- NexCAR19: India’s own CAR-T Cell Therapy
- Customized Debt Financing
- UNESCO’s Creative Cities Network
- State Food Safety Index (SFSI) 2023 Report
- Black Stork
NexCAR19: India’s own CAR-T Cell Therapy
Context:
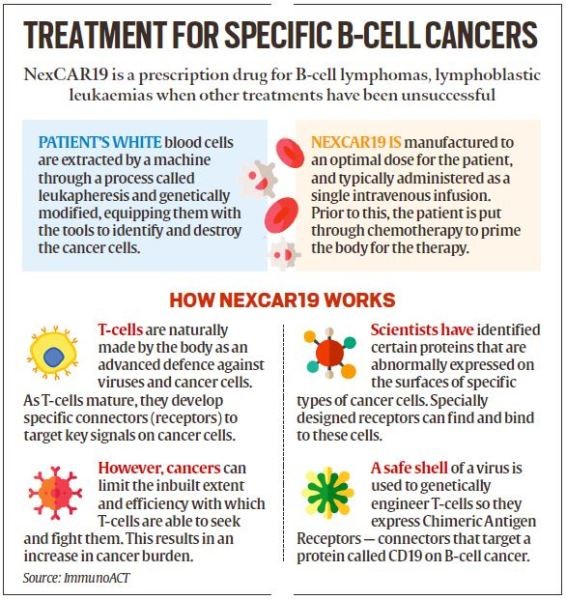
India has reached a significant milestone in cancer treatment with the CDSCO’s approval of NexCAR19, the country’s first homegrown CAR-T Cell Therapy.
Developed by ImmunoACT, a company incubated at IIT Bombay, NexCAR19 is poised to revolutionize cancer treatment in India, improving its accessibility and affordability.
Understanding CAR-T Cell Therapy Innovative Approach:
- CAR-T cell therapy involves the modification of T-cells, a type of white blood cell, to transform them into powerful cancer-fighting agents.
- Targeting Cancer: These genetically enhanced cells are reintroduced into the patient’s body, where they can recognize and eliminate cancer cells.
- This approach is particularly effective against blood cancers like leukemia and lymphomas.
- A Game-Changer: Unlike traditional chemotherapy or immunotherapy, CAR-T therapy offers the potential for a cure and long-lasting benefits, making it a transformative treatment option.
- NexCAR19: India’s Homegrown CAR-T Therapy NexCAR19 is engineered to target cancer cells carrying the CD19 protein, a marker found on cancer cells.
- This precision enhances the effectiveness of the treatment. India now joins a select group of nations with its CAR-T and gene therapy platform, reducing its reliance on imports.
- Initially, NexCAR19 is approved for patients aged 15 and older with B-cell lymphomas who have not responded to standard treatments, leading to relapse or recurrence.
Effectiveness and Unique Characteristics
- Around 70% of patients respond positively to NexCAR19 treatment, with some even achieving complete remission. Laboratory and animal studies suggest lower drug-related side effects, including reduced neurotoxicity and Cytokine Release Syndrome (CRS).
- Clinical trials for pediatric patients are currently underway at Tata Memorial Hospital, expanding the potential applications of this therapy.
- Accessibility and Affordability ImmunoACT is actively pursuing licenses and collaborations with various hospitals, such as Tata Memorial, Nanavati, Fortis, and Jaslok, in multiple cities.
- CAR-T therapy is expected to become available in a few weeks to a few months, subject to final government approvals. Initially priced at Rs 30-40 lakh, ImmunoACT aims to eventually reduce the cost to Rs 10-20 lakh, making the therapy more accessible.
- While regulatory agencies like CDSCO’s approval should lead to potential insurance coverage, the extent of coverage may vary, and ongoing discussions with insurers and the government are in progress.
Customized Debt Financing
Context:
In a recent event hosted by REC Limited, a workshop was held to explore the concept of Tailored Debt Financing for Commercial Mining, Mine Developers, and Operators. The workshop covered various aspects of debt financing and customization options for businesses seeking funding.
Here are the key points discussed:
- Debt Financing and Equity Financing:
- Debt financing involves companies raising funds for their operational or capital needs by selling debt securities to individual and institutional investors.
- Investors who provide these funds become creditors, with a commitment to receive the borrowed amount along with interest.
- Equity financing, on the other hand, involves issuing shares of stock to the public, which is distinct from debt financing.
- Customizations in Debt Financing:
- Debt financing offers flexibility with customizable features, including loan amount, interest rate, repayment structure, and collateral.
- Customization should always be approached with consideration of associated risk factors.
- The specific conditions of each company, such as financial health, cash availability, payment consistency, project timelines, and relationships with financial institutions, play a significant role in tailoring debt products.
- Borrowing companies can choose between existing products that suit their needs or collaborate with lenders willing to create tailored solutions.
- Types of Customization:
- Amount Customization: This involves adjusting the loan amount to align with the company’s financial requirements and repayment capacity to maintain an optimal balance.
- Repayment Pattern Customization: The repayment schedule can be adapted to suit the company’s cash flow and business cycle, with options like bullet payments, quarterly payments, or revenue-linked payments.
- Adjustable Interest Rates: Companies can choose between fixed or floating interest rates to manage cash flows. Fixed rates offer certainty, while floating rates respond to policy changes.
- Amortising vs. Revolving Limits: Borrowers can select between term loans and revolving credit lines based on their business needs. Revolving credit lines allow drawdowns and repayments.
Prepayment Flexibility: Some loans offer the ability to prepay, but this may involve considerations like lock-in periods and prepayment penalties to align with expected cash inflows.
UNESCO's Creative Cities Network
Context:
UNESCO has recently recognized Kozhikode as a ‘City of Literature’ and Gwalior as the ‘City of Music,’ acknowledging their contributions to culture and creativity. These cities’ journeys towards UNESCO recognition exemplify their distinct cultural strengths.
Kozhikode:
- Kozhikode, celebrated for its literary culture, embarked on its path to UNESCO recognition in 2022, driven by the Kerala Institute of Local Administration’s efforts.
- Kozhikode’s partnership with the University of Prague, the inaugural ‘City of Literature’ in 2014, underscored the city’s global literary aspirations.
- Ludmila Kolouchova, a research student from the University of Prague, conducted a comparative study, highlighting Kozhikode’s literary prowess, showcasing its 500 libraries and 70 publishers.
- Through events like the annual Kerala Literature Festival and numerous book fairs, Kozhikode effectively showcased its vibrant literary scene, ultimately securing its place on UNESCO’s Creative Cities list.
Gwalior:
- Gwalior, renowned as the ‘City of Music,’ takes pride in its rich musical heritage, boasting illustrious figures such as Tansen and Baliti Bawra.
- It is the birthplace of the prestigious Gwalior Gharana, one of the oldest Hindustani musical traditions.
- Gwalior’s cultural identity, rooted in its historic core, serves as a valuable cultural asset.
- Moreover, Gwalior’s official designation as a ‘Smart City’ by the Indian Government is attributed to its strategic location, connecting it to major commercial centers and popular tourism circuits in India.
UNESCO Creative Cities Network (UCCN):
- Launch Year: 2004
- Eligibility: Open to UNESCO’s member states and associate members.
- Updation Time: Updated once every two years.
- Total Cities (2023): Currently, the network encompasses 350 cities from more than 100 countries.
Objective:
The UCCN aims to enhance cultural activities, products, services, and international collaboration to promote sustainable development, aligning with UN Sustainable Development Goal 11 (SDG 11) for Sustainable Cities and Communities.
Seven Creative Fields of UCCN:
- Crafts and Folk Arts
- Design
- Film
- Gastronomy
- Literature
- Media Arts
- Music
Indian Cities in UCCN:
- Crafts and Folk Arts: Jaipur (2015), Srinagar (2021)
- Design: No Indian city listed
- Film: Mumbai (2019)
- Gastronomy: Hyderabad (2019)
- Literature: Kozhikode (2023) – The first Indian city to receive the ‘City of Literature’ designation.
- Media Arts: No Indian city listed
- Music: Chennai (2017), Varanasi (2015), Gwalior (2023)
The selected cities will participate in the UCCN annual conference in 2024, to be held in Braga, Portugal, with the theme ‘Bringing youth to the table for the next decade.’
State Food Safety Index (SFSI) 2023 Report
Context:
In a recent development, the Food Safety and Standards Authority of India (FSSAI) has released its 2023 State Food Safety Index (SFSI) Report.
This report unveils several noteworthy findings:
- A substantial portion of the 20 states assessed witnessed a decline in their SFSI scores in 2023 when compared to the 2019 scores, particularly following the introduction of the ‘SFSI Rank Parameter.’
- Among the states, Maharashtra, Bihar, and Gujarat experienced the most significant reductions in their scores over the five-year period under examination.
- The report emphasizes the pivotal role played by state apex food safety authorities in ensuring food safety.
A closer look at the parameter scores reveals the following:
- The ‘Food Testing Infrastructure’ parameter exhibited the most notable drop, declining from an average of 13 out of 20 in 2019 to 7 out of 17 in 2023. States such as Maharashtra, Bihar, Andhra Pradesh, and Chhattisgarh recorded lower scores in this category.
- The ‘Compliance’ parameter also witnessed a decline, with Jharkhand receiving the lowest score (4 out of 28) in 2023.
- The ‘Consumer Empowerment Parameter’ measures the state’s performance in FSSAI initiatives such as Food Fortification, Eat Right Campus, BHOG, Hygiene Rating, and Street Food Hubs. Bihar’s score dropped from 7 to 1 in 2023, while Tamil Nadu, Kerala, and Madhya Pradesh emerged as top performers.
- In the ‘Human Resources and Institutional Data Parameter,’ the average score decreased from 11 to 7. Even top-performing states like Tamil Nadu and Uttar Pradesh saw significant score reductions.
- The ‘Training and Capacity Building Parameter’ evaluates training initiatives and capacity-building efforts, with the average score improving from 3.5 to 5, indicating a positive trend.
The new ‘SFSI Rank Parameter’ assesses the availability of human resources like Food Safety Officers, Designated Officers, and adjudication facilities. No specific word count is provided for this section.
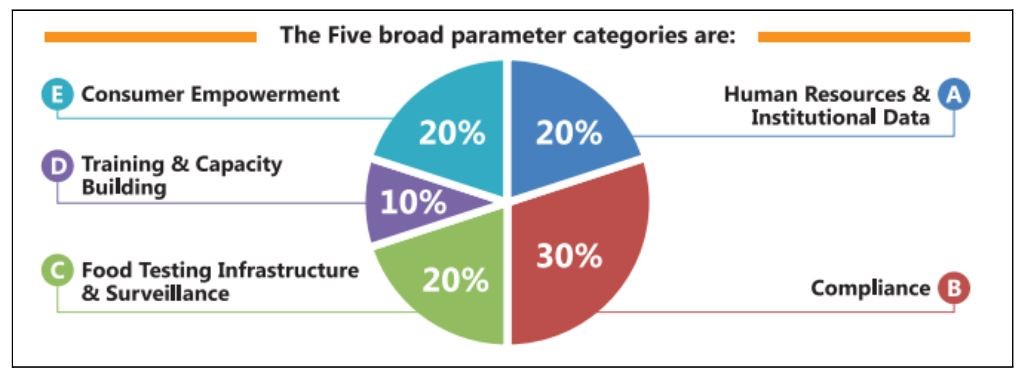
Moreover, there have been adjustments in weightage for certain parameters in 2023:
- The ‘Food Testing Infrastructure’ parameter, which previously held a 17% weightage, observed the most significant drop in scores.
- The ‘Compliance’ parameter, with a 28% weightage, saw reductions in scores across states compared to 2019.
- In the ‘Human Resources and Institutional Data Parameter,’ the weightage decreased from 20% in previous years to 18% in 2023.
- The introduction of the ‘Improvement in SFSI Rank’ parameter in 2023 carries a weightage of 10%. Notably, 14 out of the 20 large states received 0 points in this new parameter.
Finally, a brief overview of FSSAI reveals that it was established by Former Union Minister Dr. Anbumani Ramadoss, Government of India, on August 5, 2011, under the Food Safety and Standards Act, 2006, which was operationalized in 2006.
FSSAI is a statutory body with a primary responsibility of developing science-based food standards for food and food products, regulating their manufacturing, storage, distribution, sale, and import to ensure the availability of safe and wholesome food for human consumption.
Black Stork
Rare Sighting in Hastinapur Wildlife Sanctuary: The Black Stork
The Black Stork: An Overview
The Black Stork, scientifically known as Ciconia nigra, is a remarkable species of stork belonging to the Ciconiidae family.
Habitat and Migration
- It breeds in a variety of habitats, including swampy, coniferous, and mixed forests.
- During winter, it can be found in grasslands, agricultural fields, and along the margins of lakes and rivers.
This species is known for its impressive long-distance migrations, with European populations wintering in tropical Sub-Saharan Africa and Asian populations in the Indian subcontinent.
Global Distribution and Conservation Status
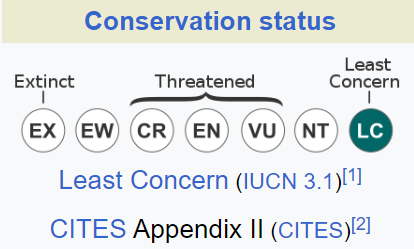
- The Black Stork is predominantly found in Europe, Asia, and several African countries.
- Its conservation status is listed as “Least Concern” by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN).
Hastinapur Wildlife Sanctuary: A Natural Haven
- The Hastinapur Wildlife Sanctuary, located in the state of Uttar Pradesh, is one of the largest wildlife sanctuaries in northern India.
Geographical Location
- It is situated alongside the northern tip of the River Ganga, flowing through the districts of Muzaffarnagar and Bijnor.
Diverse Habitat and Wildlife
- The sanctuary encompasses a variety of landforms and habitats, including wetlands, marshes, dry sand beds, and gently sloping ravines.
- Fauna within the sanctuary includes Swamp Deer, Leopards, Wild Cats, Wild Otters, Pythons, and more.
A Hub for Migratory Birds
The Hastinapur Wildlife Sanctuary is a significant component of the “Asia Flyway” project, attracting a multitude of migratory birds, both local and foreign, to the numerous water bodies in the region.