1. Prospects for the Rabi Crop
Current Sowing Status:
- Wheat: Sown on 41.3 lakh hectares (lower than 48.87 lakh hectares in 2023).
- Mustard: Reduced acreage at 75.86 lakh hectares (80.6 lakh hectares in 2023).
- Other Crops: Delays in sowing potato, mustard, chana, garlic, and fennel due to late monsoon withdrawal and high October temperatures.
Fertilizer Supply:
- Stock Levels (October 2024):
- Urea: Adequate at 6,816 lakh tonnes.
- DAP: Shortage with 3,114 lakh tonnes available.
- Farmers faced delays in alternatives like SSP.
- Challenges:
- Logistics issues caused delays in delivery.
- Need to ensure a balanced nutrient mix for crops.
Positive Factors:
- Water Availability: Reservoirs report sufficient storage for irrigation.
- Weather: An extended winter due to La Niña is expected to boost wheat and mustard yields by preventing early March heat.
- Government Measures: Emphasis on stock replenishment and advisory for timely sowing.
Food Inflation Trends:
- October Inflation:
- Food inflation at 10.89% year-on-year.
- Pulses, vegetables (potato, carrot), and onions witnessed price moderation due to new arrivals.
Crop-Specific Concerns:
- Wheat: Delay in sowing could risk yields if March temperatures rise prematurely.
- Edible Oils: Lower mustard sowing acreage could impact oilseed availability.
Market Observations:
- Onion prices moderated from ₹5,500/quintal to ₹3,700/quintal in November.
Efforts are needed to address supply chain disruptions and ensure stable prices for critical crops.
2. Supreme Court relaxed emergency anti-pollution restrictions
CONTEXT: The Supreme Court on Thursday relaxed emergency anti-pollution restrictions under stage four of the Graded Response Action Plan (GRAP-IV) to the less rigorous GRAP-II level in the National Capital Region (NCR).
But a Bench of Justices A.S. Oka and Augustine George Masih asked the Commission for Air Quality Management in NCR and Adjoining Areas (CAQM) to keep its guard up while emphasising that GRAP-III must kick in if the air quality index (AQI) deteriorated to 350 and to restore GRAP-IV in case the toxicity crossed 400 in the coming winter days. In fact, the court suggested a hybrid system incorporating GRAP-III along with the GRAP-II precautions.
The decision of the apex court to relax GRAP levels was based on submissions made by the CAQM, represented by Additional Solicitor General Aishwarya Bhati, that AQI levels had improved below the 300 mark since November 30 owing to several meteorological conditions.
Graded Response Action Plan (GRAP):
- GRAP is a framework designed to combat air pollution in the Delhi-NCR region. It was introduced as an emergency response mechanism, and its implementation is triggered when the Air Quality Index (AQI) reaches “poor” levels.
- GRAP is particularly important during the winter months when air quality tends to plummet.
Who implements GRAP?
- The Commission for Air Quality Management (CAQM) in NCR and adjoining areas oversees the implementation of GRAP.
- It collaborates with the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change (MoEFCC). The CAQM has constituted a sub-committee for the operationalization of the GRAP. This body includes officials from the CAQM, member secretaries of pollution control boards of Uttar Pradesh, Delhi, Haryana, Rajasthan, the Central Pollution Control Board, a scientist from the IMD, one from the IITM, and a Health Advisor.
- The sub-committee is required to meet frequently to issue orders to invoke the GRAP.
Commission for Air Quality Management (CAQM):
- The CAQM is a statutory body established under the Commission for Air Quality Management in National Capital Region (NCR) and Adjoining Areas, Act 2021.
- Mandate: Better coordination, research, identification, and resolution of problems surrounding the air quality index and for matters connected therewith or incidental thereto.
- It undertakes action for the prevention and control of Air pollution in Delhi-NCR & Adjoining Areas which impacts the air quality of the National Capital Territory (NCT) of Delhi.
- The Commission is required to coordinate its actions on monitoring of air quality with the government of Delhi and the adjoining states, which includes Punjab, Haryana, Rajasthan, and Uttar Pradesh.
- AQI was launched in October 2014 to disseminate information on air quality in an easily understandable form for the general public.
- AQI has been developed for eight pollutants PM2.5, PM10, Ammonia, Lead, nitrogen oxides, sulphur dioxide, ozone, and carbon monoxide.
PRELIMS PYQ
- In the cities of our country, which among the following atmospheric gases are normally considered in calculating the value of Air Quality Index? (2016)
- Carbon dioxide
- Carbon monoxide
- Nitrogen dioxide
- Sulphur dioxide
- Methane
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1, 2 and 3 only
(b) 2, 3 and 4 only
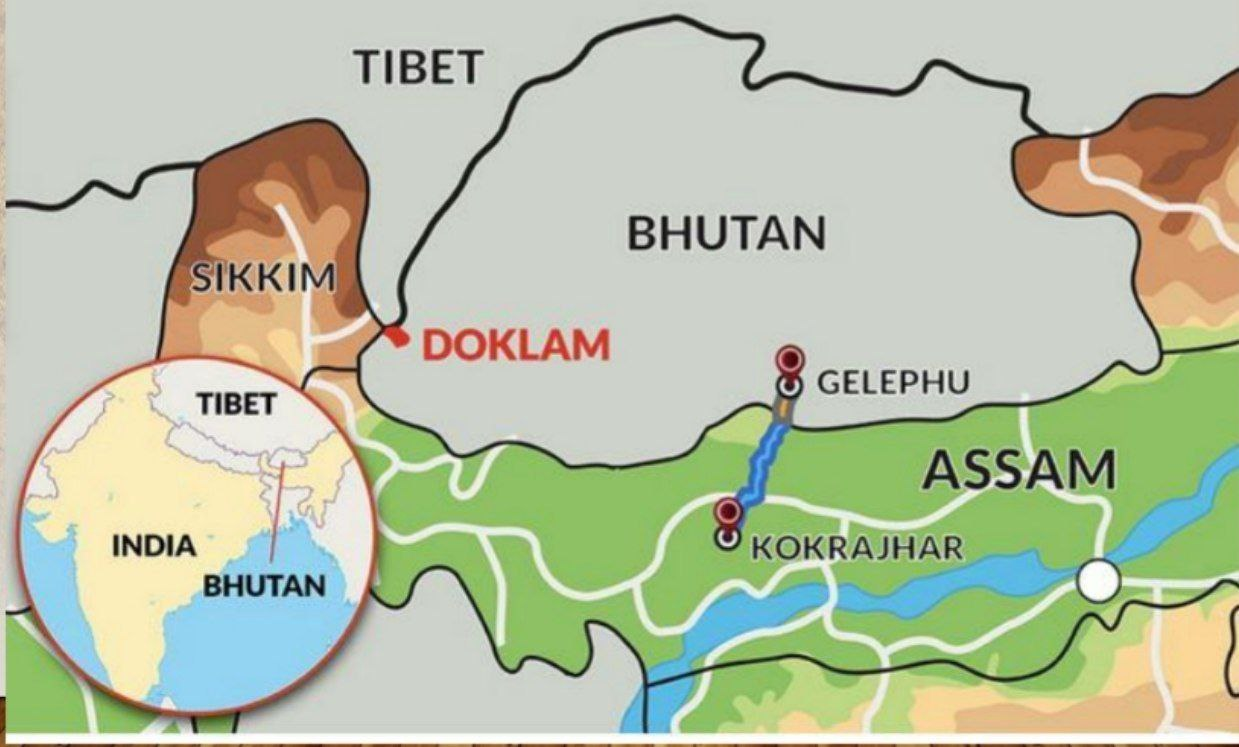
4. India and Bhutan discussed bilateral hydel power projects
CONTEXT: India and Bhutan on Thursday discussed bilateral projects in the fields of electricity and urban planning during the visit of the King Jigme Khesar Namgyal Wangchuk and Queen Jetsun Pema.
Mr. Wangchuk met Prime Minister Narendra Modi and both sides reiterated continued collaboration on multiple fronts including in the Gelephu Mindfulness City project and hydropower.
The two sides on Thursday also discussed the hydel power projects including the 1020-MW Punatsangchhu-ll hydro power project and expressed satisfaction as it was “nearing completion”.
- Both sides also discussed cross-border connectivity projects including a rail line as well as digital networks.
- India’s commitment for the Gelephu project while hosting the Bhutanese King is significant as it comes against the backdrop of diplomatic setbacks that South Block has faced in the neighbourhood, especially in Dhaka where India’s ties with the interim government of Bangladesh has failed to stabilise since the fall of the Sheikh Hasina government in August.
- In Nepal too, Prime Minister KP Sharma Oli has prioritised Kathmandu’s ties with Beijing and sealed a new Framework for Belt and Road Cooperation on Wednesday during his first foreign trip since taking power in July this year.
Nature of the Project: Gelephu Mindfulness City (GMC) is a planned carbon-neutral city in Bhutan, spanning 1,000 square kilometers.
Focus Areas: It will concentrate on eco-friendly industries such as IT, education, hotels, and hospitals.
Economic Necessity: Bhutan aims to diversify its economy beyond hydropower and tourism, addressing challenges like youth outmigration.