Index:
- Trump Declares End to U.S. Citizenship by Birth
- Central Committee Member Among 14 Maoists Killed in Gariaband Encounter
- Competent’ to Judge Indus Water Treaty Dispute, Says World Bank Neutral Expert
- Kerala’s Rising Maternal Mortality Ratio: A Demographic Transition Perspective
- India-France Cooperation on Maritime Security in the Indian Ocean Region (IOR)
- India-France Cooperation in Civil Nuclear and High-End Technologies
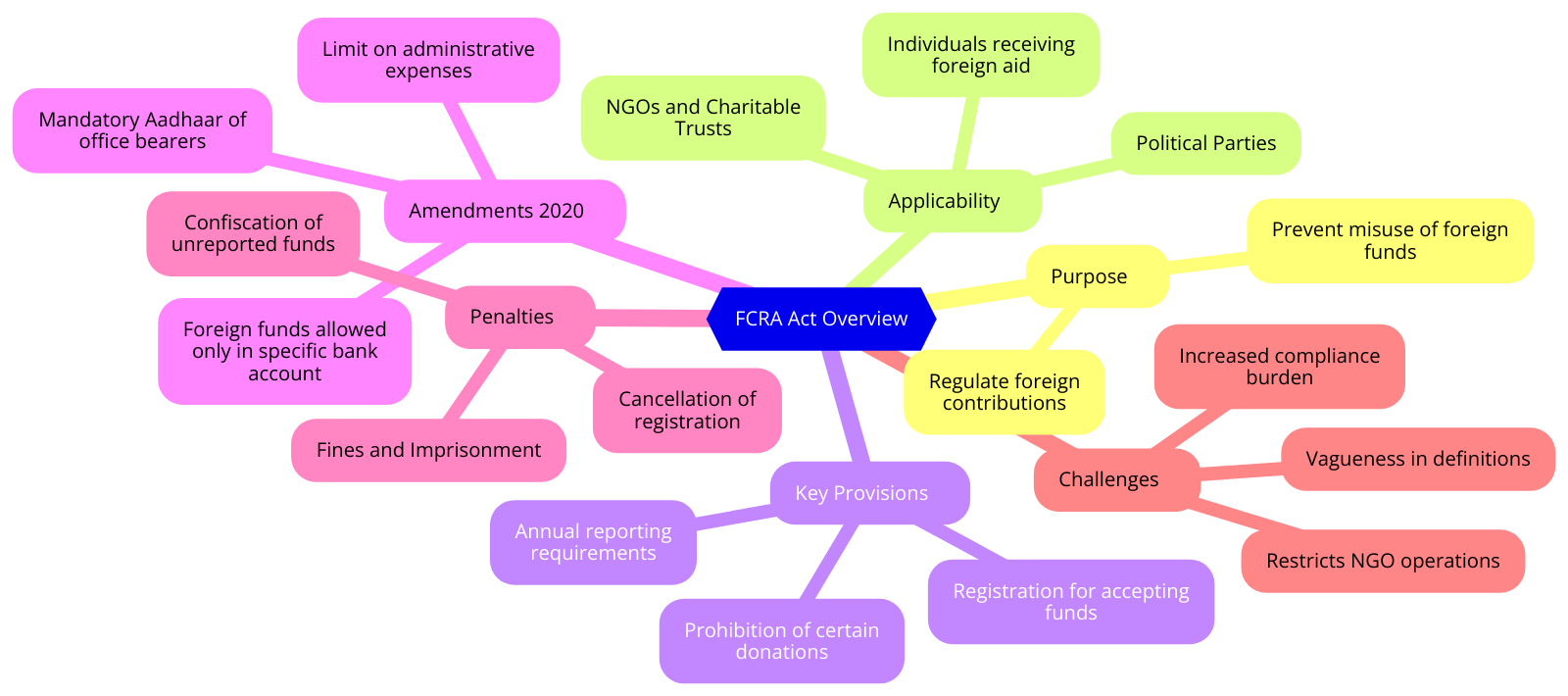
- FCRA in News
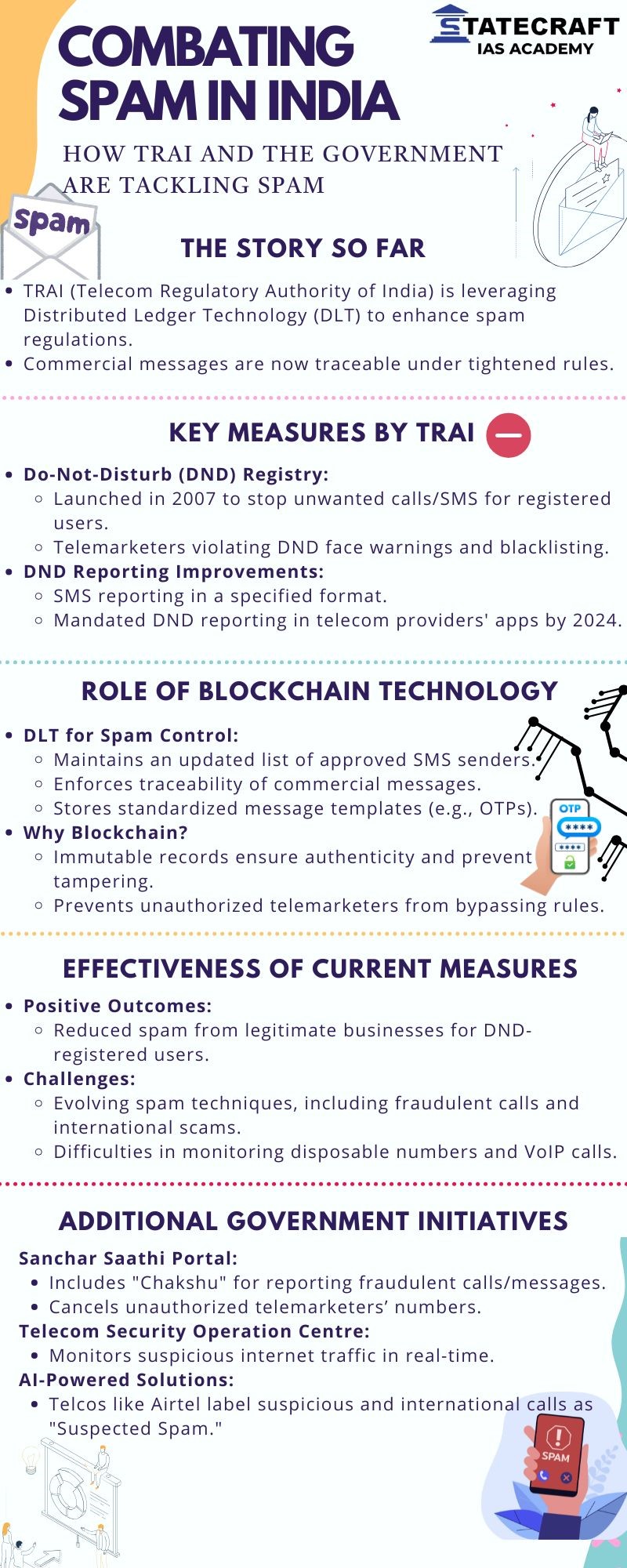
- Combating Spam in India - Infographic
- Redefining Obesity - A Modern Perspective - Infographic
1. Trump Declares End to U.S. Citizenship by Birth
Key Points:
- Executive Order:
- Signed by U.S. President Donald Trump.
- Ends the provision of birthright citizenship.
- Directly impacts Indian professionals on H-1B and other temporary visas.
- Economic Measures:
- Proposal to levy 100% tariffs on BRICS nations attempting “non-dollar” transactions.
- BRICS includes India, Brazil, Russia, China, and South Africa.
- Immigration Impact:
- Plans to crack down on undocumented and illegal immigrants.
- Estimated 7.25 lakh Indians could be affected, including 18,000 on deportation lists.
- Legal and Diplomatic Challenges:
- Democratic-led states challenge the order in U.S. federal courts.
- External Affairs Minister S. Jaishankar set to discuss bilateral relations with U.S. Secretary of State Marco Rubio.
- Concerns raised over potential violation of the U.S. Constitution.
Bilateral Relations: One-on-one meeting planned to prioritize the India-U.S. relationship and cooperation in Quad initiatives.
2. Central Committee Member Among 14 Maoists Killed in Gariaband Encounter
Key Points:
- Encounter Details:
- Location: Gariaband district, near the Chhattisgarh-Odisha boundary.
- Number of Maoists killed: 14, including Jayaram alias Chalpati, a senior central committee member.
- Bounty: ₹1 crore on Jayaram.
- Operation Highlights:
- Conducted by joint forces of:
- District Reserve Guard (DRG).
- Central Reserve Police Force (CRPF).
- Commando Battalion for Resolute Action (CoBRA).
- Special Operation Group (SOG) from Odisha.
- Area of operation: Mainpur police station jurisdiction.
- Recovered: Large cache of arms and ammunition.
- Conducted by joint forces of:
- Significance:
- Described as “another mighty blow to Naxalism” by Union Home Minister Amit Shah.
- Chhattisgarh CM Vishnu Deo Sai aims for a Naxal-free state by March 2026.
- Impact:
- High-ranking Maoist fatalities weaken Naxal leadership.
- Boosts morale of security forces.
Further intensifies anti-Naxal operations in the region.
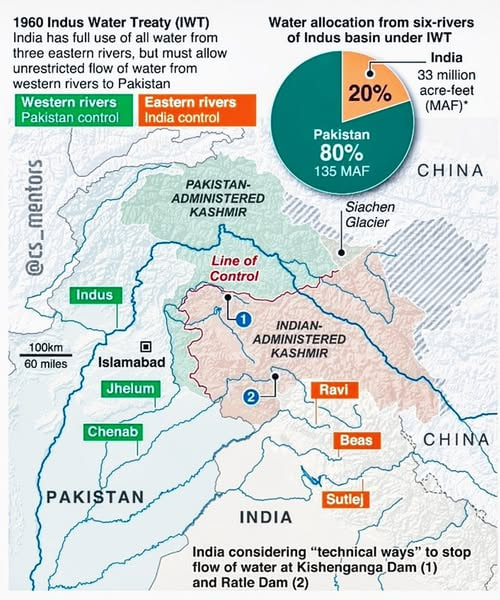
3. Competent’ to Judge Indus Water Treaty Dispute, Says World Bank Neutral Expert
Key Points:
- Neutral Expert’s Decision: Michel Lino, the Neutral Expert (NE) appointed under the Indus Water Treaty (IWT), 1960, stated he is “competent” to decide on disputes related to hydroelectric projects under the treaty.
- Context:
- The IWT regulates the use of water from the Indus River and its tributaries between India and Pakistan.
- Disputes emerged over India’s Kishenganga and Ratle hydroelectric projects.
- India’s Stance:
- India welcomed the decision but seeks resolution through technical discussions rather than arbitration.
- India decided in January 2023 to renegotiate the treaty but highlighted concerns over parallel dispute resolution mechanisms.
- Pakistan’s Stance: Pakistan referred the dispute to the Court of Arbitration in The Hague in 2016, stating it works within the treaty framework.
- World Bank’s Role:
- The World Bank facilitated parallel proceedings by appointing:
- A Neutral Expert to address technical disputes.
- A Court of Arbitration for broader issues.
- The World Bank facilitated parallel proceedings by appointing:
Next Steps: Discussions will involve both nations to address pending technical and treaty concerns.
4. Kerala’s Rising Maternal Mortality Ratio: A Demographic Transition Perspective
Key Points:
- Maternal Mortality Ratio (MMR):
- Kerala, despite having the best MMR in India, is witnessing an increase due to its demographic transition.
- MMR is calculated as the number of maternal deaths per 1,00,000 live births.
- Demographic Transition in Kerala:
- Achieved total replacement-level fertility rate (TFR = 2.1) in 1987-88, ahead of other Indian states.
- TFR below 2.1 leads to a shrinking population over generations.
- Reduced fertility and birth rates result in fewer live births, skewing MMR figures.
- Political and Economic Implications:
- Southern states with sub-replacement fertility rates may face disadvantages during Lok Sabha seat delimitation exercises based on population figures.
- Declining population growth poses challenges similar to countries like South Korea, where fertility rates continue to fall despite incentives.
- Challenges of Demographic Transition:
- Declining working-age population and growing elderly population increase the dependency ratio.
- Strains on public finances, healthcare, and social support systems.
- Nations must prepare for societal and economic consequences of aging populations.
Demographic Transition Theory:
- Transition involves four stages:
- High birth and death rates (stable population).
- Declining death rates (population growth).
- Declining birth rates (levelling out).
- Low birth and death rates (population decline).
- Driven by advancements in education, economic development, and technology.
- Policy Recommendations:
- Strengthen public finances and healthcare systems.
- Develop policies to support elderly care and healthcare financing.
Promote equal participation in household responsibilities to enable economic participation by all genders.
5. India-France Cooperation on Maritime Security in the Indian Ocean Region (IOR)
Key Points:
- Maritime Surveillance and Cooperation:
- India and France agreed to explore opportunities for coordinated maritime surveillance to counter threats to maritime security in the IOR.
- Both countries committed to enhancing existing mechanisms and supporting each other in maritime engagements.
- Strengthening Information Exchange:
- Implementation of the agreed framework for information sharing between:
- Information Fusion Centre-Indian Ocean Region (IFC-IOR), Gurugram.
- Regional Coordination Operations Centre (RCOC), Seychelles.
- Regional Maritime Information Fusion Centre (RMIFC), Madagascar.
- Implementation of the agreed framework for information sharing between:
- Threats Addressed:
- Piracy and armed robbery.
- Maritime terrorism.
- Contraband smuggling.
- Illegal, unreported, and unregulated (IUU) fishing.
- Hybrid threats (including cyber security).
- Marine pollution.
- Joint Assessments:
- India and France to develop joint threat assessments for maritime security in the IOR.
- Collaborative efforts to address emerging challenges such as cyber threats and marine pollution.
- Significance:
- Enhances India’s maritime domain awareness (MDA) in the IOR.
- Strengthens Indo-French ties in defense and maritime cooperation.
- Contributes to regional stability and the rule of law in international waters.
Recent Development: Agreement was reached during the seventh India-France Maritime Cooperation Dialogue.
6. India-France Cooperation in Civil Nuclear and High-End Technologies
Key Highlights:
- India-France Cooperation:
- Discussions focused on boosting collaboration in high-end technology sectors such as civil nuclear energy, defense, space, cyber, and Artificial Intelligence (AI).
- Foreign Office consultations were held in Paris ahead of Prime Minister Narendra Modi’s visit to France for the Summit for Action on Artificial Intelligence on February 10-11.
- Civil Nuclear Energy:
- A Special Task Force on Civil Nuclear Energy was convened as agreed during French President Emmanuel Macron’s visit to India in January 2024.
- Talks focused on the Jaitapur Nuclear Power Project in Maharashtra:
- Initial civil nuclear agreement signed in 2008; first MoU for the 990-MW Jaitapur plant inked in 2009.
- French energy company EDF provided a revised techno-commercial offer in 2022.
- Pending issues include:
- High project costs and time overruns.
- Challenges with India’s Civil Liability for Nuclear Damage Act, 2010.
- Potential future collaboration on Small Modular Reactors (SMRs).
- PM’s Upcoming Visit:
- Modi to co-chair the AI Summit, discussing bilateral priorities with French leadership.
- Collaboration opportunities in defense, cyber security, digital innovation, and AI.
- Bilateral Cooperation Areas:
- Defense and strategic technology: Continued discussions on enhancing ties.
- Space programs: Future collaboration in space technology and exploration.
- Cyber and digital infrastructure: Cooperation to counter cyber threats.
Significance:
- Strengthens India-France strategic partnership.
- Jaitapur, if finalized, would become the world’s largest nuclear power plant.
- Highlights the potential for renewable and sustainable energy solutions like SMRs.
- Enhances India’s positioning in global AI and digital technology leadership.
Challenges:
- Civil nuclear liability law remains a significant hurdle for foreign investments in nuclear energy.
Delays in major projects like Jaitapur could impact bilateral relations in energy cooperation.