Topics:
- Combating climate change & its horrific impact. (The Tribune)
- Expansion of five-nation BRICS faces diverse challenges. (The Tribune)
- NEP will play a pivotal role in propelling India. (Hindustan Times)
- The SCO is a success story that can get better (The Hindu)
- A win-win partnership on AI
Combating climate change & its horrific impacts


Introduction
- Simultaneous heatwaves in North America and Europe break records.
- Global temperatures are rising due to climate change, leading to extreme weather events.
- Himachal Pradesh in India experiences devastating rainfall and landslides.
Global Impact of Climate Change
- The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) confirms human responsibility for global heating.
- Extreme weather events and natural disasters are increasing in frequency and intensity.
- Glacial lakes are forming in the Himalayas, posing a threat to several regions.
- Rising sea levels endanger small island nations and coastal areas.
Consequences for Health and Society
- Climate change contributes to the spread of diseases and threatens basic needs.
- The world is 15°C warmer than pre-Industrial Revolution, but action remains insufficient.
India’s Vulnerability and Response
- Developing countries like India suffer disproportionately from climate change.
- India aims to transition from fossil fuels to renewable energy and is making progress in that direction.
- Policies focus on reducing greenhouse emissions, strengthening resilience, and compensating developing nations.
- Citizens and groups can contribute by adopting eco-friendly practices.
India’s Role in Addressing Climate Change
- India, as the G20 president, has a historic opportunity to lead in climate action.
- Strategies include transitioning to renewable energy, enhancing resilience, and compensating developing countries.
- India’s achievements in renewable energy and efforts towards eco-friendly technology.
Call to Action
- Strengthening national capacities and community resilience is crucial.
- Focus on protecting poor countries through technology transfer and climate financing.
- Primary healthcare strengthening in various countries should be prioritized.
Conclusion
Climate change is an urgent global crisis that requires concerted efforts from all countries. India, as the G20 president, has a vital role to play in shaping the global agenda on climate change and can demonstrate leadership by pursuing sustainable strategies and supporting vulnerable nations in their climate actions.
Expansion of five-nation BRICS faces diverse challenges

Introduction:
- BRICS nations: Brazil, Russia, India, China, and South Africa.
- 15th summit to be held in Johannesburg, South Africa, from August 22 to 24.
- Coined by economist Jim O’Neill to highlight growth potential and global economic domination.
- Originally RIC (Russia, India, China) dialogue, became BRIC with Brazil’s inclusion in 2009 and BRICS with South Africa’s inclusion in 2010.
Objectives and Success Factors:
- Commitment to an equitable multipolar world and reforming global governance for inclusivity.
- Emphasis on sustainable development, economic decentralization, and rules-based multilateral trade.
- Focus on security challenges like terrorism, money laundering, and cybercrimes.
- Successes: Established New Development Bank (NDB) and Contingent Reserve Arrangement.
BRICS Composition and Influence:
- Represents 41% of the global population and 31.5% of the global GDP (PPP).
- Attracted interest from other developing countries to join the group.
- China’s efforts to expand the group with BRICS Plus framework, aiming for China-centric bloc.
Motivations for Expansion:
- China seeks to export goods to the West-contracting markets and establish itself as a Global South leader.
- Russia supports expansion to counter Western attempts to isolate it.
- South Africa hopes for greater global decision-making weight and increased economic assistance.
Differing Views on Expansion:
- Brazil cautious about maintaining BRICS’ brand value and balanced approach to new membership.
- External Affairs Minister S Jaishankar highlights the need for cooperation between existing members and engagement with non-BRICS countries.
Challenges of Expansion:
- BRICS’ non-confrontational stance amid Western-China-Russia-Iran rivalry.
- Decision-making complexity and time-consumption with a larger group.
- Gradual expansion based on mutual complementarities and long-term functioning.
Conclusion
BRICS has been successful in promoting its objectives of a multipolar world, global governance reform, and sustainable development. The group’s composition and influence have attracted interest from other developing nations.
While China seeks to expand and enhance its influence, other members approach the issue with caution, considering the impact on decision-making and group dynamics. The expansion process is ongoing, aiming to strike a balance between strengthening the group and maintaining its original objectives.
NEP will play a pivotal role in propelling India


Context:
- NEP 2020 celebrates three years of implementation as a milestone in India’s pursuit of universal access and quality education.
- The policy addresses diverse aspects of equitable education, assessment reforms, teacher empowerment, and technological integration.
Flexibility and Equitable Education:
- NEP 2020 brings unprecedented flexibility to the education system, bridging gaps between different streams and activities.
- The National Credit Framework (NCrF) empowers learners with multiple entry and exit options and personalized learning paths.
- The Academic Bank of Credit (ABC) in higher education allows seamless credit transfer and student mobility.
Curricular Revamp and Interdisciplinary Education:
- NEP 2020 promotes a balanced and integrated educational framework.
- Universities like IIT Kanpur adopt new undergraduate curricula with interdepartmental majors, management tracks, and ethics courses.
- Emphasis on social sciences, humanities, environment, economics, and management sciences in the curriculum.
Solution-Driven Innovation:
- NEP 2020 encourages schools and colleges to become enablers of grassroots innovation.
- Initiatives like Vidya Amrit, Atal Tinkering Labs, and Smart Indian Hackathons groom young innovators.
Alignment with Education 4.0:
- NEP 2020 aligns with Education 4.0, prioritizing inclusivity and skill-based learning.
- The DIKSHA platform provides e-content in multiple Indian languages and Indian sign language.
- Emphasis on AI integration for personalized learning, automated grading, and improved teacher-student interactions.
Digital Infrastructure and AI for All:
- NEP 2020 recognizes the transformative potential of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and remote learning platforms.
- AI for All platform educates millions in 11 regional languages, and a digital university focuses on personalized learning experiences.
Research and Innovation:
- NEP 2020 acknowledges the role of research and innovation in driving sustainable growth.
- The approval of the National Research Foundation (NRF) fosters collaborative research among academia, industry, and government.
Entrepreneurship and Skill Development:
- NEP 2020 promotes entrepreneurship and skill development among students.
- IITs offer credit-based entrepreneurship opportunities and have integrated it into the curriculum.
International Collaboration:
- NEP 2020 provides scope for international collaboration and offshore campuses.
- The establishment of the first offshore IIT campus in Tanzania marks a significant development.
Holistic Transformation:
- NEP 2020 embraces a holistic, multidisciplinary, and technology-driven approach to transform India’s education system.
- It aims to create a comprehensive academic and research-oriented transformation for the future of the nation.
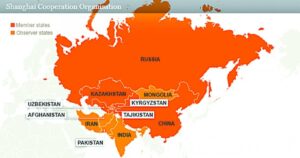
The SCO is a success story that can get better


Context
- India successfully hosted the 23rd SCO summit on July 4, 2023.
- Leaders of SCO member-states signed the New Delhi Declaration.
- Statements were issued on countering radicalisation and exploring cooperation in digital transformation.
- Iran was granted full SCO membership, and Belarus signed a memorandum of obligations to join as a member-state.
- The SCO adopted its economic development strategy for the period until 2030.
Challenges Faced by the World:
- Geopolitical tensions, economic slowdown, energy crises, food shortage, and climate change.
- Major risks include power politics, economic coercion, technology decoupling, and ideological contest.
SCO’s Role and Achievements:
- Commitment to a shared future for mankind, supporting core interests and regional cooperation.
- Building partnerships based on dialogue and cooperation instead of confrontation and alliance.
- Being a guardian of regional peace, stability, and prosperity.
Strategic Goals for the Future:
- Strengthening strategic communication and practical cooperation among member-states.
- Enhancing solidarity and mutual trust for common security.
- Addressing external elements orchestrating a new Cold War and bloc confrontation.
- Upgrading security cooperation and countering terrorism, separatism, extremism, and transnational crimes.
- Pursuing cooperation in digital, biological, and outer space security, and promoting political settlement of hot-spot issues.
- Embracing win-win cooperation for shared prosperity and countering protectionism and unilateral sanctions.
Advocacy for Multilateralism:
- Engaging with observer states, dialogue partners, and international organizations.
- Upholding the UN-centered international system and international order based on international law.
- Promoting world peace, global development, and safeguarding international order.
China’s Commitment:
- Working with India, South Africa, and other partners to implement global initiatives.
- Pursuing common, comprehensive, cooperative, and sustainable security.
- Respecting each country’s independent choice of development path and social system.
- Supporting dialogue and diplomacy to resolve international disputes.
- Opposing hegemony, unilateralism, Cold War mentality, and bloc confrontation.
- Rejecting illegal unilateral sanctions and long-arm jurisdiction measures.
Upcoming BRICS and G-20 Summits:
- South Africa and India to preside over BRICS and G-20 summits, respectively.
- Opportunities to shape a multipolar world order, promote inclusive global development, and improve international governance architecture.
CONCLUSION
Overall, the SCO reaffirmed its commitment to cooperation and addressed various challenges faced by the world, while emphasizing the importance of multilateralism and global partnerships. China expressed its dedication to promoting peace, security, and prosperity, and standing against unilateralism and hegemony.
A win-win partnership on AI
![]()

Context
- Indian talent has contributed significantly to digital technologies worldwide.
- Indian engineers are at the forefront of developing generative AI.
- But still many big tech companies with vast computing power are based in Silicon Valley, not in India.

The Case for Openness in AI Technologies:
- The debate on whether big tech companies should keep AI models in-house or make them open has favored openness.
- Open-sourcing foundational technology is practical and beneficial.
- Embracing openness can boost India’s digital economy.
Meta’s Open Approach to AI Innovation:
- Meta has a history of openly sharing AI technologies and has released over 1,000 AI models and data sets for researchers.
- Meta has seen a strong demand for AI technologies from Indian researchers, start-ups, and developers.
- Open innovation in AI needs to be done responsibly.
Collaboration and Guardrails:
- Openness should be accompanied by collaboration across industry, government, academia, and civil society.
- Meta’s commitment to openness benefits both the company and others in the market.
- The role of both proprietary and open AI models exists, but openness is essential to spread the benefits of AI.
India’s Unique Position:
- India has the presidency of the Global Partnership on Artificial Intelligence (GPAI) and the G20.
- Supporting open innovation in AI during this crucial early stage can be transformative for India and the world.
Inclusive AI Development:
- To serve India’s diverse population, AI models must be inclusive and capable of understanding and addressing regional languages, dialects, and cultural nuances.
- Collaboration with linguists, sociologists, and experts from various domains can help develop AI systems that cater to the needs of different communities in the country.
Data Privacy and Security:
- Openness in AI should be balanced with robust data privacy and security measures.
- India should focus on creating policies and frameworks that safeguard user data and ensure that AI models are not misused for harmful purposes.
- Collaborating with global experts on data privacy can provide valuable insights into best practices.
Ethics and Bias Mitigation:
- Open AI models can be prone to biases present in the data they are trained on.
- It is essential to involve ethicists and diverse perspectives during the development process to identify and mitigate biases.
- Collaboration with organizations and researchers working on AI ethics can help create fair and unbiased AI technologies.
Skill Development and Education:
- India’s approach to AI innovation should include a strong emphasis on skill development and education.
- Collaborating with academic institutions and industry leaders can facilitate the creation of AI-focused curricula and training programs to nurture the next generation of AI talent in India.
Multi-Stakeholder Partnerships:
- Building effective multi-stakeholder partnerships is crucial to address complex challenges and make informed decisions on AI policy.
- Involving not only government and tech companies but also civil society, NGOs, and grassroots organizations can ensure that AI technologies align with India’s societal needs.
Adoption in Key Sectors:
- Open AI technologies should be strategically adopted in key sectors such as agriculture, healthcare, education, and governance to address specific challenges and enhance the quality of life for all citizens.
- Partnerships with domain experts and industry players can accelerate the deployment of AI solutions in these sectors.
Intellectual Property Rights:
- While open innovation is beneficial, protecting intellectual property rights is also essential to encourage continued investment in AI research and development.
- Collaborating with legal experts and international organizations can help strike a balance between openness and IP protection.
Responsible Governance:
- India’s approach to AI should prioritize responsible governance, ensuring that AI technologies adhere to ethical standards and align with national values.
- Collaboration with global governance initiatives can help create consistent standards and guidelines for AI development and deployment.
Infrastructure Development:
- Collaborating with technology providers and experts from around the world can assist in building the necessary infrastructure for AI research and development, such as high-performance computing clusters and cloud-based resources.
Conclusion
By embracing an open approach to AI innovation and fostering collaboration with various stakeholders, India can not only meet its unique needs but also position itself as a global leader in shaping the future of AI for the betterment of society.
Through responsible, inclusive, and well-governed AI technologies, India can harness the potential of AI to address societal challenges and drive economic growth and development.

