1. The Intersection of Myanmar's Civil Conflict and India's Strategic Concerns
Introduction:
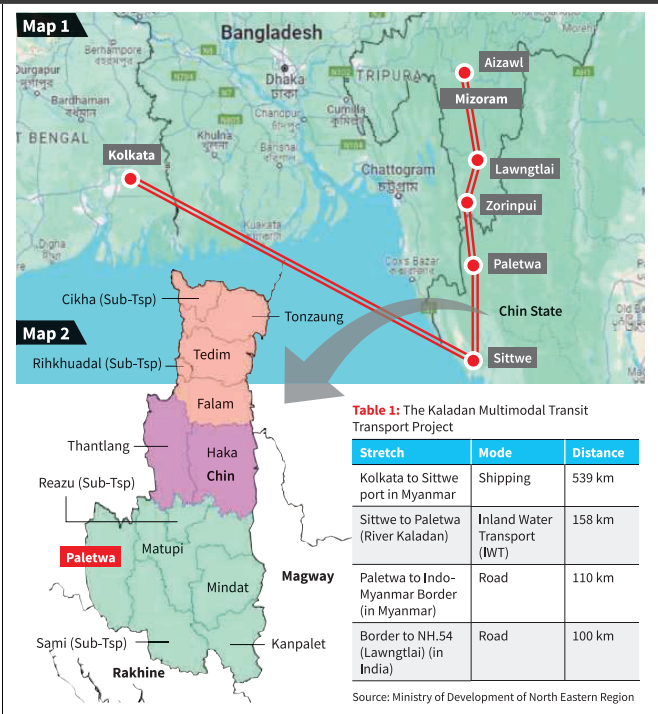
The seizure of Paletwa in Chin State by the Arakan Army has raised concerns about the progress of significant Indian ventures in Myanmar.
Myanmar Coup: A brief overview
- In February 2021, Myanmar’s military deposed the elected government led by Aung San Suu Kyi.
- Initially anticipating swift suppression of resistance, the military now contends with growing opposition.
Conflict Dynamics along Indian Borders
- The capture of Paletwa has sparked intricate dynamics between the Chin and Arakan ethnic communities. Paletwa predominantly houses the Chin people, although some in Rakhine State claim historical ownership during colonial rule.
- Inter-ethnic Cooperation: Collaborative efforts among Ethnic Armed Organizations (EAOs) are crucial for effective resistance against the military. However, reaching an inter-ethnic consensus on settlements like Paletwa poses challenges due to its strategic importance.
Impact on India’s Kaladan Project
- Developments in Paletwa hold implications for India’s Kaladan Multimodal Transit Transport Project (KMTTP) in Myanmar. The KMTTP seeks to address northeast India’s geopolitical and geo-economic challenges but has faced delays due to terrain, coordination issues, political instability, and security concerns.
- Local Perspectives: It is imperative to consider the viewpoints of local ethnic groups for expedited execution of the Kaladan project, which is of interest to communities in Mizoram and Chin State due to its potential economic benefits.
China’s Role in the Region
- The Arakan Army’s affiliation with the Three Brotherhood Alliance, reportedly supported by China, aims to safeguard Chinese investments in Myanmar. Reports indicate Chinese assistance to the Arakan Army, raising concerns in India about Beijing’s potential interference with Indian connectivity projects.
- China’s Economic Influence: China has expanded its economic footprint along Myanmar’s Bay of Bengal coast, including operationalized pipelines and agreements for a deep-sea port and special economic zone.
Conclusion
India, as a proponent of liberal democracy, faces scrutiny regarding the consequences of its external engagements on sectarian and identity-based conflicts in neighboring regions. Prioritizing humanitarian aid and development assistance while collaborating with ethnic organizations is crucial for navigating these complexities.
2. Warning Signs in the Hindu Kush Himalaya (HKH) Region
Introduction:
The International Centre for Integrated Mountain Development (ICIMOD) has emphasized the necessity for decisive measures and immediate financial support to avert the potential collapse of the Hindu Kush Himalaya (HKH) region.
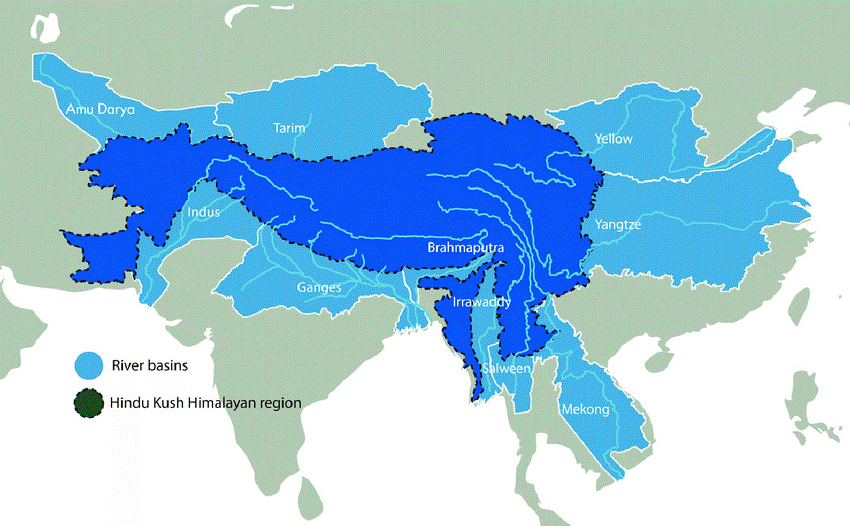
About Hindu Kush Himalaya (HKH):
- The HKH region, situated in South Asia and spanning Afghanistan, Bangladesh, Bhutan, China, India, Myanmar, Nepal, and Pakistan, covers an area of approximately 3,500,000 square kilometers.
- Known as the “Water Tower of Asia,” it serves as the origin of at least 12 major rivers, such as the Syr Darya and Amu Darya directed towards the now-dried Aral Sea, the Tarim River towards the Taklamakan Desert, and others like the Indus, Ganga, Brahmaputra, Yellow River, Yangtze,
- Mekong, Chindwin, Salween, and Irrawaddy flowing towards various seas and gulfs.
- The region is home to numerous glaciers, including Mount Everest and K2.
A Region on the Brink:
- Biodiversity Hotspot: Renowned for its exceptional biodiversity, the HKH region is often described by experts as a ‘biosphere on the brink.’
- Scope of Crisis: The alarming rate and magnitude of habitat and biodiversity loss in the HKH region necessitate urgent intervention.
Alarming Statistics:
- Biodiversity Richness: The HKH region harbors four of the world’s 36 global biodiversity hotspots, along with 575 Protected Areas and 335 important bird areas.
- Biodiversity Loss: Despite conservation endeavors, the region has witnessed a staggering 70% decline in its original biodiversity over the past century.
- Human Dependence: Approximately 85% of mountain communities in the HKH region rely on its biodiversity for sustenance, water resources, flood mitigation, and cultural heritage.
- Population Pressure: With a population of 241 million inhabitants, 31% of whom face food insecurity and half experience varying degrees of malnutrition.
Human Impact:
- Threat to Humanity: The degradation of the natural environment in the HKH region poses a significant threat not only to wildlife but also to human societies.
Water Tower of Asia: Recognized as the ‘Water Tower of Asia,’ this region provides crucial ecosystem services, including clean water, to one-third of the global population.
3. A Novel Cabbage Mutation with Potential to Enhance Agricultural Output
Introduction
- A recent study has elucidated a fascinating method for inducing sterility in a wide array of plants, such as cabbage, cauliflower, broccoli, tomato, and rice.
- This sterility is achieved through a small genetic deletion, holding great promise for augmenting crop yields via a phenomenon known as heterosis.
Unveiling Genetics
- DNA Composition: Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) comprises two lengthy strands, each composed of four nucleotide bases: Adenine (A), Cytosine (C), Guanine (G), and Thymine (T). These bases pair up (A-T and G-C) through hydrogen bonds.
- Genomic Arrangement: The genome of the cabbage plant (Brassica oleracea) encompasses roughly 1.06 billion base pairs distributed across 18 chromosomes. Each chromosome pair, originating from pollen and egg, shares a largely identical sequence.
- Role of Genes: Genes are distinct DNA sequences, typically spanning several thousand base pairs. Upon expression, a segment of a gene is transcribed into RNA, serving as a template for protein synthesis.
- Protein Synthesis: RNA undergoes processing by cellular machinery called ribosomes, directing the assembly of amino acids into proteins.
Significance of Sterility in Hybrid Vigor
- Discovery of Ms-cd1: Approximately 44 years ago, researchers identified a cabbage plant with a natural mutation known as Ms-cd1. This mutation resulted in male sterility in the plant, with a key twist: the eggs of the mutant plant remained fertilizable by pollen from normal plants, producing viable seeds.
- Hybrid Seeds: Seeds from mutant plants arose from out-crossing, where eggs were fertilized by pollen from different strains. These hybrid seeds, also termed out-cross seeds, yield more resilient plants with heightened vigor, termed heterosis.
- Dominant Mutation: The Ms-cd1 mutation was observed to be dominant, indicating that its presence in just one chromosome of the pair caused male sterility, regardless of the status of the other chromosome.
- Recessive Mutations: Researchers demonstrated that mutations in both copies of the Ms-cd1 gene were requisite for male fertility, rendering the mutations recessive.
Critical Absence of a Base Pair
- Genetic Mapping: Through genetic mapping, researchers discerned a vital difference between the mutated and non-mutated Ms-cd1 genes: the mutated gene lacked a single DNA base pair in its promoter region.
- Function of Promoter: The promoter sequence binds to regulatory proteins that govern the timing and location of gene transcription into RNA.
- ERF Binding: In the mutated gene, the absence of this base pair disrupted its binding to the regulatory protein ERF, permitting continued expression of the Ms-cd1 gene, resulting in male sterility.
- Precision in Protein Levels: Proper pollen development hinges on a precise balance of Ms-cd1 protein levels, with ERF binding regulating its expression at various developmental stages.
Extension of the Discovery
- Cross-Species Applicability: The dominant mutant gene was introduced into other plant species, including rice, tomato, and Arabidopsis. In all instances, the recipient plants exhibited disruptions in pollen development.
- A Promising Tool: The genetic deletion of a single base pair emerges as a potent tool for generating hybrid seeds, not only in cabbage but also in various other crops.
- Implications for Agriculture: This breakthrough holds the potential to harness heterosis and augment crop yields across different plant species, addressing global food security challenges.
Conclusion
The genetic deletion responsible for inducing male sterility in plants signifies a remarkable advancement in agricultural science, offering the possibility of bountiful harvests through hybrid seeds.
This discovery paves the way for sustainable agriculture and underscores the pivotal role of genetic research in tackling the world’s escalating food demands.
5. The 2024 Amendment Bill for Water Pollution Prevention and Control
Context:
The Water (Prevention and Control of Pollution) Amendment Bill, 2024 has been introduced by the Central government in the Rajya Sabha. The current Water Act, enacted in 1974, has witnessed limited amendments over the years, with minor revisions in rules and slight modifications in certain sections.
This is notable given the significant changes in urbanization, industrialization, and consequent pollution levels experienced by the country in recent decades. In contrast, the Environmental Impact Assessment (EIA) 2006 has undergone numerous amendments.
Key Highlights of the Bill:
- Applicability: The Bill extends to Himachal Pradesh and Rajasthan, as well as any other state that passes a resolution under the Water (Prevention and Control of Pollution) Act, 1974.
- Provision for Central Government: The Bill empowers the Central Government to prescribe the manner of nomination of the chairman of the State Pollution Control Board and to exempt certain categories of industrial plants from the application of Section 25 concerning restrictions on new outlets and discharges.
- Guidelines Issuance: The Central Government may issue guidelines regarding the grant, refusal, or cancellation of consent by any State Board for the establishment of industries, operations, processes, or treatment and disposal systems.
- Rationalization of Criminal Provisions: The Bill proposes rationalizing criminal provisions to ensure that citizens, businesses, and companies operate without fear of imprisonment for minor procedural defaults. It decriminalizes minor offenses, replacing them with monetary penalties credited to the Environmental Protection Fund.
The deteriorating quality of Indian waterbodies due to unchecked urbanization and development is a pressing issue. Encroachment and pollution-induced eutrophication have led to the loss or considerable shrinkage of many waterbodies. Water contamination, categorized as point source and non-point source pollution, is a significant concern. Major effluents contaminating water bodies include inorganic, organic, biological, and radiological contaminants, posing severe health risks to human populations.
6. Centre's New Anti-Cheating Bill
Introduction:
- The Public Examinations (Prevention of Unfair Means) Bill, 2024, tabled in Lok Sabha, aims to counteract unethical behavior in public examinations, thereby fostering transparency and reliability in the examination ecosystem.
- This comprehensive legislative framework encompasses various facets of unfair practices within public exams and prescribes severe penalties for transgressions.
Instances of Unethical Behavior:
- Outlined in Section 3 of the Bill, at least 15 actions are categorized as “unfair means” in public examinations, predominantly driven by monetary or illicit motives.
- These actions range from question paper leaks to unauthorized access to question papers or answer sheets, tampering with answer sheets, providing unauthorized solutions, and orchestrating counterfeit examinations.
Definition and Coverage of Public Examinations:
- A “public examination,” as defined under Section 2(k), encapsulates any examination administered by designated “public examination authorities” delineated in the Bill’s Schedule or notified by the Central Government.
- These designated authorities, as listed in the Schedule, encompass institutions such as UPSC, SSC, RRBs, IBPS, and NTA, entrusted with the conduct of various national-level examinations.
- Furthermore, the purview of the Bill extends to Ministries, Departments, and their attached or subordinate offices under the Central Government responsible for staff recruitment.
Imposition of Penalties:
- Section 9 of the Bill establishes stringent measures, rendering offenses cognizable, non-bailable, and non-compoundable.
- Cognizable offenses empower authorities to effect arrests without a warrant, while the non-bailable nature of offenses necessitates the discretion of a magistrate regarding bail.
- Moreover, non-compoundable offenses preclude complainants from withdrawing cases, thereby mandating legal proceedings.
Prescribed Punishments:
- Individual offenders may face imprisonment ranging from three to five years and fines up to Rs 10 lakh. Failure to remit fines can lead to additional imprisonment, in accordance with the provisions of the Bharatiya Nyaya Sanhita, 2023.
- Service providers facilitating examination conduct can be penalized with fines up to Rs 1 crore, among other consequences.
- In cases of organized paper leaks constituting “organized crime,” offenders may incur imprisonment for a minimum of five years, extendable up to ten years, along with a fine not less than one crore rupees.
Rationale Behind the Legislation:
- The prevalence of widespread paper leaks in recruitment exams across the nation has significantly disrupted the recruitment process, adversely impacting millions of aspirants.
- The absence of substantive legislation to address such malpractices necessitated the formulation of a comprehensive central legislation like the current Bill.
- The primary objectives of the legislation include ensuring transparency, fairness, and credibility in public examinations, while dissuading individuals and entities from exploiting vulnerabilities in the system for undue advantages.
Model Draft for States:
The Bill is crafted to serve as a guiding framework for states to adopt as per their discretion, aiding them in preventing disruptions in their respective state-level public examinations.
Conclusion:
The enactment of this legislation marks a significant stride towards preserving the sanctity of public examinations in India. By imposing severe penalties for unethical practices and combatting paper leaks, the legislation endeavors to reassure candidates that their genuine efforts will be duly acknowledged, thus securing their futures.
Furthermore, the potential of the Bill to serve as a model for state-level legislation amplifies its efficacy in curtailing examination-related malpractices.