Topics
- Havana Syndrome
- Delhi Service Bill 2023
- Pravasi Kaushal Vikas Yojana
- ECOWAS
- Vaquita Porpoise
- GSAT 24
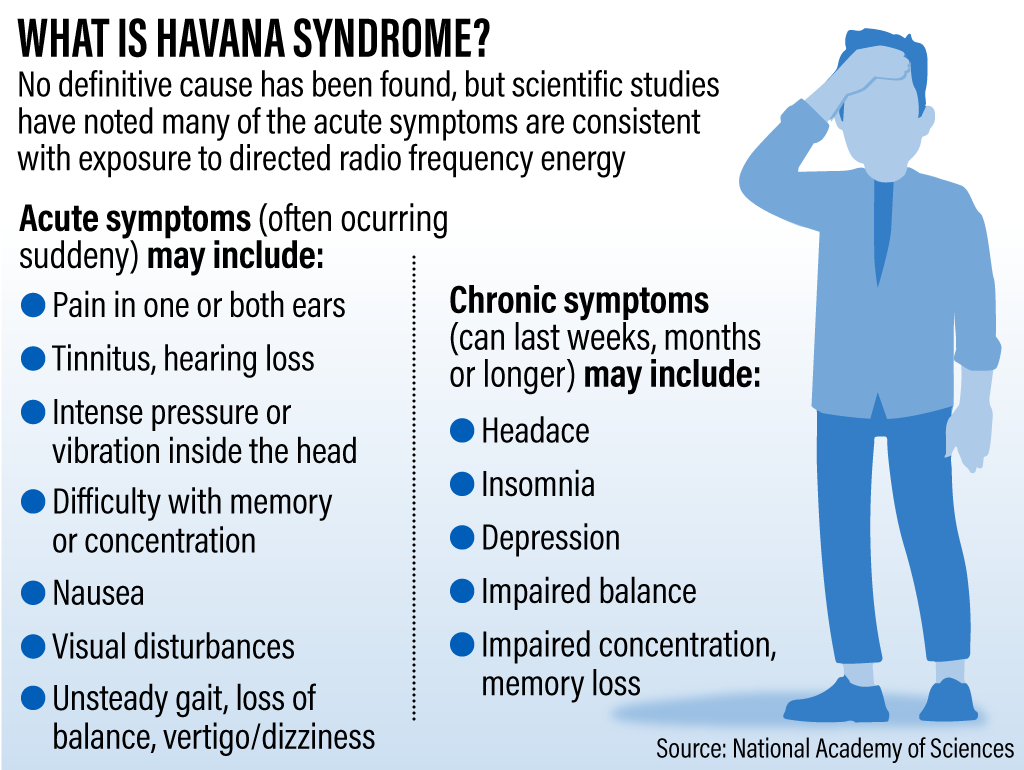
HAVANA SYNDROME
Context: Govt. to probe Havana Syndrome cases in India
Introduction
The emergence of Havana Syndrome has raised concerns among US intelligence and embassy personnel due to its perplexing mental health symptoms.
Understanding Havana Syndrome
Origins in Cuba: The term “Havana Syndrome” originated in 2016 within the newly established US embassy in Havana, where American officials reported brain pressure, headaches, and disorientation.
- Initial suspicions pointed to a “sonic attack” orchestrated by Cuban intelligence.
Expansion of the Phenomenon
Global Occurrence: Beyond Cuba, similar symptoms were observed among US officials stationed in China, Russia, Poland, Georgia, Taiwan, Colombia, Kyrgyzstan, Uzbekistan, Austria, and even near the White House in Washington DC.
Havana Syndrome’s Appearance in India
Singular Case: Up to July 2023, the lone reported instance of Havana Syndrome in India involved a US intelligence officer in 2021.
Indian Stance
Absence of Knowledge: Indian security authorities disclaim possessing microwave-based counter-espionage technology, raising doubt about their involvement.
Geopolitical Perspective: Given the favorable US-India relations, the likelihood of an Indian agency or foreign entity targeting US officials using such means seems implausible.
Potential Causes of Havana Syndrome
- Microwave Influence: Scientific investigations and medical evaluations have indicated that high-powered microwaves could have adversely affected the nervous system, leading to the reported symptoms.
- Microwave Weapon Theory: Speculation links the syndrome to beams of high-powered microwaves transmitted via a specialized device known as a “microwave weapon.”
- Historical Context: The use of microwaves for counter-intelligence by both Russia and the US since the Cold War adds to the theories.
Challenging the Havana Syndrome Hypothesis
Insufficient Proof: Despite prolonged data collection and experiments, concrete evidence supporting the existence of a “microwave weapon” remains elusive.
Psychological Amplification: Some medical experts posit that the syndrome might be a psychological ailment intensified by the fear of being targeted.
Impact on Relations
2023 Security Agency Report: The involvement of foreign adversaries in these “anomalous health incidents” was deemed unlikely, potentially affecting US-Cuba relations.
Conclusion
Continued Enigma: Havana Syndrome continues to perplex experts and policymakers globally, with its origins and causes still lacking definitive proof.
Ongoing Concerns: As India investigates this issue, the worldwide puzzle surrounding Havana Syndrome remains a persistent worry for intelligence communities and governments.
DELHI SERVICE BILL 2023
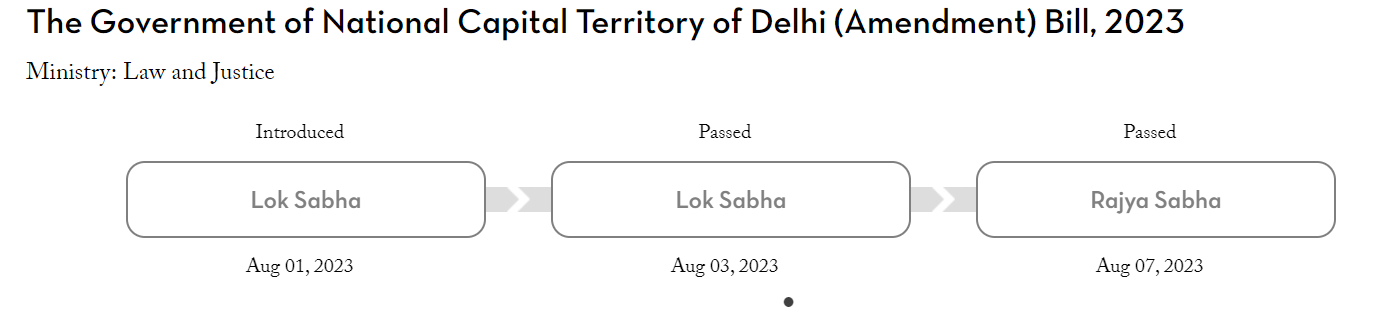
Context: The Rajya Sabha’s Approval of the Delhi Services Bill, 2023
The Rajya Sabha has granted its approval to the Government of National Capital Territory of Delhi (Amendment) Bill, 2023, just four days following its clearance by the Lok Sabha. The bill is poised to become law upon the President of India’s signature.
Delhi Services Bill, 2023: A Backgrounder
The Supreme Court’s Ruling and the Subsequent Ordinance
In May 2023, the Supreme Court ruled in favor of the Delhi government, granting it control over the majority of services in Delhi, excluding matters related to public order, land, and police cases. However, on May 19, the Centre introduced an ordinance to countermand the court’s decision, granting more power to the Lieutenant Governor (LG) concerning the appointment and transfer of bureaucrats.
Key Features of the Bill
Provisions and Changes Introduced by the Bill
- National Capital Civil Services Authority: The bill establishes the National Capital Civil Services Authority, responsible for advising the LG on specific service-related concerns, including transfers, vigilance, and disciplinary proceedings.
- Powers of the LG: The bill expands the LG’s discretionary authority, enabling the LG to override the recommendations of the Authority and act based on individual judgment in certain matters.
- Disposal of Matters by Ministers: The bill permits Delhi government ministers to issue standing orders for matter resolution, contingent on consultation with the respective Department Secretary. However, for specific sensitive issues, the LG’s opinion must be sought before issuing any orders.
- Duties of Secretaries: Department Secretaries are mandated to bring particular matters to the attention of the LG, Chief Minister, and Chief Secretary, especially those with the potential to create disputes with other state governments, courts, or the central government.
- Important Changes Related to Services:
- The bill eliminates a provision from the ordinance that restricted the Delhi Assembly’s authority to legislate regarding ‘State Public Services and State Public Service Commission.’
- This grants the assembly the ability to regulate services. The National Capital Civil Service Authority (NCCSA) will no longer be obligated to present an annual report to Parliament and the Delhi Assembly, freeing it from this reporting requirement.
- The bill also modifies the appointment cycle for chairpersons and members of various authorities, boards, commissions, and statutory bodies in Delhi.
- It removes the need for “orders/directions of ministers” in cases that must be sent to the central government before reaching the Lieutenant Governor and Chief Minister.
- Appointment of Delhi LG Powers:
- The bill empowers the Lieutenant Governor to choose members of the Delhi government’s Boards and Commissions from a list of names suggested by the NCCSA, including recommendations from the Delhi Chief Minister. These Boards and Commissions are established through regulations passed by the Delhi Assembly.
Constitutional Debate
Debates Surrounding the Bill’s Implications
- Violation of Triple Chain of Accountability: Critics contend that the bill might undermine the principle of parliamentary democracy by potentially granting the central government authority over Delhi’s services, thereby disrupting the three-way accountability between civil servants, ministers, and the electorate.
- LG’s Discretionary Powers: The bill extends the LG’s discretionary powers, enabling him to overrule the decisions of the Council of Ministers, which could obstruct the functioning of the democratically elected government.
- Unclear Terms: Certain terms in the bill, such as the “sole discretion” of the LG and the criteria for matters brought to his attention, are considered ambiguous and could lead to implementation confusion.
- Opposition’s Concerns: Opposition leaders strongly oppose the bill, asserting that it undermines democratic traditions, federalism, and the authority of an elected government.
Conclusion
The Delhi Services Bill, 2023, has emerged as a focal point of contention between the Delhi government and the central government.
While proponents argue that it clarifies power distribution, opponents contend that it might infringe upon parliamentary democracy and the constitutional separation of powers.
PRAVASI KAUSHAL VIKAS YOJANA
Introduction
- The Pravasi Kaushal Vikas Yojana (PKVY) is a pivotal skill development initiative designed to equip Indian youth aspiring for overseas employment with essential competencies.
- This scheme is overseen by the National Skill Development Corporation (NSDC), working in collaboration with the Ministry of External Affairs (MEA) and the Ministry of Skill Development and Entrepreneurship (MSDE).
Aims and Objectives
- PKVY operates with the overarching goal of positioning India as the global Skill Capital.
- By preparing and certifying Indian candidates for international employment, it addresses the demand for skilled workers in various sectors on the international stage.
Implementing Authorities
- PKVY’s execution involves multiple stakeholders, primarily the Ministry of External Affairs and the Ministry of Skill Development and Entrepreneurship.
- The National Skill Development Corporation (NSDC) plays a crucial role in the implementation process, partnering with training institutions and maintaining a close consultation with the mentioned ministries.
Key Program Features
- Under PKVY, individuals seeking overseas employment receive targeted training aligned with international standards.
- This training covers sectors with high demand in the global labor market.
- The program not only imparts necessary skills but also nurtures the confidence of Indian youth, ensuring they feel comfortable and capable when venturing into foreign vocational environments.
Fostering International Collaboration
- NSDC’s efforts are fortified by international collaboration facilitated through Memoranda of Understanding (MoUs) signed between 2011 and 2015.
- These agreements establish partnerships with various countries and agencies, including Germany, Canada, Australia, Singapore, the UK, the US, the European Union, France, Iran, and China. Such collaborations enrich the program’s scope and effectiveness.
By amalgamating the synergies of various governmental bodies, training institutions, and international alliances, the Pravasi Kaushal Vikas Yojana (PKVY) stands as a cornerstone initiative, nurturing skilled Indian youth for success on the global employment stage.
ECOWAS
Context: West African Leaders Discuss Niger’s Situation After Defiance by Junta
- West African leaders are engaged in discussions concerning the situation in Niger after the military junta, which took control on July 26, refused to comply with a deadline to reinstate the deposed president.
- The junta faces the possibility of military intervention if they fail to comply.
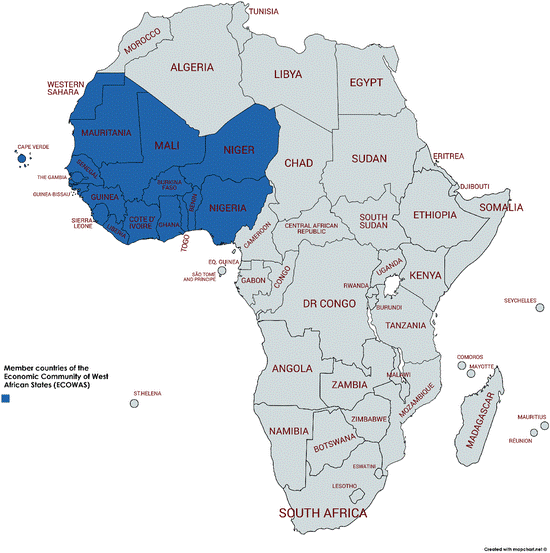
Economic Community of West African States (ECOWAS)
- The Economic Community of West African States (ECOWAS) is at the center of these discussions.
- ECOWAS has a history of intervening in member states facing internal turmoil, and it directed the junta to step down.
- However, the coup leaders responded by closing Niger’s airspace and vowing to protect the country.
Overview of ECOWAS
- About: ECOWAS is a regional political and economic union consisting of fifteen countries situated in West Africa.
- Origin: The union was established on May 28, 1975, through the signing of the Treaty of Lagos. A revised version of this treaty was agreed upon and signed in Cotonou on July 24, 1993.
- Mission: ECOWAS’s primary mission is to advance economic integration within the region.
- Objectives: ECOWAS is a fundamental regional entity within the broader African Economic Community (AEC). It aspires to achieve “collective self-sufficiency” for its member states by constructing a single, substantial trade bloc. This goal involves establishing a comprehensive economic and trading union.
Peacekeeping Role: Apart from its economic objectives, ECOWAS also functions as a peacekeeping force in the region. Member states periodically coordinate joint military interventions to address political instability and unrest within the bloc’s member countries.
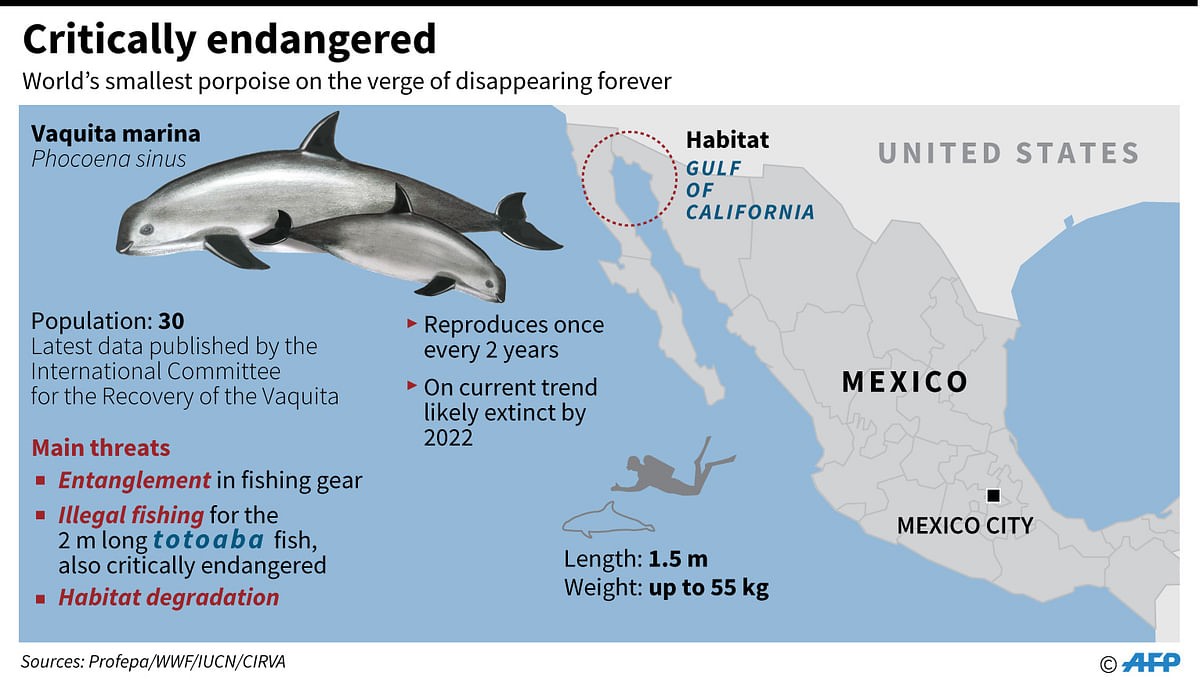
VAQUITA PORPOISE
Context: Extinction Alert for Vaquita Porpoise: A Critical Situation
Introduction:
- The International Whaling Commission (IWC) has recently sounded an ‘extinction alert’ for the vaquita porpoise, a highly endangered marine mammal.
- This alert draws attention to the fact that there are now only 10 surviving individuals of this species in the Gulf of California, also known as the Sea of Cortez, situated in Mexico.
Habitat and Drastic Population Decline
- The vaquita porpoise’s habitat is confined to the northernmost region of the Gulf of California, Mexico.
- A stark decline in their numbers has been observed: from an estimated population of approximately 570 in 1997, the vaquita population has dwindled to a mere 10 animals by 2018.
Key Characteristics of the Vaquita Porpoise
- The vaquita porpoise holds the distinction of being the world’s smallest cetacean and is critically endangered.
- Its habitat range is exceptionally limited, residing within a compact area of 1,500 square miles in the upper Gulf of California, near San Felipe, Mexico.
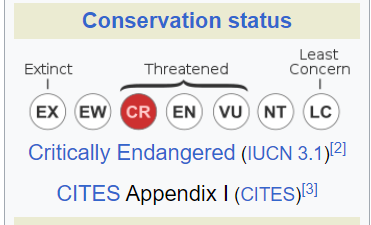
Conservation Status and Precarious Threats
- The vaquita porpoise has been assigned a critically endangered status by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN).
- The primary threat responsible for the drastic decline in vaquita population is bycatch. This occurs when these porpoises unintentionally become caught in gillnets that are set up to catch shrimp and fish, including the totoaba.
- The totoaba, a sizeable and endangered fish species, is targeted due to its high demand in illegal international markets.
It’s crucial to note that the totoaba is also granted protection under Appendix I of the Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora (CITES).
GSAT 24
- GSAT 24 is a communication satellite built by Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) for NewSpace India Limited (NSIL).
- It was launched on June 23, 2022 from the Satish Dhawan Space Centre in Sriharikota, Andhra Pradesh.
- It is a 4-tonne class satellite with 24 Ku-band transponders that provide pan-India coverage for meeting direct-to-home (DTH) application needs.
- It is the first demand driven communication satellite mission undertaken by NSIL after the space sector reforms in India.
- It has been leased to Tata Play, a leading DTH service provider in India, for its entire operational life.
Benefits of GSAT 24
- GSAT 24 will enable Tata Play to provide its users with an even sharper picture and sound quality, and an ability to carry 50 per cent more channels.
- Tata Play will be able to transmit up to 900 channels using the GSAT 24 satellite, which makes it the largest satellite bandwidth provider among all DTH platforms in India.
- GSAT 24 will also ensure that Tata Play’s services are available across the country, including the hilly regions of North-East and Andaman & Nicobar islands1.
- GSAT 24 will boost India’s self-reliance and indigenous capabilities in the field of space and communication.
GSAT 24 will also open up new opportunities for NSIL and ISRO to collaborate with private players in the space sector and offer customized satellite solutions.