Index:
- RBI Retains Repo Rate Amid High Inflation
- Cyclone FENGAL - A Case Study
- Oilfields (Regulation and Development) Amendment Bill, 2024
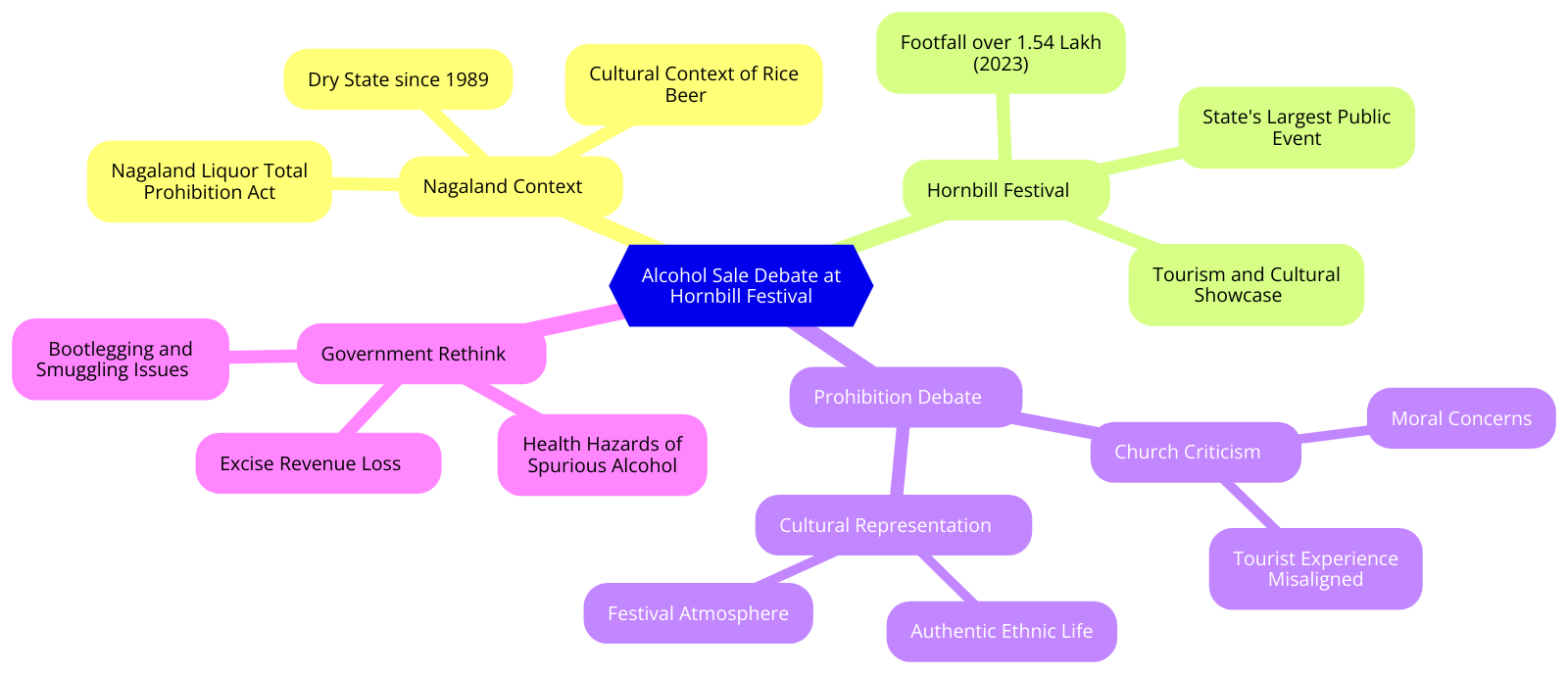
- Hornbill Festival in Nagaland and Liquor controversy - Flowchart
- HTS Militant Group Captures Damascus, Assad Flees
- Chandigarh Leads in Enforcing New Criminal Laws
- Other Headlines of the Day
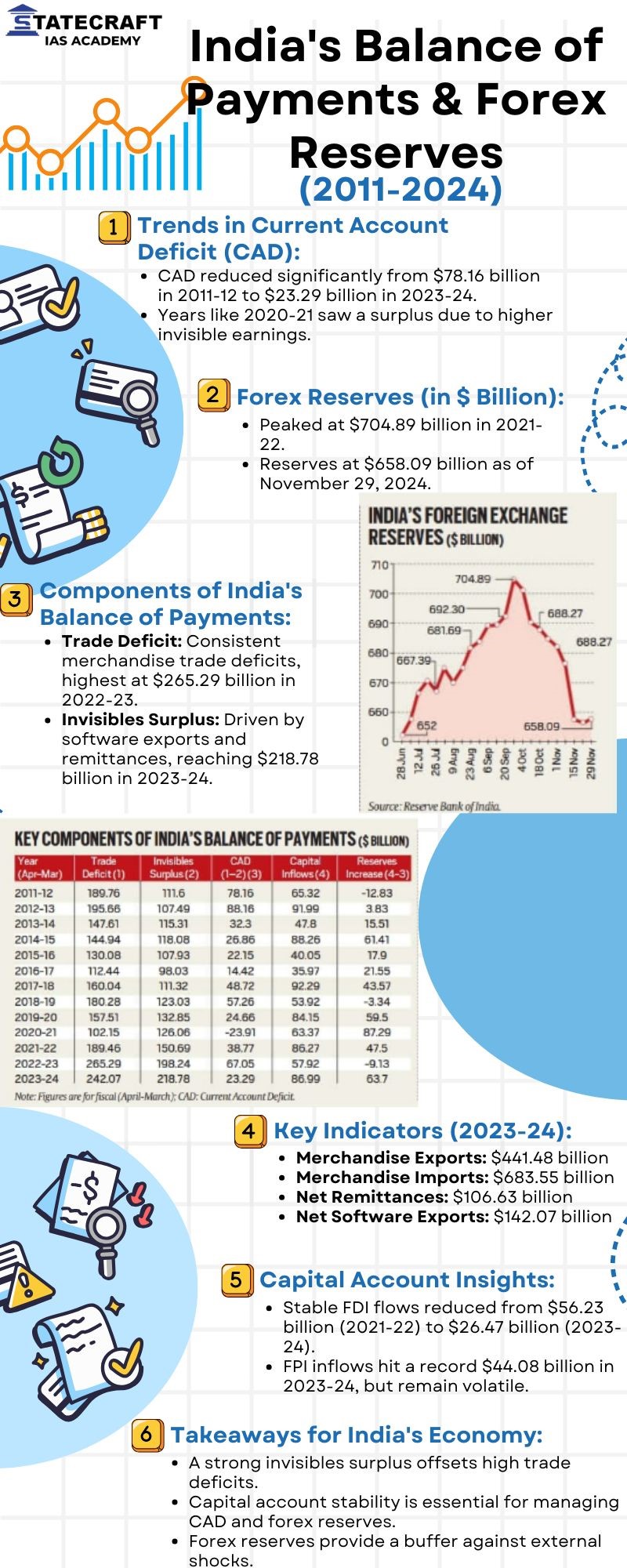
- India's Balance of Payments & Forex Reserves
1. RBI Retains Repo Rate Amid High Inflation
Key Highlights
- Repo Rate:
- The Monetary Policy Committee (MPC) of the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) decided to maintain the repo rate at 5% for the 11th consecutive time.
- The decision reflects the RBI’s focus on curbing inflation while supporting growth.
- Cash Reserve Ratio (CRR):
- The CRR has been cut by 50 basis points to 4%, aimed at easing liquidity conditions.
- This measure will infuse ₹1.16 lakh crore into the banking system, helping banks offer more credit and soften interest rates.
- Inflation Outlook:
- Inflation surged to a 14-month high of 2% in October 2024 due to food price increases.
- Retail inflation for 2024-25 has been revised to 8%, higher than the previous projection of 4.5%.
- Economic Growth Forecast:
- Real GDP growth for the July–September quarter dropped to 4%, the lowest in seven quarters.
- GDP growth projection for 2024-25 has been downgraded to 6% from the earlier 7.2%.
- Key Statements:
- RBI Governor Shaktikanta Das emphasized balancing inflation management and economic growth.
- Persistently high inflation has reduced disposable income, impacting private consumption and real GDP growth.
- Policy Stance:
- The MPC maintains a neutral stance, prioritizing inflation control while keeping growth resilient.
Implications
- The measures are expected to:
- Stabilize the economy in the short term.
- Boost credit growth and lower borrowing costs for businesses and consumers.
- Support resilience amid global and domestic uncertainties.
GS 3 – Economy
2. Cyclone FENGAL - A Case Study
Context:
- Cyclone FENGAL made landfall near Puducherry on November 30, 2024.
- Despite being classified as a low-intensity cyclone (wind speed: 75–95 km/h), it caused large-scale destruction.
- Classification of Cyclones (IMD):
- Based on associated wind speeds:
- Low Pressure: <31 km/h
- Depression: 31–49 km/h
- Deep Depression: 50–61 km/h
- Cyclonic Storm: 62–88 km/h
- Severe Cyclonic Storm: 89–117 km/h
- Very Severe Cyclonic Storm: 118–221 km/h
- Super Cyclone: >222 km/h
- Comparison of FENGAL with Past Cyclones:
- Historical devastating cyclones:
- Odisha Super Cyclone (1999): 260 km/h
- Cyclone Phailin (2013): 215 km/h
- Cyclone Amphan (2020): 185 km/h
- Observation: FENGAL was a low-intensity storm compared to these cyclones.
- Impact of FENGAL:
- Geographical Spread: Tamil Nadu & Puducherry severely affected.
- Rainfall Statistics:
- Mailam (Villupuram): 510 mm in 24 hours.
- Puducherry: 490 mm in a single day (broke the 2004 record of 211 mm).
- Casualties: 12 lives lost (mostly in Tamil Nadu).
- Infrastructure Damage:
- Air, rail, and road transport disrupted.
- Highways inundated.
- Overflowing rivers and lakes.
- Agriculture: Standing crops destroyed over large areas.
- Reasons for High Destruction Despite Low Intensity:
- Slow Movement: FENGAL moved slowly (sometimes <6 km/h) during genesis and landfall.
- Stationary Behavior: Stayed stationary for ~12 hours after landfall near Puducherry, leading to continuous rainfall and high winds.
- Maintained Intensity Post-Landfall: Unusual for cyclones, which typically weaken after landfall.
- Key Takeaways for Disaster Management:
- Slow-moving cyclones can cause disproportionate damage due to prolonged exposure to heavy rains and winds.
- Enhanced focus required on post-landfall behavior for better prediction and mitigation.
- Comparison with other recent cyclones (e.g., Cyclone Dana in October 2024) shows varying human impacts depending on the movement and behavior of storms.
GS Paper I: Geography (Cyclone mechanisms and their effects).
GS Paper III: Disaster Management and Mitigation Strategies.
3. Oilfields (Regulation and Development) Amendment Bill, 2024
Context:
- The Rajya Sabha passed the Oilfields (Regulation and Development) Amendment Bill, 2024.
- Aims to amend the Oilfields Act, 1948, governing exploration and extraction of petroleum and natural gas.
Key Features of the Bill:
- Expanding Definition of Mineral Oil:
- Current Scope: Petroleum and natural gas are defined as mineral oil.
- Amendment: Includes all naturally occurring hydrocarbons like coalbed methane, shale gas, and gas hydrates.
- Introducing Petroleum Lease:
- Replaces traditional leases with petroleum leases allowing private players to undertake activities like prospecting, exploration, and extraction.
- The “petroleum lease” will define the rights and duties of leaseholders.
- Expanding Centre’s Regulatory Powers:
- Gives the Centre authority to regulate operations such as oil production and processing units.
- Introduces rules to promote sustainable practices, e.g., reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
- Decriminalisation of Offences:
- Replaces criminal penalties with fines for violations, such as unauthorized operations or royalty non-payment.
- Current punishment: Six months imprisonment or fine of ₹1,000. Proposed fine: ₹25 lakh for first violations, followed by ₹10 lakh for subsequent breaches.
Rationale for the Bill:
- To boost domestic oil and gas production.
- Encourages private sector participation.
- Promotes sustainable practices for greenhouse gas reduction.
- Aligns with India’s goal of becoming self-reliant in energy.
Concerns Raised:
- States’ Rights:
- Critics argue it encroaches upon state powers under the Indian Constitution (Entry 50 of the State List).
- States fear losing control over local royalties and revenues from mineral oil exploration.
- Centralized Powers: Some view expanded central regulatory powers as undermining federalism.
- Environment and Local Impact: Environmentalists highlight the need to prioritize sustainability in the wake of severe environmental impacts.
Why is the Bill Criticized?
- Opposition: Parties argue the bill dilutes states’ power to manage local resources and could reduce financial returns.
- Federal Concerns: Critics label the bill’s provisions as moving toward a “dangerously unbalanced” federal structure.
- Judicial Scrutiny: Supreme Court upheld states’ power to tax mining activities, hinting at possible constitutional conflicts.
GS Paper II:
- Federal Structure and State-Centre Relations.
- Government policies and interventions for development.
GS Paper III:
- Energy security and sustainable development.
Environmental impact of resource extraction.
5. HTS Militant Group Captures Damascus, Assad Flees
Key Developments
- Seizure of Damascus:
- Militant group Hayat Tahrir al-Sham (HTS) captured Damascus, marking the end of President Bashar al-Assad’s regime after a 13-year civil war.
- The situation represents a seismic shift in West Asia, impacting the region’s political landscape.
- Fate of Assad:
- President Assad fled Damascus on Sunday to an unknown destination.
- Later reports suggested that he and his family reached Moscow, as per Russian news agencies citing Kremlin sources.
- Impact on Allies:
- The capture of Damascus is a major setback for Russia and Iran, who were Assad’s key allies during the war.
- The ousting weakens their influence in the region, raising questions about future dynamics in West Asia.
- Role of HTS:
- HTS, formerly the Nusra Front (an al-Qaeda affiliate), severed ties with al-Qaeda in 2016 under the leadership of Abu Mohammed al-Jolani.
- Their rise highlights the continuing influence of militant groups in Syria’s power vacuum.
- Call for Elections:
- Syrian Prime Minister Mohammad Ghazi al-Jalali announced plans for free elections to allow the people to choose their leadership democratically.
Indian Context
- The Indian Embassy in Damascus remains operational, with officials and Indian nationals reported to be safe.
- The Ministry of External Affairs (MEA) is in close contact with Indians in Syria, ensuring their safety amid the crisis.
Implications
- Geopolitical Shifts:
- The fall of Assad marks a realignment of power in West Asia, with potential repercussions for regional stability.
- The reduced influence of Russia and Iran could alter their foreign policy strategies.
- Humanitarian Crisis: Syria faces further challenges, including displaced populations, economic collapse, and the resurgence of militant groups.
- Global Security: The empowerment of HTS could lead to greater security concerns, as militant groups may seek to expand their influence beyond Syria.
GS Paper 2: International Relations – Regional and global impact of civil wars, implications for India’s foreign policy.
GS Paper 3: Internal Security – Rise of militant groups, implications for counter-terrorism strategies.
6. Chandigarh Leads in Enforcing New Criminal Laws
CONTEXT: Chandigarh has become the first Union Territory/State to fully implement the three new criminal laws introduced in India:
- Bharatiya Nyaya Sanhita (Replaces the Indian Penal Code, 1860)
- Bharatiya Sakshya Adhiniyam (Replaces the Indian Evidence Act, 1872)
- Bharatiya Nagarik Suraksha Sanhita (Replaces the Code of Criminal Procedure, 1898)
- These laws emphasize time-bound investigations, zero FIRs, and digital evidence handling to modernize India’s criminal justice system.
Key Reforms in Chandigarh
- Technological Integration:
- Tablets Provided: 170 tablets supplied to police for crime scene documentation with mandatory audio-visual recording of search-and-seizure operations.
- DigiLocker for Evidence:
- Crime scene videos and related evidence are uploaded to DigiLocker with time-stamped hash values to ensure data integrity.
- Courts can access recordings securely, maintaining the chain of custody.
- Enhanced Infrastructure:
- Increased internet speed at police stations.
- Set up videoconferencing facilities for speedy trials and online testimonies.
- Established 80 videoconferencing locations, including hospitals, courts, and forensic stations, for official and private witnesses to depose.
- Facial Recognition:
- Deployment of “Chitra Khoji” software to match suspect photos with a database of over 1 crore prisoners.
- Zero FIRs:
- 14 Zero FIRs registered since July 1, with all cases pertaining to sexual offenses against women.
- Cases can be filed irrespective of jurisdiction, ensuring prompt action and victim assistance.
- Digitization of Courts:
- Two courts are fully digitized; 30 more are under preparation.
- Online trials conducted for sensitive cases like those involving gangsters to ensure security.
- Improved Conviction Rate:
- Nationwide, the new laws have raised the conviction rate from 58% to 85%.
- Chandigarh registered 1,179 FIRs, filed 245 chargesheets, and achieved convictions in 4 cases under the new laws.
Features of the New Criminal Laws
- Time-Bound Investigations: Mandates prompt case registration and time-bound investigation processes.
- Zero FIR Provision: Victims can register FIRs at any police station, irrespective of jurisdiction, ensuring accessibility and speedy action.
- Mandatory Audio-Visual Recording: Crime scene investigations and search-and-seizure operations require mandatory audio-visual documentation.
- Videoconferencing in Trials: Allows for remote trial procedures, reducing costs, improving security, and increasing efficiency.
Challenges and Way Forward
- Challenges:
- Infrastructure gaps in rural or resource-constrained areas.
- Training police and judicial officials to adopt new technology.
- Recommendations:
- Nationwide rollout of similar reforms with adequate funding.
- Regular training programs for law enforcement and judicial personnel.
GS Paper 2: Governance – Police reforms, digitization in public administration.
GS Paper 3: Internal Security – Use of technology in law enforcement and justice delivery.