NEW BILL TO ADDRESS SUPREME COURT RULING ON CEC AND ECS APPOINTMENT
Context
- A recent development in the Rajya Sabha involves the introduction of a new Bill designed to counteract the effects of a Supreme Court decision concerning the appointment of the Chief Election Commissioner (CEC) and Election Commissioners (ECs).
- This legislation proposes a restructured selection process, featuring a committee consisting of the Prime Minister, Leader of Opposition in the Lok Sabha, and a designated Cabinet Minister.
- The objective of this initiative is to respond to a Supreme Court verdict that demanded the involvement of these key political figures in the appointment process.
Supreme Court’s Verdict and Legislative Gap
- On March 2, a unanimous ruling by a Supreme Court bench this year mandated the inclusion of the Prime Minister, Leader of Opposition, and Chief Justice of India (CJI) in the process of appointing CEC and ECs.
- This intervention by the Court was prompted by the absence of a parliamentary law, as stipulated by Article 324 of the Constitution, to guide the appointment procedure.
Revamped Legislative Approach
- The proposed Bill has a twofold aim: to rectify the constitutional void and to establish a systematic legislative framework for selecting members of the Election Commission of India (ECI).
- Search Committee: The Bill proposes the establishment of a Search Committee, led by the Cabinet Secretary and comprised of two other government officials with expertise in election matters. This committee’s responsibility is to compile a list of five potential candidates suitable for appointment.
- Selection Committee: At the heart of this new process is the Selection Committee, which comprises the Prime Minister, the Leader of the Opposition in the Lok Sabha, and a Cabinet Minister chosen by the Prime Minister. This committee is entrusted with finalizing the appointment of CEC and ECs.
Addressing Supreme Court’s Concerns
The Supreme Court’s concerns are two-fold:
- Parliamentary Authority: The Parliament holds the authority to address the issues highlighted by the Supreme Court’s ruling and to neutralize its impact through legislative measures that align with the intent of the judgment.
- Preserving Independence: The Supreme Court’s verdict underlines the importance of an independent body overseeing elections, in harmony with the original intent of the Constitution.
Raised Concerns
- Composition of Selection Committee: The composition of the Selection Committee raises apprehensions about the impartiality of the selection process.
- Leader of Opposition’s Absence: Given that the Prime Minister and a designated Cabinet Minister hold the majority in the three-member panel, the Leader of the Opposition’s influence is diminished even before the process commences.
- Exclusion of CJI: The Bill excludes the Chief Justice of India from the panel, contrasting the Supreme Court’s March 2 ruling that led to the formulation of this legislation.
Conclusion:
The proposed Bill represents a significant effort to fill the legislative void created by the Supreme Court’s decision, aiming to streamline the appointment process for the Election Commission.
While the Parliament has the authority to shape this process, the critical concern remains the genuine independence and credibility of the selection procedure.
It is imperative to maintain a delicate equilibrium among various stakeholders to uphold the integrity of India’s democratic electoral mechanisms.
HELA CELLS: THE REMARKABLE IMPACT OF HELA CELLS ON SCIENTIFIC PROGRESS
Introduction: What are HeLa Cells?
In 1951, Henrietta Lacks, diagnosed with cervical cancer, underwent a tissue biopsy at Johns Hopkins Hospital, leading to the discovery of an exceptional line of human cells.
Unveiling the Unknown: Pioneering Phenomenon
A fraction of Henrietta Lacks’ tumor cells, termed HeLa cells, exhibited an extraordinary ability to perpetually divide and multiply under laboratory conditions.
Distinctive Attributes of HeLa Cells
- Endless Proliferation: In contrast to regular human cells with finite lifespans, HeLa cells showcased continuous division, allowing for perpetual growth.
- Scientific Marvel: This unique property revolutionized research by providing a consistent and adaptable platform for various experiments.
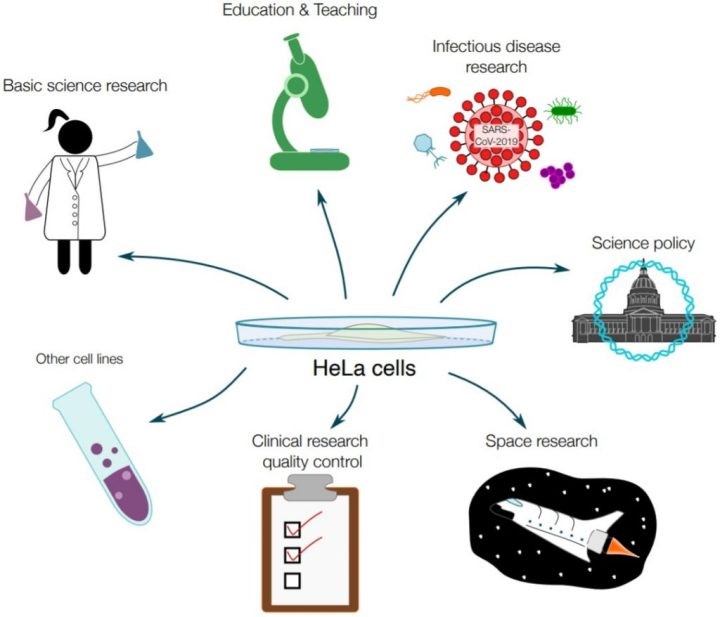
Utility for Scientific Progress
- Polio Vaccine: HeLa cells played a pivotal role in cultivating the poliovirus, facilitating the development of the polio vaccine.
- Cancer Research: HeLa cells contributed insights into cancer biology, aiding in treatment testing and comprehension of disease mechanisms.
- Genetic Insights: These cells marked the first successful human cell cloning, deepening our understanding of genetics and cellular biology.
- Drug Testing: HeLa cells transformed drug testing, aiding in drug development and safety profile assessment.
- Space Exploration: The cells’ significance extended to space exploration, enhancing our understanding of cellular behavior in microgravity.
Ethical Dilemmas and Controversies
- Informed Consent Absence: Ethical concerns arose due to the use of HeLa cells without Henrietta Lacks’ consent, especially in the context of medical experimentation on African American patients.
Patient Rights and Acknowledgment: Discussions emerged regarding patient rights, fair compensation, and the recognition of individuals whose contributions underpin scientific advancement.
PANCHAYAT DEVELOPMENT INDEX
Context:
- The Ministry of Panchayati Raj is organizing a significant event, the Two-Days National Writeshop on Panchayat Development Index Portal.
- This event is scheduled to take place from August 10th to 11th, 2023, at the esteemed Dr. Ambedkar International Centre in New Delhi.
- The main purpose of this event is to focus on the creation of a Baseline Report and the computation of the Panchayat Development Index, both of which hold crucial importance in the domain of local development and progress.
Emphasizing the Importance of the Baseline Report
- The central aim of the Two-Days National Writeshop is to highlight the significance of the Baseline Report.
- This report acts as a foundational reference point for local actions that are designed to be measured along specific dimensions.
- These actions are vital in the pursuit of achieving local targets that align with the broader objective of realizing the Sustainable Development Goals, particularly in the context of rural areas.
Panchayat Development Index (PDI)
- The Panchayat Development Index (PDI) is a novel initiative introduced by the Ministry of Panchayati Raj.
- Its primary objective is to evaluate the progress of local development through the rural self-government institutions known as panchayats in India.
- The PDI is underpinned by the concept of Localization of Sustainable Development Goals (LSDGs).
- This concept aims to harmonize national and global development objectives with the distinct local context and priorities.
A Comprehensive Statistical Tool
- The PDI is meticulously designed to function as a concise and all-encompassing statistical tool.
- This tool serves to capture a wide array of developmental aspects at the level of individual panchayats.
- In pursuit of this comprehensive assessment, the PDI encompasses nine fundamental themes that collectively embody the vision of an ideal village:
- Poverty-free
- Healthy
- Child-friendly
- Water-sufficient
- Clean and green
- Self-sufficient
- Socially just and secure
- Well-governed
- Women-friendly
Incorporating Multiple Dimensions of Development
- Within each of these themes, the PDI takes into careful consideration the diverse dimensions of development.
- This includes evaluating the inputs, outputs, and outcomes of various developmental interventions.
By holistically assessing these elements, the PDI provides a nuanced understanding of the progress made in each theme, contributing to a more comprehensive picture of local development.
National Social Assistance Programme
Context:
- An audit conducted by the Comptroller and Auditor General of India (CAG) has exposed irregularities in the disbursement of funds within the Ministry of Rural Development’s National Social Assistance Programme (NSAP) between 2017 and 2021.
- The audit highlights that approximately Rs 79 crore was mistakenly allocated to ineligible recipients during this period.
Flaws in Beneficiary Payments
- The CAG report points out several issues related to beneficiary payments, with a prominent concern being the absence of a comprehensive database of qualified beneficiaries in all states except Haryana and Kerala.
- This significant oversight resulted in eligible recipients being excluded from the program, while substantial sums were disbursed to individuals who did not meet the eligibility criteria.
National Social Assistance Programme: An Overview
- The National Social Assistance Programme (NSAP), initiated on August 15, 1995, operates under the Ministry of Rural Development. Its establishment aligns with the Constitutional Directive Principles outlined in Articles 41 and 42.
These articles underscore the shared responsibility of both Central and State Governments in providing aid to citizens facing unemployment, old age, sickness, disability, and other forms of distress, within the financial limitations and developmental capabilities.
Component Schemes of NSAP
At present, the NSAP comprises five distinct schemes:
- Indira Gandhi National Old Age Pension Scheme (IGNOAPS),
- Indira Gandhi National Widow Pension Scheme (IGNWPS),
- Indira Gandhi National Disability Pension Scheme (IGNDPS),
- National Family Benefit Scheme NFBS) and
- Annapurna
These schemes collectively aim to provide crucial financial support to marginalized segments of society, yet the recent audit underscores the necessity for stringent oversight and proper beneficiary tracking to ensure the effective and targeted disbursement of funds.
Integration of NavIC with Aadhaar Enrolment Devices to Enhance Services
Context
The integration of India’s Navigation with Indian Constellation (NavIC) into Aadhaar enrolment devices represents a strategic move by the Department of Space (DoS) to enhance essential services through the fusion of advanced technologies.
Historical Background: Initially conceived as the Indian Regional Navigation Satellite System (IRNSS), NavIC aimed to establish an autonomous navigation infrastructure to cater to both civilian and strategic needs.
Reducing Foreign Reliance: NavIC’s primary objective was to reduce reliance on foreign navigation systems like GPS and establish an independent and self-sufficient platform.
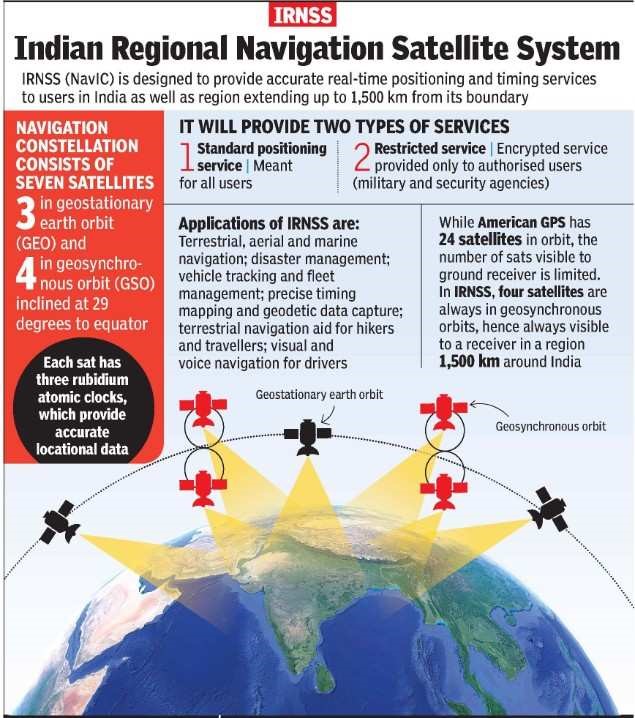
Comprehensive Satellite Constellation: NavIC boasts a constellation of 7 satellites strategically positioned.
Chronology of Deployment: The deployment of satellites such as IRNSS-1A, IRNSS-1B, IRNSS-1C, IRNSS-1D, IRNSS-1E, IRNSS-1F, and IRNSS-1I began in July 2013, marking a phased deployment approach.
Key Features and Technical Advancements
- Service Differentiation: NavIC offers two distinct services – the Standard Position Service (SPS) for civilian users and the Restricted Service (RS) for strategic applications. These services operate in both L5 (1176.45 MHz) and S band (2498.028 MHz).
- Coverage Extent: NavIC covers India and extends up to 1,500 km beyond its borders. Upcoming satellites will introduce the L1 band, compatible with civilian applications.
Integration of NavIC and Aadhaar Enrolment Devices
Field Trials and Expert Input: Successful field trials conducted by the DoS have contributed valuable technical insights, leading to the finalization of procurement specifications for the integration of NavIC into Aadhaar enrolment devices.
Current Usage: Presently, GPS is utilized in Aadhaar enrolment kits for location-based services, enabling the collection and verification of personal data during enrolment.
Diverse Applications
- Disaster Management: NavIC assumes a critical role in the National Disaster Management Agency’s system for disseminating alerts during natural disasters such as earthquakes, floods, landslides, and avalanches.
- Ocean Information Dissemination: The Indian National Centre for Ocean Information System employs NavIC to broadcast alerts about cyclones, high waves, and tsunamis to deep-sea fishermen.
Standardization Initiatives: Several organizations, including the Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS), Telecom Standards Development Society of India (TSDSI), Telecom Engineering Centre (TEC), and international bodies like the International Electrotechnical Committee (IEC), are actively engaged in establishing interoperability standards for NavIC.
IMPACT OF EL NINO SOUTHERN OSCILLATION (ENSO) ON DIFFERENT REGIONS OF INDIA
Context:
A recent research paper published in August 2023 in the journal Nature Scientific Reports has highlighted the varying impact of the El Nino Southern Oscillation (ENSO) on different parts of India.
The northern regions experience a more significant impact, while the central parts have a lesser impact, and the southern areas have consistently experienced a certain level of impact.
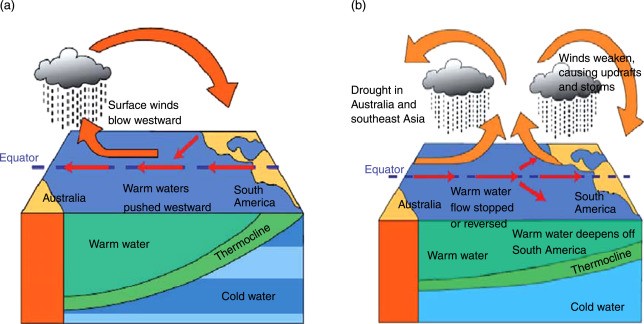
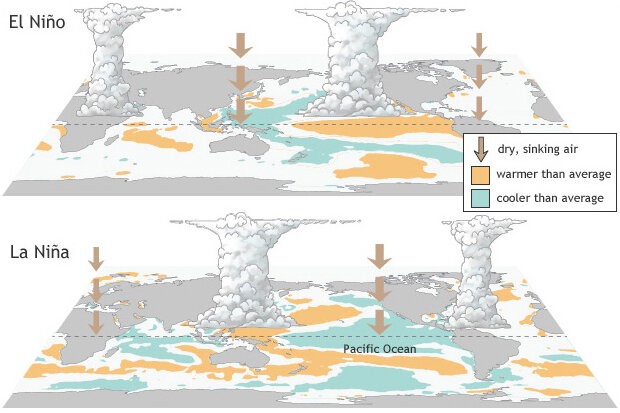
- El Nino, named after the warm ocean surface waters along the coast of Ecuador and Peru, refers to the periodic development of these warm waters.
- The occurrence of El Nino events is irregular, with intervals ranging from 2 to 7 years, averaging around once every 3-4 years.
- After an El Nino event, weather conditions typically return to normal, but in some instances, unusually strong trade winds can lead to the accumulation of cold water in the central and eastern Pacific, resulting in a phenomenon known as La Niña.
Global Impact of El Nino on Oceanic and Atmospheric Conditions
- El Nino exerts its influence on various aspects, including ocean temperatures, ocean currents’ speed and strength, coastal fisheries’ health, and local weather patterns, spanning regions from Australia to South America and beyond.
Notably, South America experiences a substantial increase in rainfall during El Nino events, which can contribute to coastal flooding and erosion.
El Nino’s Influence on Indian Monsoon Rainfall
- The relationship between El Nino and Indian monsoons is characterized by an inverse correlation.
- Historical data reveals that some of the most notable droughts in India, including significant instances like those in 2002 and 2009, have been associated with El Nino events.
- However, it’s important to note that not all El Nino years result in droughts in India.
- For instance, the strong El Nino year of 1997/98 did not lead to a drought due to the influence of the Indian Ocean Dipole (IOD).
Diverse Effects of El Nino on Indian Agriculture
- The impact of El Nino on India’s agrarian economy is significant.
- The phenomenon tends to suppress the production of crucial summer crops like rice, sugarcane, cotton, and oilseeds.
- While a moderate El Nino event in 2002 resulted in one of the worst droughts, the relationship between El Nino and drought is complex and can be influenced by other climatic factors such as the IOD.
Conclusion,
The recent research paper sheds light on the multifaceted influence of the El Nino Southern Oscillation on India, highlighting its varying impacts across different regions and its intricate interplay with monsoon patterns and agricultural productivity.