|
|
||
|
27 March 2024 |
||
|
- District Election Management Plan
- Concerns around Reverse Osmosis (RO) Water Purification
- Robusta Coffee price touches All-time High
- Monuments of National Importance
- International Seabed Authority
- Baltimore’s Francis Scott Key Bridge
- India Employment Report 2024

- District Election Management Plan
https://ceomadhyapradesh.nic.in/Links/Manual/Manual%20on%20DEMP,%202023.pdf

Context:
- The organization of elections in contemporary times has become increasingly intricate, requiring thorough planning and execution to maintain the principles of fairness and inclusivity.
- Central to this planning is the District Election Management Plan (DEMP), a comprehensive document developed with data and analysis.
- The DEMP plays a crucial role in ensuring smooth and effective elections by addressing various challenges and complexities, thereby upholding the integrity of the democratic process.
Definition:
The District Election Management Plan (DEMP) is a structured plan devised by the Election Commission of India (ECI) to manage and supervise the electoral process at the district level.
Timeline:
- According to ECI guidelines, the DEMP must be prepared at least six months prior to the anticipated polling day, with provisions for updates and revisions closer to the election date.
Collaborative Effort:
- Implementing the DEMP requires collaboration among diverse stakeholders, including election officials, administrative bodies, law enforcement agencies, and other relevant entities.
- Additionally, engagements with political parties and media are scheduled to ensure comprehension and adherence to electoral regulations.
Features of the District Election Management Plan (DEMP):
District Profile:
- Constituency Details: Presentation of political boundaries and electoral constituencies.
- Demographic and Infrastructure Data: Presentation of essential statistics concerning population, infrastructure, administrative structure, and socio-economic factors.
Polling Station Infrastructure:
- Facility Enhancement: Strategies aimed at improving the accessibility and availability of polling stations, ensuring necessary facilities such as ramps, electricity, lighting, drinking water, toilets, and internet connectivity.
Inclusivity Measures:
- Support for Vulnerable Groups: Special provisions for voters with disabilities (PwD) and senior citizens, including assistance desks, round-the-clock control centers, and options for voting from home.
Systematic Voters’ Education and Electoral Participation (SVEEP) Plan:
- Objective: To increase electoral participation through strategic measures.
- Data-Driven Strategy: Utilization of voter turnout data to identify stations with low turnout for targeted interventions.
- Awareness Activities: Inclusion of social media campaigns, engagement with community and youth organizations, and pre-election events to enhance awareness and participation.
Personnel Management:
- Database Creation: Establishment of a comprehensive database of election personnel.
- Categorization and Assessment: Classification of personnel by category and assessment of their requirements, along with strategies to address staffing gaps across various election roles.
Force Deployment and Security:
Collaborative Planning: Detailed planning and coordination with district police, including identification of vulnerable polling stations based on historical incidents and voter turnout.
Model Code of Conduct (MCC) Enforcement:
- Training: Training of district-level teams to effectively enforce the MCC.
Electronic Voting Machines (EVMs):
- Importance in Electoral Process: EVMs play a critical role in ensuring the integrity, transparency, and accuracy of the electoral process.
- Management Protocols: Effective strategies are necessary to ensure secure storage, availability, transportation, and maintenance of EVMs and Voter Verifiable Paper Audit Trails (VVPATs).
- Integration with DEMP: Incorporating EVM management within the DEMP aims to streamline the voting process, making it more organized and accessible.
Broader Governance Implications:
- The meticulous planning, collaborative approach, and transparency embedded within the DEMP can serve as a model for broader governance, emphasizing the importance of proactive planning, data-driven decision-making, and stakeholder engagement in addressing challenges effectively.
Voter Verifiable Paper Audit Trail (VVPAT):
- Feedback Mechanism: VVPAT or Verifiable Paper Record (VPR) is a supplementary verification system used alongside EVMs to provide tangible feedback to voters.
- Verification Process: VVPAT machines enable voters to verify that their votes have been accurately registered and allocated to the intended candidate by displaying the candidate’s name and party/individual symbol on a paper slip.
- Instant Verification: This system offers immediate feedback to voters, confirming that their votes have been correctly recorded and assigned to their chosen candidate.
Historical Context in India:
- Pilot Implementation: The VVPAT system was initially introduced on a trial basis in eight out of 543 parliamentary constituencies during the 2014 Indian general election.
- Full-Scale Implementation: Following the successful pilot project, the VVPAT system was subsequently deployed across all 543 Lok Sabha constituencies during the 2019 Indian general election.
- Concerns around Reverse Osmosis (RO) Water Purification
https://www.forbes.com/home-improvement/home/reverse-osmosis-water-pros-cons/#:~:text=Reverse%20osmosis%20will%20also%20remove,decreases%2C%20making%20it%20more%20acidic.
Context:
In recent years, Reverse Osmosis (RO) technology has become increasingly popular due to its efficacy in purifying water by removing impurities, pathogens, and reducing Total Dissolved Solids (TDS) levels.
However, there are growing concerns regarding the depletion of vital minerals such as calcium and magnesium during the filtration process.
Reverse Osmosis (RO) Water Purification Method
Overview:
- RO, short for Reverse Osmosis, is a method of water purification.
- It utilizes a semi-permeable membrane to filter out contaminants from water.
Key Components of RO System:
- Semi-permeable Membrane: Contains minuscule pores ranging from 0.0001 to 0.001 microns.
- Pressure: Forces water through the membrane under pressure.
Working Mechanism:
- Filtration: The membrane traps contaminants like dissolved solids, chemicals, microorganisms, and impurities.
- Permeation: Clean and purified water molecules pass through the membrane.
Effectiveness:
- Comprehensive Removal: RO effectively eliminates a wide range of impurities, including salts, heavy metals, bacteria, viruses, and organic compounds.
Applications:
- Residential: Utilized for drinking and cooking purposes.
- Industrial: Deployed across various industries to enhance water quality for specific needs.
Reasons for the Growing Demand for RO Water:
- Water Quality Concerns: Many regions, especially rural areas, face challenges with poor groundwater quality or tap water containing a brackish taste, unpleasant odor, and contaminants like chlorine or heavy metals.
- Perceived Health Benefits: Consumers often view RO water as healthier and safer compared to untreated or municipally supplied water, despite limited scientific evidence supporting this belief.
- Convenience: Accessibility through purification plants and domestic RO systems, along with easy installation and maintenance, contributes to RO being a preferred choice.
- Urbanization and Population Growth: The increase in urbanization and population drives demand, particularly in areas dealing with groundwater contamination and municipal water quality issues.
- Technological Advancements: Continuous innovations in RO technology lead to more efficient and cost-effective systems, expanding access to clean water to a broader consumer base.
Concerns Related to the RO Process
- Mineral Reduction:
- Effective yet De-mineralizing: Despite its effectiveness in removing impurities, RO also eliminates beneficial minerals like calcium and magnesium.
- Health Implications: The loss of these essential minerals can pose potential health risks, especially in regions with prevalent micronutrient deficiencies.
- Studies and Findings:
- TDS Levels: Research indicates a significant decrease in Total Dissolved Solids (TDS) levels post-RO treatment, often falling below the recommended threshold of 50 mg/l.
- National Observations: A nationwide study covering approximately 4,000 locations discovered TDS levels as low as 25 to 30 mg/l, suggesting a significant shortage of essential minerals.
- “Dead Water” Phenomenon: RO-treated water commonly exhibits TDS levels ranging from 18 to 25 mg/l, termed colloquially as “dead water,” suitable for non-consumptive purposes like battery maintenance but unsuitable for drinking.
- Health Concerns:
- Potential Health Risks: Reduced intake of essential minerals such as calcium and magnesium may contribute to various health issues like joint pain, coronary heart disease, back pain, and vitamin B12 deficiency.
- WHO’s Perspective: The World Health Organization has raised concerns about consuming RO water, citing instances where populations experienced health complications like cardiovascular disorders and muscular cramps due to acute magnesium deficiency.
- Robusta Coffee price touches All-time High
In News:
- Farmers cultivating Robusta Coffee in South India are rejoicing as their harvest fetches record-high prices.
- In the Wayanad market, the farmgate price of raw Robusta coffee berries has surged to ₹172 per kilogram (kg), a substantial increase from ₹115 per kg last year.
Background on Coffee Cultivation in India
- The history of coffee cultivation in India traces back to the planting of seven seeds by saint Baba Budan around 1600 AD in Chikmagalur, Karnataka.
- Commercial coffee plantations took root in the 18th century, driven by British entrepreneurship.
- Presently, India ranks among the top 10 coffee-producing nations, contributing approximately 3% of the global output.
Unique Agro-climatic Conditions for Coffee
- Indian coffee holds a distinctive position, being shade-grown at elevated altitudes, unlike other major producers who cultivate coffee in flatlands.
- It thrives in tropical and semi-tropical climates, requiring temperatures between 16°C to 28°C, rainfall ranging from 150 to 250 cm, and well-drained slopes for optimal growth.
- Extreme conditions such as low temperatures, frost, prolonged dry spells, and harsh sunlight are detrimental to coffee plants. Additionally, coffee plants exhibit better growth in the laterite soils of Karnataka.
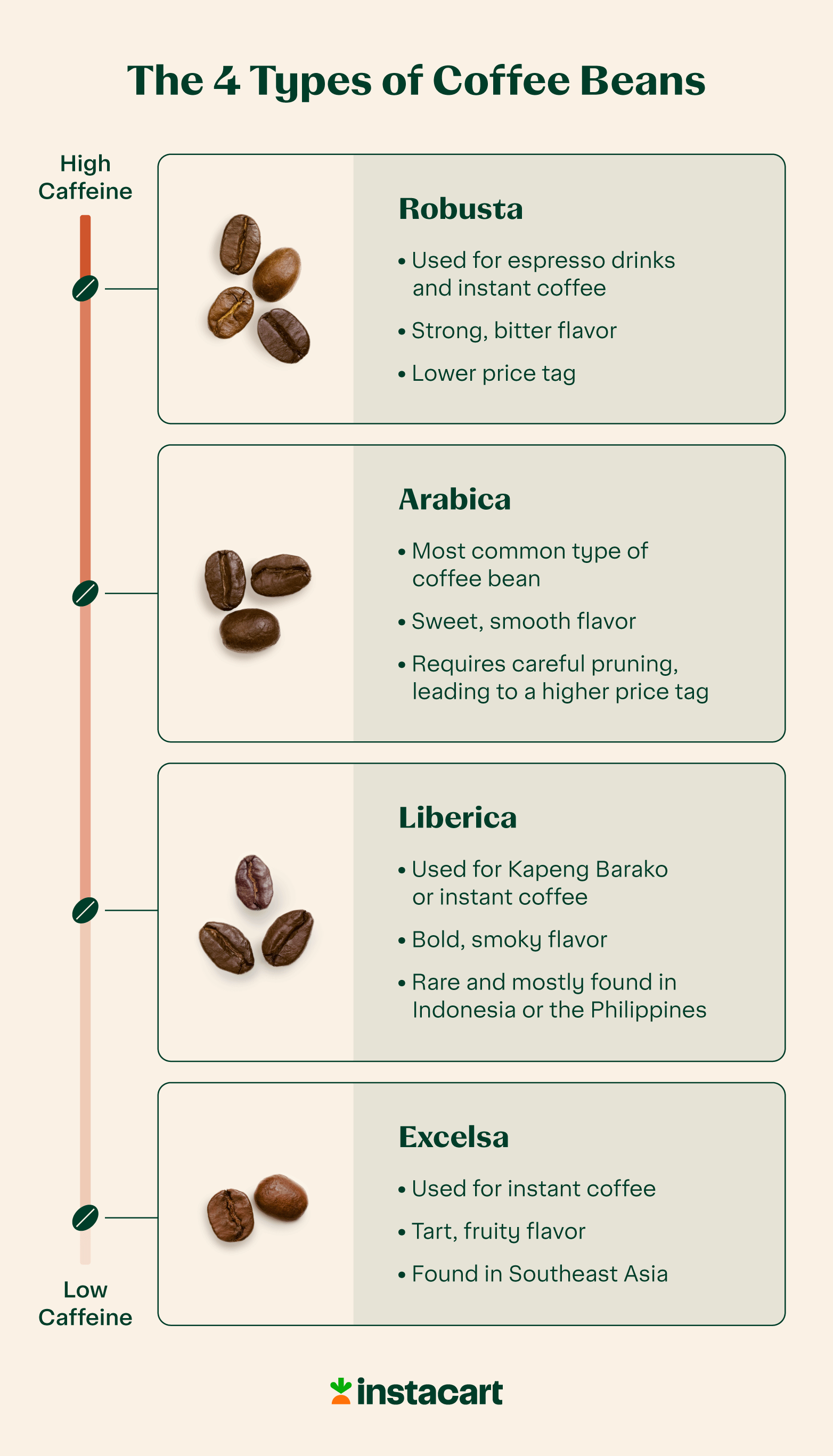
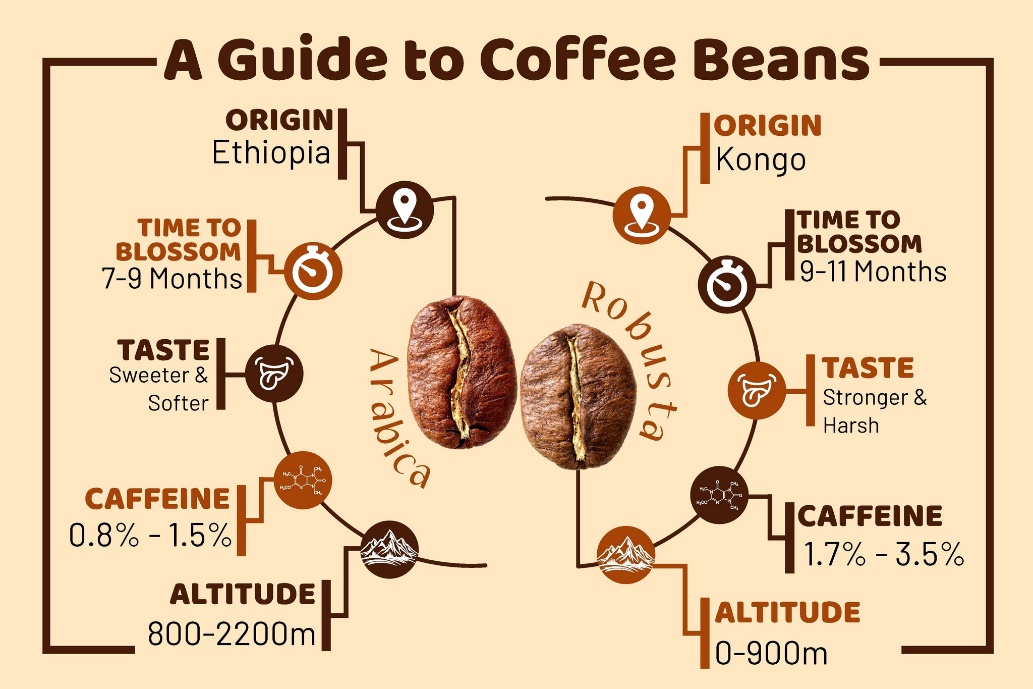
Market Dynamics
- Karnataka leads coffee production in India, contributing approximately 70% of the total output, followed by Kerala and Tamil Nadu.
- Regions such as Orissa and the North-eastern areas have smaller shares in production.
- Arabica coffee commands a higher market value compared to Robusta due to its mild aromatic flavor profile.
- India exports over 70% of its coffee production, making it the eighth-largest coffee exporter by volume according to The Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO).
- Export trends show a seasonal peak from March to June.
- Monuments of National Importance
https://timesofindia.indiatimes.com/india/monuments-of-national-importance-list-needs-rationalisation-economic-advisory-council/articleshow/97360231.cms

Context:
The Archaeological Survey of India (ASI) has made the decision to remove 18 monuments from its list of “centrally protected monuments” after determining that they lack national significance.
Definition of Monument of National Importance:
A Monument of National Importance is a designation conferred by the Archaeological Survey of India (ASI) and encompasses various categories:
- Remains of ancient monuments
- Sites of ancient monuments
- The land containing fences or protective structures for preserving the monument
- Land providing unrestricted access to the monument
Preservation Efforts:
- According to the Ancient Monuments and Archaeological Sites and Remains Act of 1958, the ASI is tasked with conserving monuments of cultural and historical significance.
This entails:
- Prohibiting construction activities within 100 meters of monument sites.
- Requiring prior approval for any repairs or alterations within 200 meters of the monuments.
- Authority to delist monuments deemed to have lost national importance under Section 35 of the Act.
- Upon delisting, the ASI relinquishes responsibility for the protection of the monument.
- Monuments are considered “untraceable” by the ASI if their location is unknown or if they have been lost.
- Recommendations made by the Economic Advisory Council’s (EAC-PM) in January 2023 proposed updating the list of national monuments, including the delisting of “missing” and minor monuments.
- The Comptroller and Auditor General (CAG) identified 92 monuments as “missing” in a performance audit circa 2013.
- The ASI located 42 of the “missing” monuments and suggested categorizing them based on their national significance and architectural value.
- International Seabed Authority
https://www.bbc.com/news/world-asia-india-68613351
Overview of the International Seabed Authority (ISA)
- The ISA, established under the United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS) of 1982 and subsequent 1994 Agreement, is an autonomous international organization.
- Its primary mandate involves organizing and regulating mineral resource activities within the international seabed area for the collective benefit of humanity.
- Additionally, the ISA is tasked with ensuring environmental protection against detrimental impacts arising from deep-sea operations.
Key Aspects of the International Seabed Authority (ISA)
- Establishment: Formally operational since June 1996, the ISA was established on November 16, 1994. It operates as an independent international organization with its headquarters located in Kingston, Jamaica.
- Membership: Comprising 169 members, including 168 sovereign states and the European Union, the ISA operates under the principle of the common heritage of mankind, recognizing the international seabed and its resources as belonging to humanity at large.
Exclusive Rights and Jurisdictional Extensions
- Exclusive Economic Zones (EEZ): Nations possess exclusive control over resources within their EEZ, extending up to 200 nautical miles from their coastlines.
- Continental Shelf Extensions: Certain coastal states may extend their jurisdiction beyond the 200-mile limit, encompassing the underlying seabed known as the continental shelf.
- ISBA Approval Process: Claims for extended jurisdiction are evaluated by the ISA through a scientific commission, which assesses the evidence provided by claimants to determine approval.

India’s Application for Exploration Rights
- India recently applied to the ISA, located in Jamaica, seeking permission to explore two expansive regions of the Indian Ocean seabed falling beyond its territorial jurisdiction.
- This application highlights India’s interest in harnessing deep-sea resources and aligning with international legal frameworks governing such activities.
- Baltimore’s Francis Scott Key Bridge
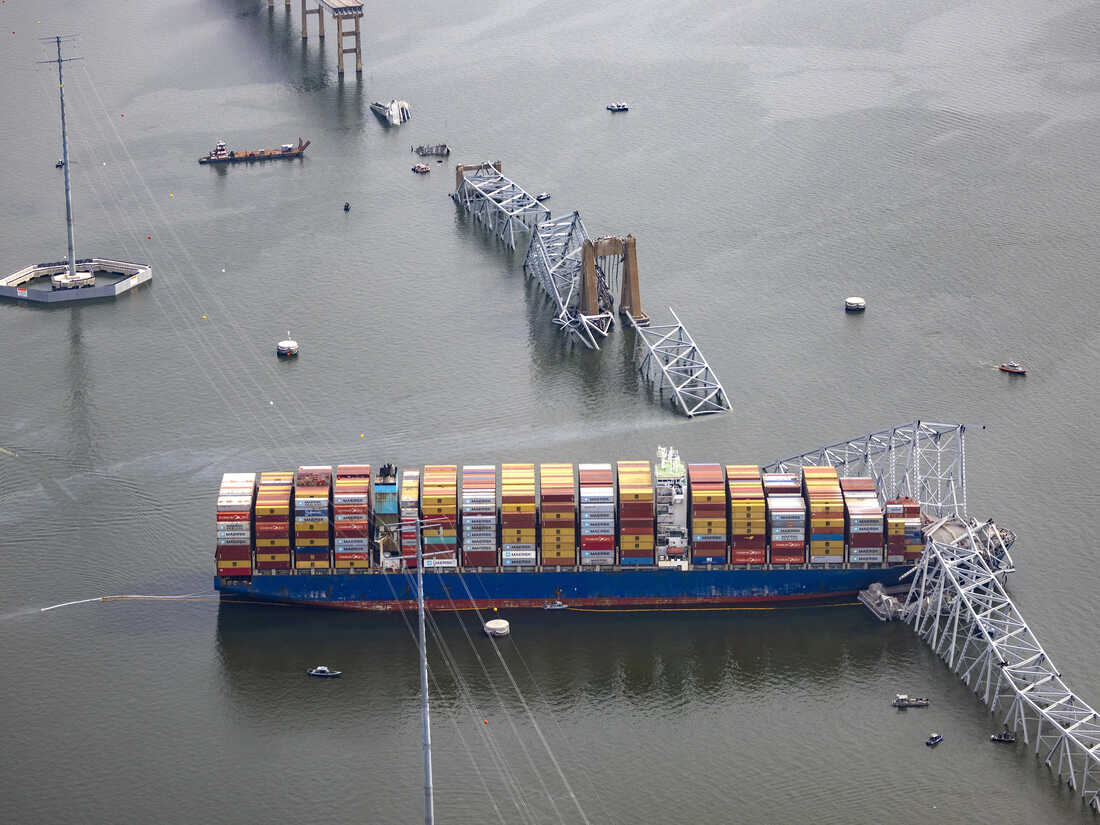

Background
The collapse of Baltimore’s Francis Scott Key Bridge occurred following a collision between a container ship and a pylon.
Bridge Overview
- The Francis Scott Key Bridge served as one of the primary routes across Baltimore Harbor, accommodating approximately 31,000 vehicles daily or 11.3 million annually.
- Constructed of steel, the bridge spans four lanes and stands at a height of 185 feet (56 meters) above the river.
- It was inaugurated in 1977 and traverses the Patapsco River.
- The bridge provides access to the Port of Baltimore, known for being Maryland’s deepest harbor within the Chesapeake Bay.
- Cause of Collapse: Engineers attribute the collapse to the bridge’s metal truss-style design with a suspended deck. The collision with the main concrete pier, supported by underwater soil, formed part of the foundation and exacerbated the collapse.
- India Employment Report 2024
Context:
The recent release by the International Labour Organisation (ILO) focusing on India underscores the nation’s potential to harness a demographic dividend, albeit amidst persisting challenges related to youth unemployment.
Key Points from the Report:
- Titled “India Employment Report 2024,” it highlights that India’s youth, constituting 27% of the population in 2021, is projected to decrease to 21% by 2036, with an annual addition of 7-8 million youth to the workforce.
- The report emphasizes the predominance of lower-quality employment among Indian youth compared to adults, with a significant portion engaged in vulnerable occupations or informal sectors.
- While youth wages tend to increase with age, they remain lower across all employment categories compared to adults, indicating suboptimal working conditions.
- Notably, the report points out disproportionately high rates of unemployment among graduate youth, particularly among women, with the latter facing nearly five times the unemployment rate compared to men.
- Furthermore, in 2022, women not engaged in employment, education, or training constituted a substantially larger proportion compared to men, representing approximately 95% of the total youth population in this category.
Dimension-Disruptive Factors:
- Rapid technological advancements, notably in artificial intelligence (AI), contribute to labor market uncertainties.
- India’s demographic dividend is expected to persist for another decade, with the youth population projected to remain at 23% of the total in 2036, down from 27% in 2021.
- The rise of digital platforms and the gig economy introduces numerous new job opportunities, albeit primarily temporary, informal, and non-standardized in nature.
- Algorithmic management in gig economy platforms diminishes autonomy and flexibility for workers, while also introducing challenges related to subjective and potentially biased performance ratings.
Required Measures:
- The report advocates for prioritizing labor-intensive manufacturing employment to absorb the surplus unskilled labor force, alongside fostering growth in modern manufacturing and services sectors, with a particular focus on supporting micro, small, and medium-sized enterprises through decentralized approaches.
- Emphasizing investment in environmentally sustainable practices, the report highlights the importance of green and blue economies, as well as rural infrastructure development.
- Establishing integrated markets is identified as crucial for revitalizing employment opportunities in both farm and non-farm sectors within rural areas.



