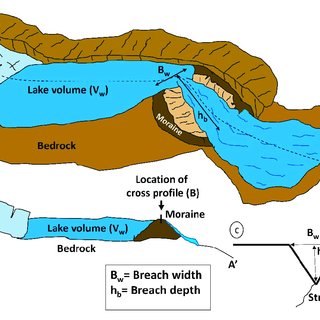
Glacial Lake Categories;
- Explanation of the four primary categories of glacial lakes: Moraine-dammed, Ice-dammed, Erosion, and others.
- Distribution of expanding glacial lakes, with emphasis on the prevalence of Moraine-dammed lakes.
Formation Process;
- Mechanism of glacial lake formation through meltwater accumulation and glacier retreat.
- Role of moraines in acting as natural barriers and facilitating lake formation.
Characteristics of Glacial Lakes;
- Discussion on the variability in size and geographical distribution of glacial lakes.
- Identification of the primary water sources for glacial lakes.
Importance of Glacial Lakes;
- Significance of glacial lakes in regulating water flow in glacier-fed rivers.
- Contribution of glacial lakes to biodiversity and landscape evolution.
Ecological Challenges;
- Threats posed by glacial lake outburst floods (GLOFs) to downstream communities and infrastructure.
- Risks associated with the rapid expansion of glacial lakes due to increased glacier melting.
Conclusion:
Summary of ISRO’s research findings on glacial lake dynamics. Implications for understanding the impact of climate change on Himalayan glaciers and downstream regions.
Pink Hydrogen: Leveraging Nuclear Energy for Sustainable Production
Overview:
The utilization of nuclear energy has the potential to drive the production of ‘pink’ hydrogen in India, necessitating amendments to existing legislation.

About Pink Hydrogen:
- Pink hydrogen is synthesized through electrolysis powered by nuclear energy and is interchangeably referred to as purple or red hydrogen.
- The high temperatures generated by nuclear reactors can facilitate more efficient electrolysis or fossil gas-based steam methane reforming processes.
- Nuclear power presents several advantages for pink hydrogen production, notably in reducing production costs and emissions, thus positioning it as a sustainable and economically viable alternative to traditional methods.
Applications:
- Pink hydrogen holds promise as a substitute for fossil fuels across various sectors such as cement, steel, aviation, and heavy transportation.
- It serves as both a feedstock and energy source without contributing to greenhouse gas emissions.
Understanding Electrolysis:
- Electrolysis stands as a promising avenue for carbon-neutral hydrogen production from both renewable and nuclear resources.
- It involves utilizing electricity to split water into hydrogen and oxygen, a process conducted within a device known as an electrolyzer.
Golden Trevally Fish: Successful Captive Breeding Achievement
Overview:
The ICAR-Central Marine Fisheries Research Institute (CMFRI) has achieved a breakthrough in the captive breeding of golden trevally (Gnathanodon speciosus), marking a significant milestone in marine fisheries research.

About Golden Trevally Fish:
- Renowned as the golden kingfish, the golden trevally is a prized marine species sought after for its premium quality meat and aesthetic appeal.
- It emerges as an ideal candidate for mariculture due to its rapid growth rates, superior meat quality, and substantial market demand for both consumption and ornamental purposes.
- This reef-associated species often cohabitates with larger fishes such as skates, sharks, and groupers.
- Fish landing data in India indicates that golden trevally are predominantly landed at reef area fishing grounds along the coasts of Tamil Nadu, Puducherry, Kerala, Karnataka, and Gujarat.
Key Information about Central Marine Fisheries Research Institute:
Established by the Government of India in 1947 under the Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers Welfare, CMFRI became a part of the Indian Council of Agricultural Research (ICAR) in 1967. Its mandates include:
- Monitoring and assessment of exploited and under-exploited marine fisheries resources within the Exclusive Economic Zone.
- Investigation of fluctuations in marine fisheries abundance concerning environmental changes.
- Development of mariculture technologies for various marine organisms to supplement capture fishery production.
Conclusion;
One of CMFRI’s notable achievements is the development and refinement of the “Stratified Multistage Random Sampling Method” for estimating fishery catch and effort along India’s extensive coastline spanning over 8000 km.
Voyager 1 and Voyager 2: Pioneering Space Probes
Overview of Voyager 1:
- Recent announcement by NASA regarding Voyager 1’s resumption of data transmission after a period of signal disruption.
Voyager 1 Spacecraft:
- Launch date: September 5, 1977, shortly followed by its twin, Voyager 2.
- Mission Objective: Exploration of the outer Solar System and beyond, including flybys of Jupiter and Saturn to study their moons, rings, and magnetic fields.
- Milestones: Voyager 1 holds the record for the farthest human-made object from Earth and was the first spacecraft to cross the heliosphere into interstellar space.
- Discoveries: Notable findings include a thin ring around Jupiter, two new Jovian moons (Thebe and Metis), and additional moons and a ring (G-ring) at Saturn.
- Golden Record: Voyager 1 carries a golden record containing sounds and images representing Earth’s life and culture, intended for potential encounters with extraterrestrial life forms.
- Future Expectations: NASA predicts operational capabilities until at least 2025, with Voyager 1 expected to be approximately 13.8 billion miles from the Sun.
Voyager 2 Spacecraft:
- Launch date: August 20, 1977, as part of NASA’s Voyager program alongside Voyager 1.
- Mission Objective: Exploration of the outer planets and their moons, followed by an interstellar mission.
- Notable Achievements: Voyager 2 is the second spacecraft to enter interstellar space and has studied all four giant planets of the Solar System up close. It made significant discoveries, including a 14th moon at Jupiter, new moons and rings at Uranus and Neptune, and observed a “Great Dark Spot” on Neptune.
- Shared Features: Voyager 2, like its counterpart, carries a golden record.
Conclusion:
The groundbreaking contributions of Voyager 1 and Voyager 2 to space exploration.Recognizing their ongoing impact and continued relevance in the field of astrophysics.
Crystal Maze 2: Advancing Air-to-Surface Capabilities
Overview;
- Recent successful test firing conducted by the Indian Air Force (IAF), showcasing the capabilities of the Crystal Maze 2 missile.

Crystal Maze 2 Missile:
- Origin: Developed in Israel, Crystal Maze 2, also known as ROCKS, is a medium-range ballistic missile.
- Targeting Capabilities: Designed to engage high-value stationary and relocatable assets, such as long-range radars and air defense systems, belonging to potential adversaries.
Features of Crystal Maze 2:
- Enhanced Range: Crystal Maze 2 surpasses its predecessor, Crystal Maze 1, with extended stand-off range capabilities as an air-to-surface missile.
- Target Range: Capable of striking targets located over 250 kilometers away.
- Warhead Options: Equipped with either a penetration or blast fragmentation warhead, providing versatility in engaging different types of targets.
- GPS-denied Environments: Crystal Maze 2 demonstrates effectiveness even in environments where GPS signals are unavailable.
Deployment Strategy:
- Launch Method: ROCKS is released from a safe distance outside the surface-to-air defended area.
- Trajectory: Follows a high-velocity trajectory to minimize risks to both aircraft and missiles during deployment.
Conclusion:
The significance of Crystal Maze 2 in enhancing India’s air-to-surface capabilities. Recognition of the successful test firing as a milestone in the development and deployment of advanced missile systems by the Indian Air Force.
Indian Telecom Services Performance Indicator Report
Context:
The Telecom Regulatory Authority of India (TRAI) recently released the “Indian Telecom Services Performance Indicator Report” for the October-December 2023 quarter.
Internet Subscribers:
- Total internet subscribers increased from 918.19 million to 936.16 million, consisting of 38.57 million wired and 897.59 million wireless subscribers.
- Broadband internet users rose to 904.54 million, while narrowband subscribers decreased to 31.62 million.
Wireline Subscribers:
- The number of wireline subscribers grew from 30.98 million to 31.84 million, indicating a quarterly growth of 2.79% and a year-on-year growth of 15.98%.
- Wireline tele-density also saw an increase from 2.22% to 2.28%.
Monthly Average Revenue per User (ARPU):
- Wireless services’ monthly ARPU increased from Rs.149.66 to Rs.152.55.
- Prepaid ARPU rose from Rs.148 to Rs.149.56, while postpaid ARPU increased from Rs.167.93 to Rs.189.08.
Voice Services:
- The overall Minutes of Usage (MOU) per subscriber per month rose from 948 to 955, with prepaid MOU at 989 and postpaid MOU at 536.
Telecom Revenue:
- The Annual Gross Revenue (AGR) of the telecom service sector reached Rs.84,500 crore, with growth rates of 2.13% for Gross Revenue (GR), 1.70% for Adjusted Gross Revenue (ApGR), and 1.88% for AGR.
- Year-on-year growth rates for GR, ApGR, and AGR were recorded at -4.16%, 5.84%, and 7.84%, respectively.
Quality of Service (QoS):
- Both wireline and mobile service providers showed adherence to and decline in various QoS parameters as specified.
TV and Radio Services:
- The permitted satellite TV channels numbered 920.
- There are 363 satellite pay TV channels, comprising 259 SD and 104 HD channels.
- The active pay Direct-to-Home (DTH) subscriber base totaled approximately 63.52 million.
- FM radio operators reported 388 operational private FM radio channels, generating advertisement revenue amounting to Rs.485.47 crore.
Europe’s Accelerated Warming
Introduction:
- Overview of the World Meteorological Organization’s findings indicating Europe’s rapid warming compared to the global average.
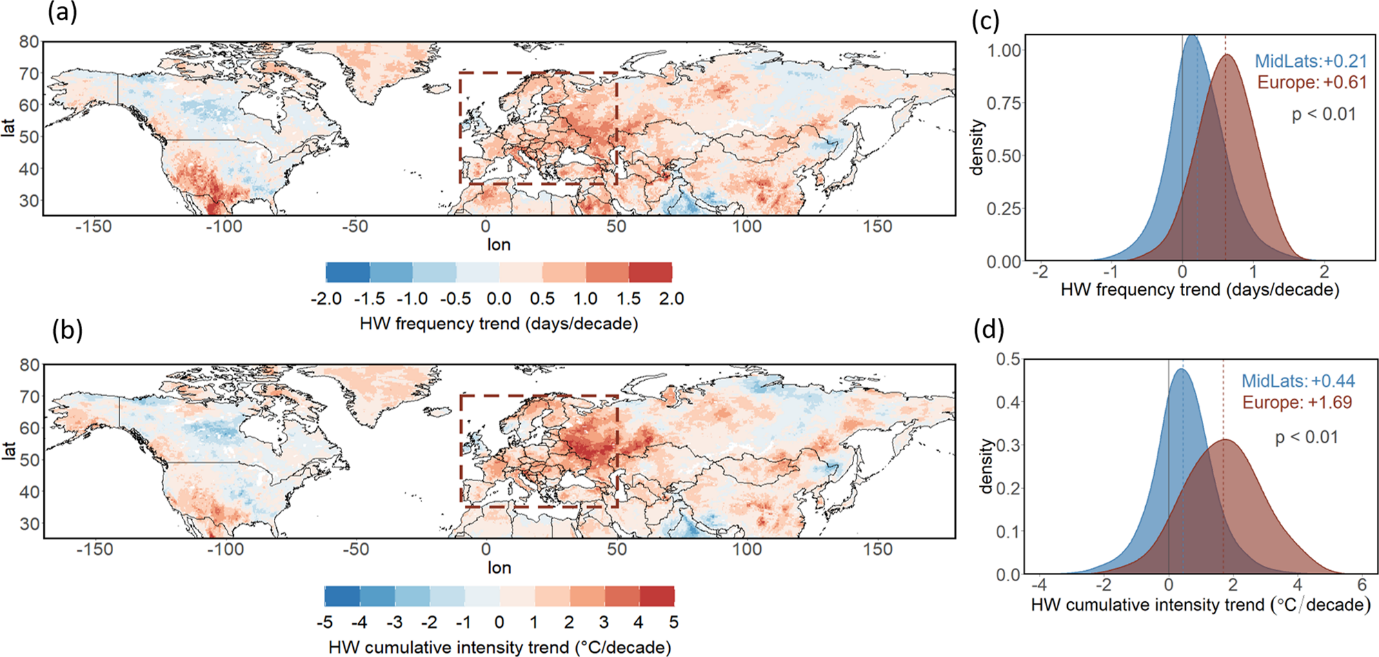
Temperature Trends:
- Analysis of Europe’s second-warmest year in 2023, with average temperatures surpassing the reference period by 1.02 to 1.12 degrees Celsius.
- Regional variations in temperature increases, with some areas experiencing temperatures akin to the pre-industrial era.
Extreme Weather Events:
- Increased occurrences of extreme heat stress and reduced cold stress days, with ‘feel like’ temperatures exceeding 46°C.
- Notable droughts and wildfires in certain regions, alongside widespread flooding incidents.
- Record warmth in European waters contributing to marine heatwaves.
Monthly Temperature Patterns:
- Month-by-month breakdown of temperature anomalies, highlighting warmer-than-average conditions throughout most of the year.
- Variations in temperature patterns across different regions of Europe.
Glacier Loss:
- Examination of glacier volume reduction in the Alps, including a 10% loss over the past two years and a 4.4% decrease in 2023 alone.
Conclusion:
Recap of key findings emphasizing the urgency of addressing climate change impacts in Europe. Implications for future climate resilience and mitigation efforts.
NABARD’s Climate Strategy for 2030
Introduction:
In response to the escalating need for sustainable financing in India, the National Bank for Agriculture and Rural Development (NABARD) has unveiled its Climate Strategy 2030 on Earth Day.

1: Focus on Green Financing:
- Green financing, which directs financial investments towards sustainable and environmentally friendly projects, plays a crucial role in advancing India’s renewable energy sector.
- India’s ambitious goal of achieving 500 GW of renewable energy capacity by 2030 necessitates significant green funding.
- The expansion of renewable energy infrastructure facilitated by green finance contributes to reducing the country’s carbon footprint.
2: Challenges in the Sector:
- Shortage of Green Finance: Despite the requirement of approximately USD 170 billion annually to achieve a cumulative total of over USD 2.5 trillion by 2030, the current inflow of green finance falls far short.
- Limited Private Sector Engagement: A significant portion of funds is directed towards mitigation efforts, with only USD 5 billion allocated for adaptation and resilience.
- Viability Concerns: Challenges related to bankability and commercial viability deter private sector involvement in these areas.
- Other Obstacles: Project risks, policy uncertainties, and the absence of standardized green finance metrics further hinder sectoral progress.
Action Plan: NABARD’s Climate Strategy 2030
NABARD’s Climate Strategy 2030 is a comprehensive framework aimed at addressing India’s increasing demand for green financing. It revolves around four main pillars:
1. Accelerating green lending across sectors.
2. Playing a broader market-making role.
3. Internal green transformation of NABARD.
4. Strategic resource mobilization.
Asia’s Predicament: Insights from WMO’s Report
Introduction:
In 2023, Asia bore the brunt of the world’s disasters, facing 79 events linked to extreme weather, climate, and water-related hazards. This report by the World Meteorological Organization (WMO) sheds light on the devastating impact, affecting over nine million people and claiming over 2,000 lives in the region.
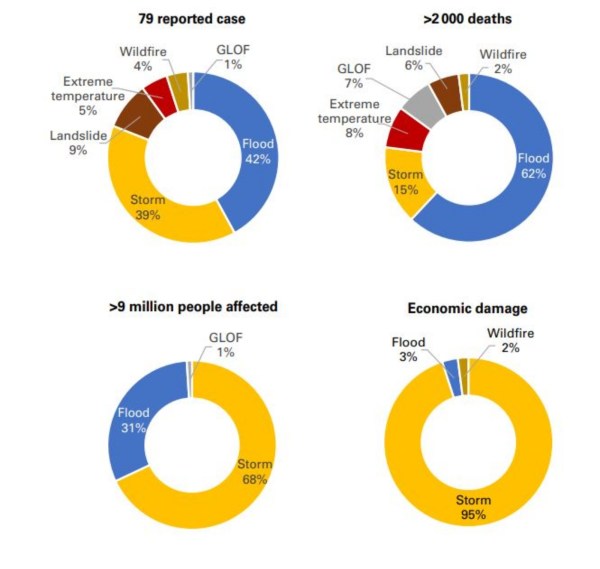
Key Highlights from the Climate Disaster Profile:
- Asia’s accelerated warming, surpassing the global average, has nearly doubled since the 1961-1990 period, with significant implications for the region’s economy and ecosystems.
- Critical climate change indicators such as rising surface temperatures, glacier retreat, and sea level rise pose significant challenges for Asia.
- In India, severe heatwaves in April and June led to approximately 110 fatalities due to heatstroke, while record-high temperatures and exceptional rainfall deficit in August can be attributed to El Niño.
- Floods emerged as the leading cause of death in reported events in 2023 by a considerable margin.
1: Importance of the Report:
- The report underscores the alarming frequency and severity of climate-related disasters in Asia, emphasizing the urgent need for proactive disaster management strategies.
- Call to Action: Urgent measures are required to mitigate climate change impacts and enhance resilience to extreme weather events in Asia.
- Enhancing Disaster Management: Effective disaster management strategies, including early warning systems, infrastructure resilience, and community preparedness, are crucial for minimizing loss of life and property during disasters.
- Regional Collaboration: Given the cross-border nature of climate-related disasters, regional cooperation and information sharing are essential for a unified response to the climate crisis.
2: Disaster Management in India:
- Disaster Risk Management involves systematic efforts to analyze and reduce the causal factors of disasters, encompassing mitigation, preparedness, rescue, relief, and recovery.
- Disaster risk reduction aims to reduce risks through proactive measures.
- Pre-disaster risk reduction includes mitigation and preparedness, while post-disaster risk reduction involves rescue, relief, and recovery efforts.
3: Necessary Steps and Initiatives:
- Expand the coverage of early warning systems to enhance preparedness.
- Climate-proofing infrastructure to withstand extreme weather events.
- Invest in disaster risk reduction measures to build resilience.
- Promote climate and disaster resilience at sub-national levels.
- Integrate potential climate change impacts into existing national frameworks and Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs), including the Disaster Management Act of 2005.

