1. PMLA Judgment Review
Background
- Supreme Court Judgment (July 2022): The Supreme Court upheld the constitutional validity of the Prevention of Money Laundering Act (PMLA), 2002, granting extensive powers to the Enforcement Directorate (ED) to arrest, summon individuals, and raid private property.
- Controversial Provisions: The judgment supported the “twin conditions” for bail under PMLA, which require the accused to prove their innocence and ensure they are not likely to commit any offense while on bail.
Key Issue: Whether the review petitions are an “appeal in disguise” against the Supreme Court’s final judgment
Key Points of Contention
- Basic Rights: Petitioners argue that the July 2022 judgment deprives accused persons of basic rights, including access to the Enforcement Case Information Report (ECIR)
- Burden of Proof: The judgment shifts the burden of proof of innocence onto the accused, contrary to the principle that the prosecution must prove guilt
- Bail Conditions: The “twin conditions” for bail make it extremely difficult for undertrials to secure bail, as they must prove their innocence without access to the ECIR
Legal Principles
- Review vs. Appeal: The Supreme Court emphasized that a review in open court should not take the tone of an appeal. Review and curative jurisdictions are rare and are entertained only in cases of apparent errors or biases in the verdict
- Judicial Scrutiny: The court will examine if the review petitions are essentially appeals against the final judgment, which is not permissible
Implications
- Judicial Precedent: The outcome of this review could set a significant precedent for the exercise of review jurisdiction by the Supreme Court.
- Rights of the Accused: A decision to amend or uphold the July 2022 judgment will impact the rights of individuals accused under the PMLA and the powers of the ED.
2. Guru Ghasidas-Tamor Pingla Tiger Reserve
CONTEXT:
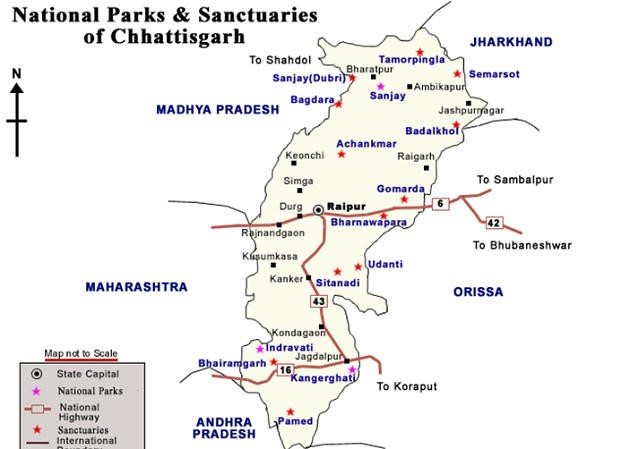
- New Tiger Reserve: Chhattisgarh has approved the creation of the Guru Ghasidas-Tamor Pingla Tiger Reserve, which will be the third largest in India.
- Location: The reserve spans 2,829.387 square kilometers across the districts of Koriya, Balrampur, Manendragarh-Chirmiri-Bharatpur, and Surajpur.
- Integration: It integrates the Guru Ghasidas National Park and the Tamor Pingla Sanctuary.
- High Court Directive: The Chhattisgarh High Court, while hearing a PIL, directed the state government to clarify its stance on declaring the area a tiger reserve
Reasons for Tiger Population Decline in Chhattisgarh (46 in 2014 to 17 in 2022)
- Scarcity of Food: Lack of prey species in the habitat
- Absence of Tigresses: Low number of breeding females.
- Poaching: Increased incidents of tiger hunting.
- Habitat Degradation: Human activities and biotic interference.
Importance and Benefits
| Challenges and Considerations
|
· Wildlife Conservation: The new reserve aims to strengthen wildlife conservation efforts, particularly for tigers | · Previous Opposition: The proposal faced opposition due to the presence of mines in the area, delaying its notification. |
· Eco-Tourism: The formation of the reserve is expected to boost eco-tourism and create employment opportunities for local villagers as guides, tourist vehicle operators, and resort managers | · Conservation Efforts: Effective management and protection measures are crucial to address the decline in tiger population, including habitat improvement, anti-poaching measures, and community involvement. |
· Economic Development: Additional funding from the National Project Tiger Authority will support new livelihood development projects in surrounding villages. |
|
Largest Tiger Reserves in India:
|
· Nagarjunasagar-Srisailam Tiger Reserve: Located in Andhra Pradesh, it is the largest tiger reserve in India, covering 3,296.31 square kilometers. · Manas Tiger Reserve: Located in Assam, it is the second largest, spanning 2,837.1 square kilometers. |
Historical Context
- Formation: Originally part of the Sanjay-Dubri National Park in Madhya Pradesh. After Chhattisgarh’s formation in 2000, the park was renamed Guru Ghasidas National Park.
- Tiger Reserve Status: Declared as the 53rd Tiger Reserve in India and the 4th in Chhattisgarh in 2021.
Flora and Fauna
- Flora: Predominantly tropical forests with species like Sal, bamboo, and mixed forests.
- Fauna: Home to various species including tigers, leopards, hyenas, jackals, wolves, sloth bears, barking deer, chinkara, and chital. It also serves as a corridor for tigers moving between Bandhavgarh (Madhya Pradesh) and Palamau (Jharkhand) Tiger Reserves.
3. Visa Facilitation for Chinese Technicians and Impact on Indian Manufacturing
CONTEXT: Introduction of the New Portal to streamline the approval process for short-term business visas for Chinese technicians.
- This initiative aims to support production units and enhance output under the Production Linked Incentive (PLI) scheme. The portal began functioning in early August 2024.
- Background and Rationale: Domestic industry faced delays in fulfilling export orders due to visa processing hold-ups for Chinese technicians, a situation that worsened after the Galwan clash in 2020.
- Industry Dependency on Chinese Technicians:
- Significant reliance on Chinese professionals due to their lower cost compared to technicians from Western or Southeast Asian countries.
- Engineering and electronic items constitute nearly 60% of India’s imports from China, critical for fulfilling export orders.
- Government Measures and Challenges:
- The Galwan clash in 2020 led to a series of measures to limit Chinese influence, including changes to the FDI policy under Press Note 3 (PN3).
- Since the introduction of PN3, India has approved only 25% of the total 435 foreign direct investment (FDI) applications from China.
- Economic Impact and Policy Recommendations:
- Despite the limitations, China remains a minor player in India’s FDI landscape, with a 0.43% share in total FDI equity inflows from April 2000 to December 2021.
- The Economic Survey suggests revisiting the stance towards Chinese investments to boost exports and integrate India into global supply chains.
- The “China-plus-one” strategy could benefit India by either connecting more with China’s supply chain or by promoting increased FDI from China.
- Strategic Choices for India:
- India faces a choice between deepening integration into China’s supply chain and focusing on attracting Chinese FDI to bolster its manufacturing sector and export capabilities.
- Encouraging FDI from China could help India mirror the success of East Asian economies in boosting exports to major markets like the US.
4. Pyrocumulonimbus Clouds
CONTEXT: The wildfires currently raging in the United States and Canada are so intense that they have created ‘pyrocumulonimbus’ clouds, which have the potential to spit out thunder and spark more fires. –
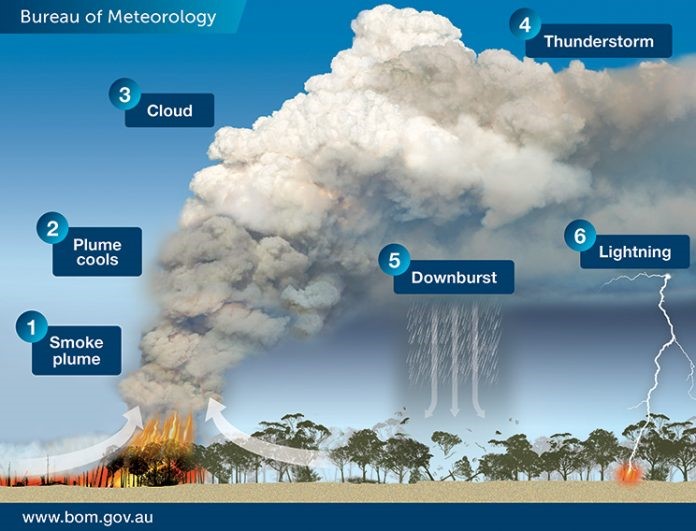
Pyrocumulonimbus Clouds: These are thunderstorm clouds formed by intense heat from the Earth’s surface, typically from large wildfires or volcanic eruptions.
Formation Process:
- Heat Source: Intense heat from wildfires or volcanic eruptions warms the surrounding air.
- Updraft: The hot, buoyant air rises, carrying water vapor, smoke, and ash into the atmosphere.
- Cooling and Condensation: As the air rises, it cools and expands. Water vapor condenses on ash particles, forming a grey or brown cloud known as a pyrocumulus cloud.
- Intensification: If there is sufficient water vapor and the updraft is strong, the pyrocumulus cloud can evolve into a pyrocumulonimbus cloud, reaching heights of up to 50,000 feet.
Characteristics
- Thunderstorms: These clouds can generate their own thunderstorms, producing lightning but not much rain.
- Fire Spread: Lightning from these clouds can spark new wildfires, and strong winds can make the spread of the wildfire faster and unpredictable.
Increasing Frequency
- Climate Change: The frequency of pyrocumulonimbus clouds has increased, likely due to climate change, which leads to more intense and frequent wildfires.
- Statistics: Before 2023, an average of 102 pyrocumulonimbus clouds were recorded globally each year. In 2023, 140 were recorded in Canada alone.
Implications
- Environmental Impact: These clouds can inject large amounts of smoke and ash into the stratosphere, affecting air quality and weather patterns.
- Wildfire Management: Understanding these clouds is crucial for predicting and managing wildfires, as they can exacerbate fire condition.