1. Gobekli Tepe and the Ancient Calendar Discovery
CONTEXT: An ancient calendar found in Turkey may have documented a 13,000-yr-old disaster
- Discovery and Significance
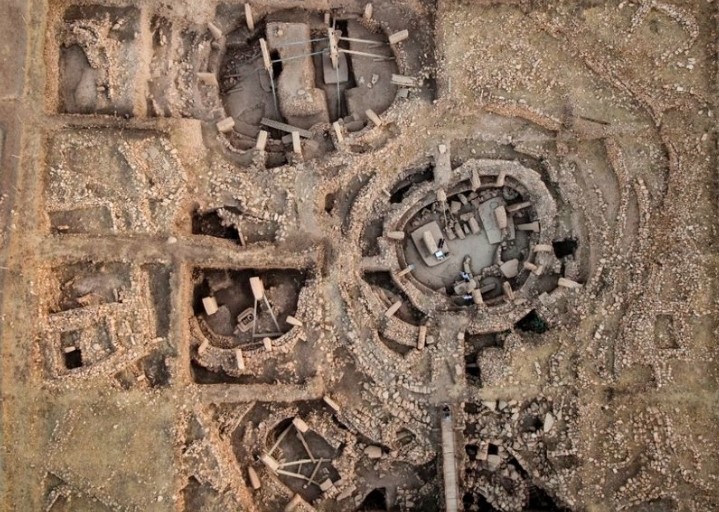
- Site: Gobekli Tepe, (an ancient archaeological site with temple-like enclosures) located in southern Turkey.
- Publication: Recent research published by Sweatman suggests that intricate carvings on the pillars at Gobekli Tepe represent an ancient lunisolar calendar. In 2017, Sweatman proposed that the carvings at Gobekli Tepe memorialized the comet impact and served as an astronomical observatory.
- Astronomical Event Documented
- Event: The calendar is believed to record a major comet strike that occurred approximately 13,000 years ago (around 10,850 BC).
- Impact: This comet strike is associated with ushering in a 1,200-year ice age and the extinction of many large animals. It also likely influenced significant changes in human lifestyle and agriculture, contributing to the rise of early civilizations.
- Scepticism: Some archaeologists, questioned the interpretation of the carvings as having a hidden or encoded meaning.
- Recent Research Insights
- Calendar Structure: The V-shaped symbols on the pillars were interpreted as markers of the lunar cycle, potentially representing individual days.
- Solar Calendar: The research posits that the markings depict a 365-day solar calendar, consisting of 12 lunar months plus 11 extra days, used for tracking time and marking seasons.
Summer Solstice: The final V symbol on the pillar is associated with the summer solstice constellation, depicted around the neck of a bird-like beast.
2. India's Retail Inflation Trends
CONTEXT: Retail inflation slips to 59-month low Record low.
- Recent Inflation Data
- July 2024: Retail inflation in India fell to 54%, the lowest level in nearly five years.
- June 2024: Retail inflation was 08%.
- Historical Context: July’s inflation rate is the lowest since September 2019 and is below the 4% median target set by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI).
- Inflation by Demographic
- Urban Consumers: Inflation dropped to just under 3% in July from 4.4% in June.
- Rural Consumers: Experienced higher inflation at 4.1% in July, down from 5.7% in June.
- Food Prices: Rural food inflation was 5.9% compared to 4.6% in urban areas. In June, rural food inflation was 9.15%, while urban food inflation was 9.6%.
- Sectoral Inflation Trends: Significant reductions in vegetable inflation, but persistent high inflation in pulses and cereals
- Vegetables: Significant decline in inflation to 6.8% in July from 29.3% in June.
- Personal Care and Effects: Inflation increased to 8.44% from 8.2% in June.
- Pulses: Inflation remained high at 14.77%, continuing for the 14th consecutive month.
- Meat, Fish, and Eggs: Recorded inflation rates of 6% and 6.8%, respectively.
- Cereals: Inflation remains above 8%, a concern for both the government and RBI.
- Regional Variations
- Higher than National Average: States such as Bihar (5.9%), Assam (5.1%), and Odisha (4.8%) recorded higher inflation rates.
- Lower than National Average: States like Jharkhand (1.7%), Delhi (2.1%), and Chhattisgarh (2.2%) experienced lower inflation rates.
- Implications and Future Outlook
- RBI’s Inflation Projection: The RBI has raised its inflation projection for the July to September quarter to 4.4%. This suggests that inflation may increase in the coming months.
- Vegetable Inflation Base Effect: The favourable base effect on vegetable inflation may only be temporary and might persist until August.
- Economic Analysis
Paras Jasrai’s Insights: The senior economic analyst highlighted that the decrease in vegetable inflation is temporary, and concerns remain about high inflation in cereals and pulses.
3. Impact of Monsoon on Food Inflation and Agriculture
- Monsoon and Rainfall Patterns
- June: 10.9% below average rainfall.
- July: 9% above average.
- August: 26% above average.
- Season Total (June-August): 6.3% above normal.
- Regional Deficiencies: Some areas still short, but irrigation helps.
- Impact on Agriculture
- Kharif Crops: Increased rainfall has led to higher sowing of key kharif crops such as paddy, pulses, maize, and oilseeds.
- Cotton: Acreage for cotton has decreased due to farmers switching to groundnut, maize, or paddy. Issues such as pink bollworm attacks and lack of new yield-protecting technologies are contributing factors.
- Water Resources: Improved monsoon has recharged groundwater tables and filled major reservoir dams to 64.7% of their full capacity, surpassing last year’s 60.8% and the 10-year average of 53.7%.
- Climate Forecast
- El Niño and La Niña: The transition from El Niño to a neutral phase has led to the current favorable monsoon conditions. Forecasts predict a La Niña development by September, which typically boosts rainfall and could positively impact the rabi cropping season.
- Previous Effects of El Niño: The last El Niño phase (April 2023 to May 2024) had suppressed monsoon and post-monsoon rains, contributing to delayed winter and higher-than-normal temperatures in certain regions.
- Food Inflation and Economic Impact
- Current Inflation Trends: Food inflation, which had been above 8% year-on-year since November 2023, dropped to 5.4% in July 2024. This decrease is attributed to the high base effect from last year’s inflation rate of 11.5% in July.
- Reserve Bank of India (RBI) Policy: The RBI has maintained its interest rates, considering the significant impact of food prices on inflation expectations among households and firms.
- Future Outlook and Policy Implications
- Bumper Harvest: A favorable monsoon and good harvest prospects are expected to ease food inflationary pressures. This could provide the government with an opportunity to lift export and stocking limits on cereals, sugar, and pulses.
Trade and Import Policies: The government might also keep the zero/low-duty import window open for major food commodities to manage supply and price stability.
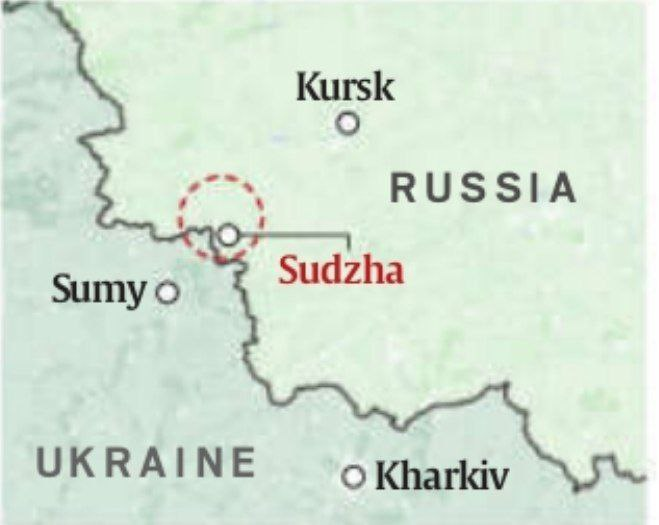
4. Ukrainian Incursion into Russia's Kursk Oblast: Overview
CPONTEXT: Ukrainian troops have penetrated about 30 km into Russia’s Kursk Oblast.
- Clashes: Fighting is ongoing near the villages of Tolpino and Obshchy Kolodez.
- Troop Involvement: The operation involves three Ukrainian brigades, totaling 6,000-8,000 troops.
- Russian Response: Around 76,000 people have been evacuated from the region, and a state of emergency has been declared.
Motivations
- Negotiating Leverage: Capturing land may strengthen Ukraine’s position for potential peace talks.
- Strategic Goals: Possible objectives include capturing the Kursk nuclear power plant or forcing Russian redeployment from the east.
- Retaliation: The attack might be a response to Russia’s seizure of Ukraine’s Zaporizhzhia nuclear plant.
Future Outlook
- Sustainability: It’s uncertain if Ukraine can hold the gained territory due to resource and troop requirements.
Expert Views: The move could either shift war momentum or complicate Ukraine’s eastern defensive efforts, according to military analysts.
6. Tungabhadra Dam Gate Incident: Key Points
CONTEXT: On August 10, 2024 one of the 33 crest gates of the Tungabhadra Dam was washed away due to a broken chain link.
Current Status
- Repairs: Can only begin after 60-65% of the reservoir water is discharged. New stop-lock gates are being fabricated and repair work is expected to complete within a week.
- Reservoir Levels: The dam was at full capacity (1,633 ft) with a current level of about 1,631 ft. Accumulated silt has reduced the original capacity by 30%.
Reasons and Implications
- Gate Failure: Old chain links used to operate the gates broke under pressure.
- Flood Alert: Issued for downstream areas due to potential flooding from increased outflows.
- Farmer Concerns: Upstream farmers worry about irrigation impacts, while downstream communities fear flooding and water shortages.
Historical and Strategic Context
- Construction: The dam, completed in 1953, was designed to mitigate recurrent famine impacts in
- Catchment Area: Tungabhadra River flows through Karnataka and Andhra Pradesh, covering a catchment area of 70,000 sq km and providing water for irrigation and industry.
Next Steps
- Expert Consultation: Ongoing to address the situation and complete repairs.
Flood Monitoring: Heavy rainfall could exacerbate the issue, but no significant rain is forecasted soon.
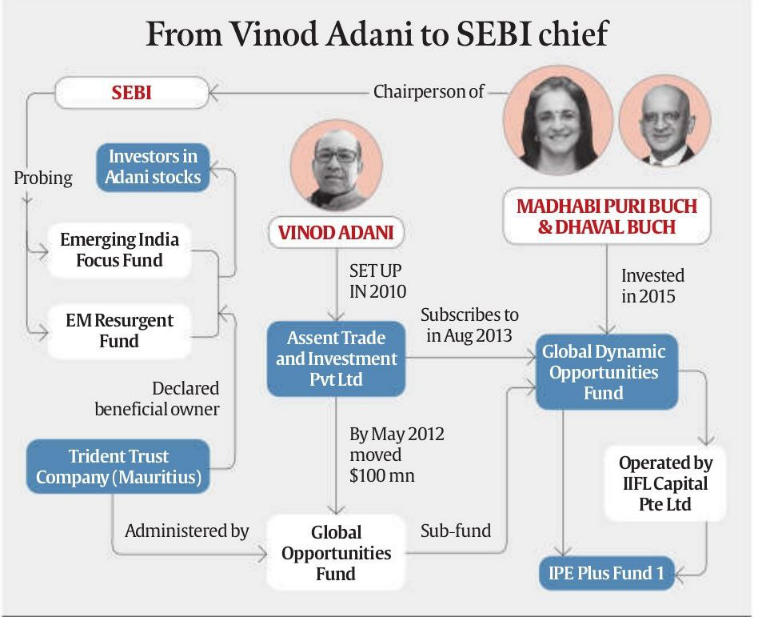
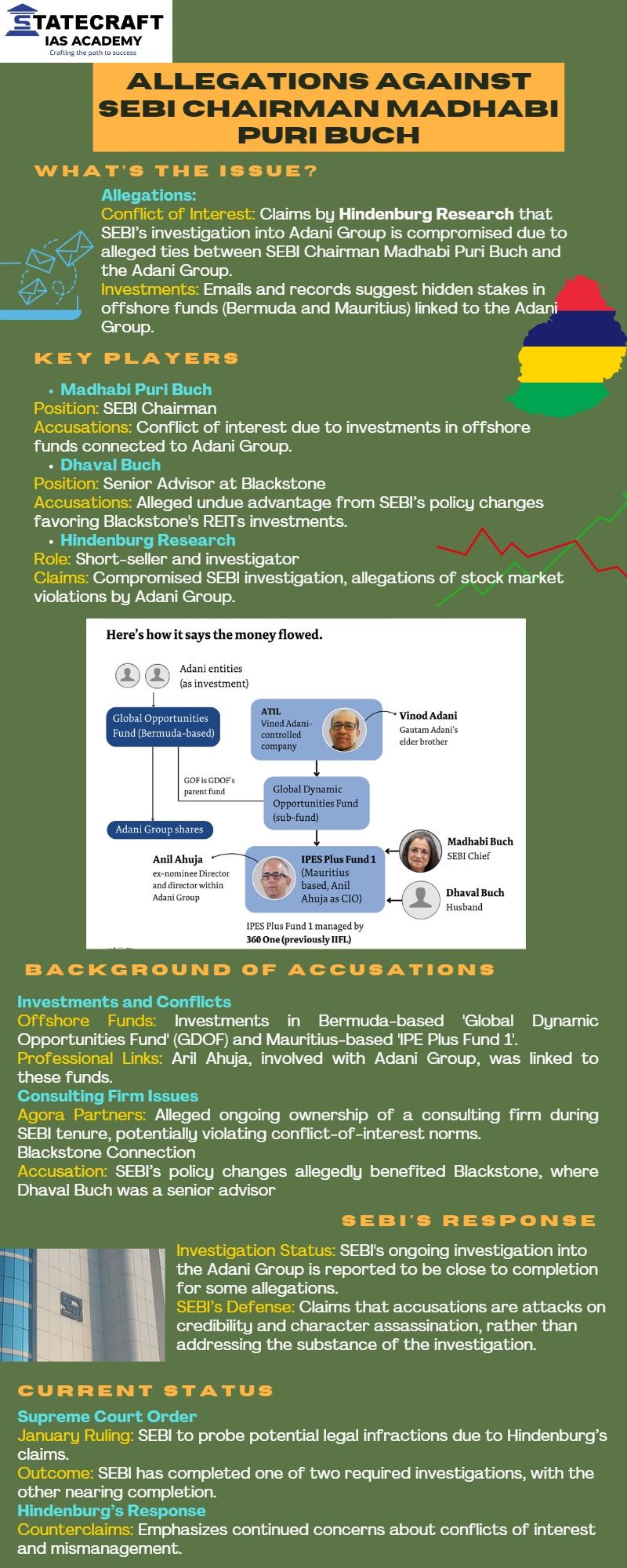
7. Hindenburg-Adani-Buch Saga: Key Points
Background
- Hindenburg’s January 2023 Report: Accused Adani Group of stock manipulation and accounting fraud. The report led to a dramatic fall in Adani’s stock prices and the cancellation of a major public offering.
- Regulatory Actions: The Supreme Court set up a committee to investigate potential regulatory failures and directed Sebi (Securities and Exchange Board of India) to probe violations by Adani Group. Sebi’s investigation is ongoing, with some progress reported.
Recent Allegations
- New Claims: Hindenburg Research has alleged that Sebi Chairperson Madhabi Puri Buch and her husband, Dhaval Buch, held stakes in offshore funds used in the Adani scandal. They claim these investments might explain Sebi’s alleged leniency towards Adani.
- Hindenburg’s Accusations: The firm suggests that the Buchs’ investments in these funds were made before Madhabi Puri Buch joined Sebi but were possibly used to avoid regulatory scrutiny.
Responses and Developments
- Sebi’s Defense: Sebi has defended Madhabi Puri Buch, asserting she has complied with disclosure requirements and recused herself from conflicts of interest.The regulator has conducted a thorough probe and advised investors to stay informed.
- Buchs’ Defense: Madhabi and Dhaval Buch deny the allegations, stating their investments were made before her Sebi tenure and were handled transparently.
Current Status
- Sebi’s Investigation: The regulator is finalizing its probe into the Adani case and has been actively seeking assistance from various agencies.
- Investor Advisory: Sebi has recommended that investors remain calm and exercise due diligence amid ongoing investigations and allegations.