Topics
- Prison Reforms
- Project Devika
- Gnanamuyarchi
- BharatNet Project
- Indian Eagle Owl
- Perucetus Colossus Whale: Heaviest Animal that Ever Lived
Prison Reforms
News:
The Ministry of Home Affairs has formulated a set of directives aimed at reducing overcrowding in correctional facilities.
It has urged states and Union Territories to consider the release of indigent inmates currently incarcerated due to their inability to pay fines or secure bail owing to financial limitations.
Statistics
According to the latest report by the National Crime Records Bureau (NCRB), Prison Statistics India 2021, the current prison statistics in India are as follows:
- There are 1,319 functioning jails in India, with a total capacity of 4,25,609 prisoners.
- The number of prisoners lodged in various jails as on 31st December, 2021 was 5,54,034, which is 13.4% higher than the previous year.
- The occupancy rate of Indian prisons was 130.2%, which means that the prisons were overcrowded by 30.2%.
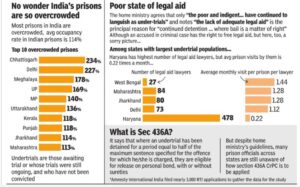
- Out of the total prisoners, 77% (4,27,000) were undertrials, while only 22% (1,23,000) were convicts. The remaining 1% (4,034) were detainees and others.
- Among the convicts, the highest percentage (29.9%) was for offences affecting the human body, followed by offences against property (23.6%) and offences under special and local laws (21.8%).
Challenges
- Overcrowding,
- poor sanitation,
- lack of medical care,
- human rights violations,
- corruption,
- discrimination, etc.
Various Committees for Prison Reforms in India
- The Indian Jail Reform Committee (1919-20): It was headed by Sir Alexander Cardew and suggested the reform of prisoners rather than simply their deterrence. It also recommended classification of prisoners, provision of education, vocational training, recreation, etc.
- The All-India Jail Manual Committee (1957-59): It was headed by Dr. W.C. Banerjee and prepared a model prison manual for the guidance of state governments. It also emphasized on the welfare and rehabilitation of prisoners.
- The Mulla Committee (1980-83): It was headed by Justice A.N. Mulla and reviewed the laws, rules and regulations for protecting society and reforming offenders. It also suggested measures to reduce overcrowding, improve living conditions, provide legal aid, etc.
- The Justice Krishna Iyer Committee (1987): It was headed by Justice V.R. Krishna Iyer and focused on the problems of women prisoners and children in prisons. It also advocated for alternatives to imprisonment, such as probation, parole, community service, etc.
- The Ribeiro Committee (1999): It was headed by Justice J.F. Ribeiro and examined the security aspects of prisons and suggested ways to prevent escapes, violence, riots, etc. It also recommended modernization of prison infrastructure, equipment and training.
- The Dharmavira Committee (2005): It was headed by Justice T.S. Dharmavira and reviewed the implementation of various recommendations made by previous committees.
- It also proposed a national policy on prison reforms and correctional administration.
Amitva Roy Committee (2018)
Constitutional Provisions
- Article 14: It guarantees equality before law and equal protection of laws to all persons, including prisoners.
- Article 19: It grants certain fundamental freedoms to all citizens, subject to reasonable restrictions. Some of these freedoms may be curtailed during imprisonment, but not completely denied.
- Article 21: It protects the right to life and personal liberty of all persons, including prisoners. It also implies the right to human dignity, fair trial, legal aid, speedy justice, etc.
- Article 22: It lays down certain safeguards for persons arrested or detained under preventive detention laws. It also provides for the right to be informed of the grounds of arrest, to consult a lawyer, to be produced before a magistrate within 24 hours, etc.
- Article 39-A: It directs the state to provide free legal aid to ensure that justice is not denied to any citizen by reason of economic or other disabilities.
- Article 51-A: It imposes certain fundamental duties on all citizens, such as respecting the Constitution, abiding by the law, promoting harmony, etc.
Conclusion
- Prison reforms in India are essential to ensure that prisons serve their purpose of punishment and rehabilitation of offenders.
- Prison reforms in India should also aim at protecting the human rights and dignity of prisoners and providing them with opportunities for reformation and reintegration into society.
- Prison reforms in India should also involve the participation and cooperation of various stakeholders, such as the judiciary, the executive, the legislature, the civil society, the media, etc.
Soucre: Economic Times
Project Devika

News: The Minister of State for Science & Technology, in an official statement, mentioned that the Devika River Rejuvenation Project, which is the first of its kind in North India, is approaching its final stages of completion.
- The Devika Rejuvenation Project, fashioned after the successful ‘Namami Ganga’ initiative, was inaugurated by the Prime Minister of India.
- This undertaking, which came at a cost exceeding Rs 190 crore, aimed to safeguard the sanctity of the revered Devika River in Udhampur, Jammu & Kashmir.
- A parallel Liquid Waste Management Project was also reviewed in conjunction with this effort.
Significance of Devika River
- The Devika River holds immense religious importance, often referred to as the sister of the sacred Ganga River.
- Due to its spiritual significance, the Urban Environmental Engineering Department (UEED) embarked on the Liquid Waste Management Project.
- This ambitious project entails the establishment of an interconnected system of pipes and manholes that will cover all households in the area under the Devika Rejuvenation Project.
Funding Allocation
The financial commitment for this endeavor amounts to Rs 190 crore. This funding is divided in a sharing ratio of 90:10 between the Central government and the Union Territory, respectively. Such allocation underscores the collaborative nature of this initiative between the two entities.
Insights into River Devika
Origin and Flow
- Emerging from the Suddha Mahadev temple in the hilly region of Udhampur, the Devika River is also known as Devika Nagari.
- Its course meanders through the terrain, eventually converging with the Ravi River as it reaches western Punjab, now located in Pakistan.
Religious Relevance
- The river has a great religious significance and is believed to have been created by Lord Shiva to wash away the sins of the people.
- Among Hindus, the Devika River enjoys a special place of reverence akin to the Ganga River. This spiritual connection has led to the endeavor of preserving its sanctity through comprehensive projects like the Devika Rejuvenation Project and the associated Liquid Waste Management Project.
Objectives of The Project
- To improve the water quality and quantity of the river by constructing sewage treatment plants, sewerage network, protection fencing and landscaping.
- To enhance the aesthetic and spiritual appeal of the river by developing cremation ghats, small hydropower plants and solar power plants.
- To conserve the biodiversity and ecology of the river by creating wetlands, fish ladders, riparian vegetation and aquatic habitats.
- To promote the socio-economic and cultural development of the region by creating recreational facilities, heritage sites, pilgrimage routes and livelihood opportunities.
Benefits
- Improvement in water quality and quantity of the river, which will reduce water-borne diseases, enhance groundwater recharge and support irrigation.
- Enhancement in aesthetic and spiritual appeal of the river, which will attract pilgrims, tourists and devotees from across the country and abroad.
- Conservation of biodiversity and ecology of the river, which will preserve the endemic flora and fauna, maintain ecological balance and mitigate climate change impacts.
- Promotion of socio-economic and cultural development of the region, which will generate employment opportunities, boost local economy, revive traditional practices and foster community participation.
Gnanamuyarchi

News: Discovery of 18th Century Palm Manuscripts titled “Gnanamuyarchi” in Northern Italian Armenian Monastery
Introduction
- Palm manuscripts dating back to the 18th Century with the title “Gnanamuyarchi” have been unearthed in an Armenian monastery situated in Northern Italy.
- These manuscripts have unveiled a significant historical find that sheds light on the past.
Scholar’s Access to Manuscripts
- A doctoral scholar affiliated with the Special Centre for Tamil Studies at Jawaharlal Nehru University (JNU) was granted access to these remarkable manuscripts.
- This access has facilitated the exploration of the content within and the insights it offers.
Possible Translation of Ignatius’ Spiritual Exercise
- A prominent professor specializing in the field has proposed the intriguing possibility that these manuscripts might contain a copy of the initial translation of Ignatius’ Spiritual Exercise into Tamil.
- This discovery could have profound implications for our understanding of the cultural and linguistic exchange during that era.
Attribution to Michele Bertoldi (Gnanaprakasasamy)
- Evidence suggests that this translation is potentially the work of Michele Bertoldi, known as Gnanaprakasasamy in Tamil.
- His involvement in this translation adds another layer of significance to these manuscripts, linking them to a known historical figure.
Prose Text from the Early 18th Century
- The content of the discovered manuscripts is identified as a prose text originating from the early 18th Century, with its likely creation timeframe estimated around the 1720s.
- Notably, this text was reprinted multiple times during the 19th Century by the Mission Press in Puducherry, indicating its enduring significance.
Misidentification and Unveiling of Tamil Origin
- Curiously, the library had initially categorized these manuscripts as “Indian Papyrus Lamulic Language–XIII Century.”
- Surprisingly, it was only through this recent discovery that the authorities realized the manuscripts were written in Tamil, shedding light on the misidentification that had persisted until now.
Speculations about Manuscript Transfer
- The individuals overseeing the monastery propose an intriguing hypothesis regarding the journey of the manuscripts.
- They speculate that the Armenians residing in Chennai might have been responsible for bringing these manuscripts to Italy.
- This speculation adds a layer of mystery to the origin and dissemination of these historically significant texts.
BharatNet Project

Context: Government Approved for ₹1.39 Lakh Crore BharatNet Project to Connect Villages
About BharatNet Project:
Objectives:
- Connecting 6.4 Lakh Villages with Last-Mile Broadband
- The BharatNet project aims to provide last-mile broadband connectivity to 6.4 lakh villages, encompassing all gram panchayats across India, using optical fiber technology.
Implementation: Executed by Bharat Broadband Network (BBNL)
- The responsibility for the project’s execution lies with Bharat Broadband Network (BBNL), a special purpose vehicle operating under Bharat Sanchar Nigam Limited (BSNL).
Tie-up with VLEs: Collaboration with Village Level Entrepreneurs (VLEs)
BBNL will partner with village level entrepreneurs (VLEs) for connectivity provision, building upon a successful pilot initiative in four districts that was later expanded to cover 60,000 villages.
Progress So Far: Current Status and Future Expectations
As of now, approximately 1.94 lakh villages have been connected, with plans to cover the remaining villages within the next 2.5 years.
Services Details:
- World’s Largest Rural Connectivity Scheme with Optical Fiber Network
- BharatNet is a groundbreaking rural connectivity scheme featuring a comprehensive optical fiber network.
- Gram Panchayat: Delivering 100 Mbps Broadband to 2.5 Lakh Gram Panchayats
- The scheme’s primary objective is to provide 100 Mbps broadband connectivity to 2.5 lakh gram panchayats.
- Households: Ensuring Affordable Broadband for Rural Households
- The project aims to offer affordable broadband ranging from 2 Mbps to 20 Mbps to all households, especially those in rural areas.

Key Achievements of the Project:
- Broadband Connections: Entrepreneurial Contribution to Villages
The initial pilot project engaged 3,800 entrepreneurs, resulting in 3.51 lakh broadband connections being established in villages.
- Data Consumption: Notable Data Usage in Connected Villages
Connected households in the villages displayed an average monthly data consumption of 175 gigabytes.
- Pricing and Speed: Revenue Sharing Model for Broadband Plans
The project operates on a revenue sharing model (50%) between BBNL and VLEs, offering broadband plans priced between ₹399 and ₹799 per month, featuring a minimum speed of 30 Mbps.
- Optical Fiber Laid: Extensive Optical Fiber Infrastructure
India currently boasts an optical fiber cable (OFC) network of 37 lakh route kilometers (rkm), with BBNL contributing 7.7 lakh rkm OFC to this network.
Indian Eagle Owl

Context:
The Indian eagle owl has recently been reclassified as a distinct species separate from the Eurasian eagle owl.
This species holds significance in the Indian Subcontinent’s ecosystems and cultures.
The Indian Eagle-Owl: Native Habitat and Appearance
- The Indian eagle-owl, also known as the rock eagle-owl, is a notable horned owl species found in the hilly and rocky scrub forests of the Indian Subcontinent.
- Its appearance is characterized by brown and grey colors, with a white throat patch adorned by small black stripes.
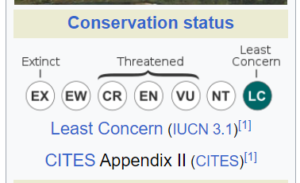
Conservation Status
The species has been categorized as “Least Concerned” by the IUCN and listed under Appendix II of CITES, indicating its relatively stable population and conservation status.
Distinctive Features of the Indian Eagle-Owl
- Separate Classification: Distinguished from the Eurasian eagle-owl, the Indian eagle-owl stands out due to its large size, with a length of up to two and a half feet and a wingspan reaching six feet.
- Nocturnal Behavior: The bird’s nocturnal habits have contributed to limited information about its behavior, enhancing its aura of mystery.
- Unique Appearance: The presence of prominent ear tufts resembling horns might have evolved as a defense mechanism against predators, giving the bird a menacing appearance.
Superstitions and Threats
In rural Indian communities, the Indian eagle-owl is associated with negative omens, and its distinctive double-hoot calls are linked to superstitious beliefs. Folklore suggests that the bird, when trapped and deprived of food, could mimic human speech, predicting the fate of those who listen.
Ecological Significance in Agricultural Landscapes
– Dietary Preferences: The Indian eagle owl’s diet mainly consists of rodents, including rats and bandicoots.
– Alignment with Habitat: Its preference for open scrublands and agricultural regions makes it a valuable asset for farmers by naturally controlling rodent populations.
– Positive Impact on Owlet Numbers: The presence of these owls near agricultural lands has shown a positive correlation with higher numbers of healthy owlets, owing to the abundance of rodent prey.
Conclusion
The reclassification of the Indian eagle owl as a separate species highlights its unique characteristics and ecological importance in the Indian Subcontinent.
Despite facing superstitious beliefs, this majestic bird plays a crucial role in maintaining the balance of local ecosystems and supporting agricultural productivity.
Perucetus Colossus Whale
Introduction
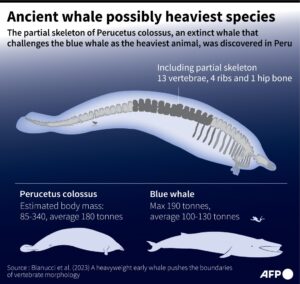
- In a significant paleontological discovery, scientists have uncovered fossils belonging to an ancient colossal whale species named Perucetus colossus in the Ica desert of Peru.
- This remarkable find sheds light on the potential existence of one of the largest and heaviest creatures to have ever lived.
The Enormous Perucetus Colossus Whale:
- The fossils of Perucetus colossus, estimated to have lived approximately 39 million years ago, were unearthed more than ten years ago in Peru’s Ica desert, renowned for its abundance of marine fossils.
- This astonishing discovery has offered a glimpse into the history and characteristics of this massive prehistoric whale.
Impressive Size and Unique Characteristics
- With each vertebra weighing over 100 kilograms and ribs measuring nearly 5 feet in length, the colossal proportions of the Perucetus colossus whale are evident.
- Despite its awe-inspiring size, the estimated length of this ancient giant was around 66 feet (20 meters), which, while impressive, is shorter than some modern blue whales that can grow over 100 feet long.
- The exceptional weight of Perucetus colossus is attributed to its dense and heavy bones. This weightiness likely resulted in its sluggish swimming capabilities, indicating a preference for shallow coastal waters as its habitat.
Exploring Feeding Habits and Ecological Niche
- While the fossils have revealed much about the physical characteristics of Perucetus colossus, certain aspects of its behavior and lifestyle remain shrouded in mystery due to the absence of its skull.
- Researchers speculate that this colossal creature may have scavenged the seafloor for sustenance or consumed substantial quantities of krill and other marine organisms.
- The precise details of its diet and feeding habits continue to intrigue scientists and warrant further investigation.
Unveiling Significance: Heavier than the Blue Whale
- If verified, the discovery of Perucetus colossus could potentially challenge the longstanding title of the blue whale as the heaviest known animal, whether living or extinct.
- This remarkable find highlights the incredible capacity of evolution to generate organisms with extraordinary characteristics that extend beyond the bounds of human imagination.
Unanswered Questions and Future Exploration
- The absence of remains such as the skull and teeth leaves pivotal questions surrounding the feeding behavior and ecological role of Perucetus colossus unanswered.
- The enigma surrounding these ancient giant piques the curiosity of paleontologists, driving them to delve deeper into its history and significance.

