Topics
- Metagenome Sequencing and Pathogen Surveillance
- Harami Nala
- Sant Guru Ravidas
- Institution of Eminence
- PM-USHA Scheme
- Urea Gold
METAGENOME SEQUENCING AND PATHOGEN SURVEILLANCE
Context
- Genome sequencing technologies have played a pivotal role in pinpointing the source of the COVID-19 pandemic, showcasing the significance of metagenomics in pathogen identification and surveillance.
- This innovation has revolutionized the way we approach emerging threats and has enabled swift responses.
Metagenomics and Its Impact on COVID-19
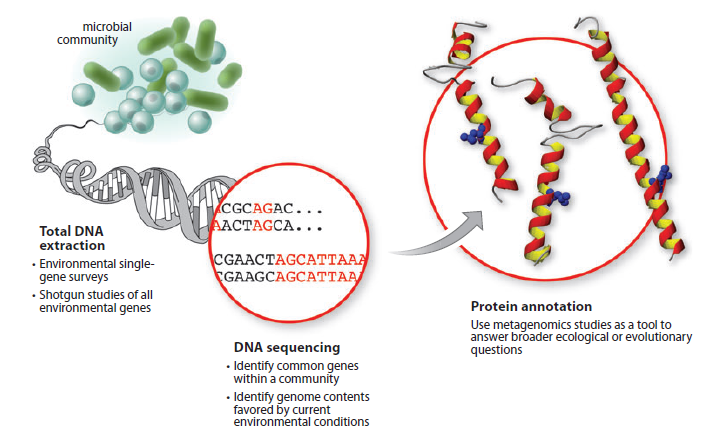
- Metagenomics, a transformative approach, has been applied to unprecedented effect in the identification of SARS-CoV-2, resulting in it being one of the most extensively sequenced organisms to date.
- This marked a departure from traditional methods, with patient samples directly subjected to genome sequencing, thereby accelerating the identification process.
Global Impact of Genome Surveillance in COVID-19
- The success of genome sequencing has led to the creation of tools like the CovidSeq assay and has catalyzed global initiatives for monitoring the SARS-CoV-2 genome.
- These initiatives have significantly enhanced our ability to monitor and respond to viral mutations and outbreaks.
Utilization of Genome Surveillance for Pathogen Tracking
- Technologies rooted in genome sequencing, including the CovidSeq assay, have been harnessed for effective detection of SARS-CoV-2.
- The GISAID repository has emerged as a key repository for global genome-sequence data, showcasing the rapid and comprehensive nature of genome surveillance activities.
- Notably, India has taken proactive steps with a national genome-sequencing and surveillance program for SARS-CoV-2.
Nigerian Study: Unveiling Pathogen Diversity through Metagenomic Sequencing
- The application of metagenomic sequencing in a Nigerian study illuminated pathogen surveillance across three distinct patient groups.
- This versatile approach uncovered 13 unique viruses among these cohorts, contributing to the identification of co-infections and previously undiagnosed conditions.
- The diagnostic potential of metagenomics was highlighted as it facilitated the identification of pesticide poisoning symptoms in specific cases.
Wide-Ranging Applications and Future Prospects
- Genome sequencing technologies are transcending their initial purpose, now being employed to detect a range of pathogens such as Zika, dengue, lumpy skin disease, and drug-resistant tuberculosis.
- Furthermore, genome surveillance has expanded to encompass diverse sources such as wastewater, air, soil, and animals, enabling early detection and proactive response strategies.
- With its speed, accuracy, and adaptability, genome sequencing stands as a cornerstone for future pathogen detection, surveillance, and response efforts.
Question: Explain the concept of metagenomics and its significance in the field of microbiology. How has metagenomics revolutionized the identification and surveillance of pathogens, especially in the context of emerging diseases like COVID-19?
HARAMI NALA
Context
- The spotlight has turned to the ‘Harami Nala’ creek, a sensitive and strategically vital waterway near the India-Pakistan border, as evidenced by the visit of Union Home Minister Amit Shah.
- This location sheds light on the intricate issues of border security and regional interactions.
Unveiling Harami Nala
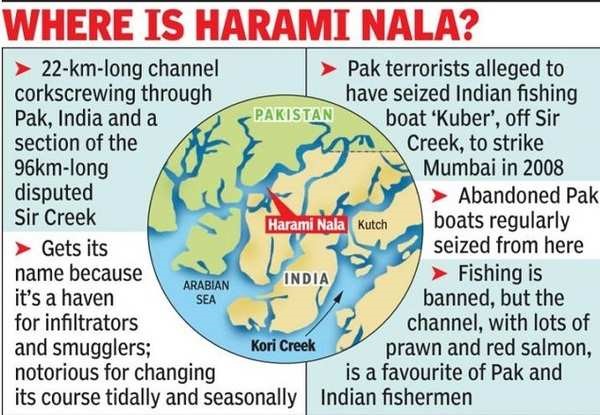
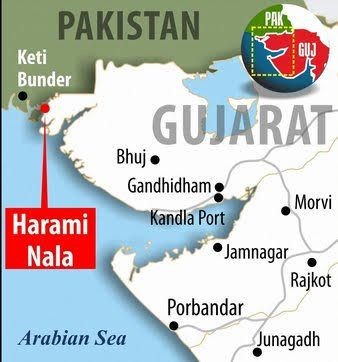
Geographical Context: Positioned at the Gujarat-Rajasthan border, ‘Harami Nala’ is a 22-kilometer tidal creek within the Kutch region of Gujarat.
It serves as a natural demarcation between India and Pakistan.
Physical Attributes: Functioning as a conduit for water and sediment, the creek is home to protected marine species.
Its water level and flow are influenced by weather conditions, spanning a range of twenty to twenty-five kilometers.
Decoding the Moniker
Etymology: Translated as the “rogue or treacherous channel,” the name ‘Harami Nala’ encapsulates the channel’s notoriety as a potential entry point for infiltrators.
Historical Background: The creek’s reputation as a pathway for criminals, terrorists, and undesirable elements from Pakistan into India has led to its name.
Incidents of infiltrations and the discovery of abandoned boats have reinforced its dubious repute.
Unlawful Activities: The channel’s ecosystem, which includes prawns and other marine life, falls victim to illegal fishing.
Despite its ecological importance, this illegal practice remains a persistent challenge.
Historical Links of Harami Nala
Geostrategic Significance: The creek’s proximity to coastal and urban centers such as Gujarat and Mumbai makes it an enticing route for potential infiltrators.
Terrorist Connection: Notably, the 2008 Mumbai attacks perpetrator Ajmal Kasab was believed to have entered India through Harami Nala, shedding light on the creek’s strategic implications.
Navigating Challenges and Complexities
Border Security: While India’s security efforts are robust, the creek’s historical exploitation for illicit activities presents an ongoing challenge.
Maritime Complexity: The interplay between maritime dynamics, security concerns, and intricate border complexities underscores the multifaceted nature of the region.
SANT GURU RAVIDAS
Context
The Prime Minister laid the foundation stone for a temple dedicated to Sant Ravidas in Sagar, Madhya Pradesh.
The temple’s construction budget is ₹100 crore.
Introduction to Guru Ravidas
- Guru Ravidas was a mystic poet-saint during the 15th to 16th century CE.
- He played a crucial role in the Bhakti movement and founded the Ravidassia religion.
- His influence extended across regions like Uttar Pradesh, Rajasthan, Maharashtra, Madhya Pradesh, Punjab, and Haryana.
- Guru Ravidas was recognized as a spiritual leader and a social reformer.
Life and Teachings of Guru Ravidas
- Guru Ravidas’s early life details are uncertain and debated among scholars.
- Born in 1450 CE in the cobbler caste.
Influence on Various Spiritual Traditions
- His devotional verses are part of the Sikh scriptures, Guru Granth Sahib.
- His poems are also found in the Panch Vani text of the Dadupanthi tradition within Hinduism.
Championing Unity and Equality
- Guru Ravidas emphasized the eradication of caste and gender-based divisions.
- He advocated for unity in the pursuit of personal spiritual growth and freedom.
Relevance of Guru Ravidas’s Philosophy
- Guru Ravidas’s philosophy of social justice, equality, and fraternity aligns with constitutional values.
- His ideals have become integral to our governing framework.
Vision of an Ideal Society
- Guru Ravidas envisioned an ideal society named “Be-gampura,” devoid of grief and fear.
- This society would be characterized by unity, absence of vulnerability, and scarcity.
- Governance would be based on the rule of law, emphasizing equality and the welfare of all.
The inauguration of the Sant Ravidas temple underscores Guru Ravidas’s enduring influence as a spiritual luminary and an advocate for societal transformation centered on unity and equality.
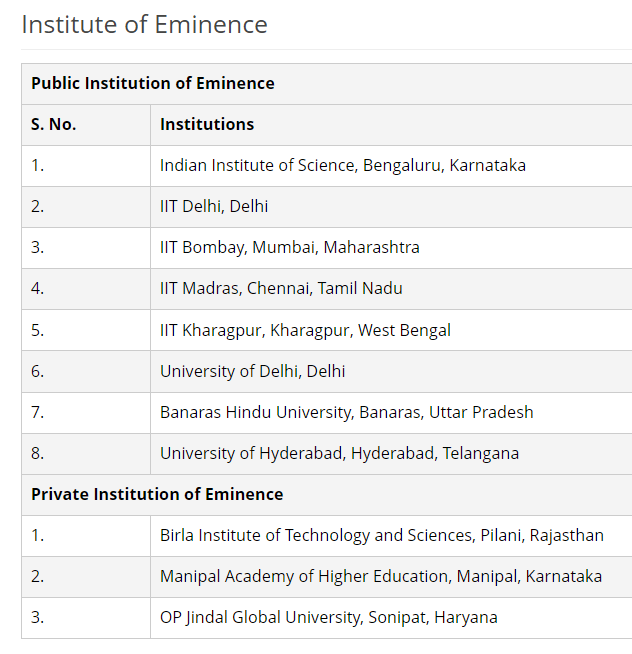
INSTITUTION OF EMINENCE
Context:
- An expert panel along with the University Grants Commission (UGC) has advised against granting the prestigious Institutions of Eminence (IoE) status to Jadavpur University and Jamia Hamdard University.
- These universities were initially shortlisted by the government for this recognition.
Withdrawal of IoE Status Proposal for Anna University by Tamil Nadu Government
- The government of Tamil Nadu has retracted its previous proposal to confer the Institution of Eminence (IoE) status upon Anna University.
- Pending Decision by Ministry of Education on Expert Committee and UGC Recommendations.
- The Ministry of Education is currently reviewing the recommendations put forth by the Empowered Expert Committee (EEC) and the University Grants Commission (UGC) regarding the IoE status for various institutions.
Institution of Eminence (IoE) Overview
- Introduced in the 2016 Union budget, the Institution of Eminence (IoE) is a recognition program aimed at enhancing the stature of higher education institutions within India.
It operates under the Ministry of Education and seeks to transform ten public and ten private universities into world-class centers for teaching and research.
IoE Objectives
- Enhancing Regulatory Framework: The program aims to create a favorable regulatory environment for selected institutions to excel in both teaching and research.
- Global Recognition: IoE status is intended to elevate chosen universities to global prominence, equipping them with the tools to become internationally renowned centers of learning and innovation.
IoE Nodal Ministry
The Ministry of Education is responsible for overseeing the implementation and administration of the Institution of Eminence (IoE) program.
IoE Selection Criteria
The selection of institutions for IoE status is based on the recommendations of the Empowered Expert Committee (EEC) led by Gopalasamy.
The criteria for selection are:
- World Rankings: Universities that appear within the top 500 of the QS World University Rankings or the top 50 of the National Institutional Ranking Framework (NIRF) rankings are eligible for IoE status.
- 2. Greenfield Institutions: Newly established institutions, referred to as “Greenfield Institutions,” are also considered. These institutions are given a three-year window for establishment and operation before being evaluated for IoE status.
IoE Benefits
- Enhanced Autonomy: Selected universities gain a higher degree of autonomy, enabling them to expand and innovate more effectively.
- 2. Skill and Quality Enhancement: The program encourages skill development and quality improvement, propelling the institutions toward becoming world-class educational hubs.
- International Presence: IoE institutions can admit up to 30% foreign students and appoint up to 25% foreign faculty members.
- Online Course Offerings: Universities can offer online courses for up to 20% of their programs.
- Global Collaborations: Institutions can engage in academic partnerships with the top 500 globally ranked institutions without seeking UGC permission.
- Fee Autonomy: IoE institutions have the liberty to set and charge fees for foreign students without constraints.
- Flexible Academic Structure: Universities are free to design their course structures in terms of credit hours and degree duration.
8. Curriculum and Syllabus Autonomy: IoE institutions have complete flexibility in designing their curriculum and syllabus, allowing for innovative and relevant educational offerings.
PM-USHA SCHEME
Context:
- Fourteen States and Union Territories have not yet signed a crucial Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) with the Union Education Ministry.
- This MoU is a prerequisite for accessing funds amounting to nearly ₹13,000 crore over the next three years under the Pradhan Mantri Uchchatar Shiksha Abhiyan (PM-USHA), a flagship scheme for State-run higher education.
- These States have expressed reservations about the MoU, primarily due to financial concerns and the absence of dedicated funds for National Education Policy (NEP) reforms.
States’ Concerns and Financial Implications:
- One of the major concerns raised by these dissenting States is the financial burden associated with the MoU.
- The PM-USHA requires States to bear 40% of the budget for the Pradhan Mantri Uchchatar Shiksha Abhiyan.
- Additionally, the States have noted that the MoU lacks provision for extra funds to support the implementation of NEP reforms.
- This financial aspect has become a sticking point in the negotiations between the Centre and these States.
Discussion and Resolution Efforts:
- In response to the concerns raised by the dissenting States, the Centre has initiated discussions to address the differences and find common ground.
- The aim is to find solutions that accommodate the financial constraints of the States while also ensuring the successful implementation of the National Education Policy.
Overview of Pradhan Mantri Uchchatar Shiksha Abhiyan (PM-USHA):
- The PM-USHA is a centrally sponsored program launched in 2013, with the goal of collaborating with over 300 state universities and their affiliated colleges.
- The primary objective of this initiative is to provide strategic funding to eligible state higher educational institutions.
- The funding allocation is determined based on established norms and is contingent upon achieving specific outcomes.
Key Aspects of PM-USHA and NEP Alignment:
- Under the PM-USHA, the Ministry seeks to enhance the quality of higher education in State Universities through a multifaceted approach, including curricular and programmatic changes, teacher training, infrastructure development (both physical and digital), accreditation, and improved employability.
- This initiative places a strong emphasis on ensuring equity, access, and inclusion in higher education.
Challenges in Implementing NEP Reforms:
- While the PM-USHA addresses various aspects of higher education improvement, the dissenting States have pointed out a critical gap regarding NEP reforms.
- Despite the MoU’s requirement for implementation, it does not outline specific provisions or funding mechanisms to support the comprehensive changes envisioned under the National Education Policy.
Conclusion:
The ongoing discussions between the Centre and the dissenting States reflect the complex interplay between financial considerations and educational reforms.
As these negotiations continue, finding a balanced and sustainable approach to accommodate both the financial concerns of the States and the imperative of NEP implementation remains a priority.
Urea Gold
Introduction to Urea Gold and its Purpose
- The recent launch of “Urea Gold,” a specialized fertilizer developed by Rashtriya Chemicals and Fertilizers Ltd (RCF), has garnered significant attention due to its innovative combination of urea and sulfur.
- This formulation aims to enhance the efficiency of nitrogen use (NUE) in agriculture, addressing the pressing issues of rising urea consumption and declining agricultural productivity.
Understanding Urea Gold
- Composition of Urea Gold
- “Urea Gold” is a fortified fertilizer created by blending urea with sulfur. This novel formulation is designed to serve as a potent agricultural solution by boosting NUE and improving overall crop performance.
- Enhancing Nitrogen Use Efficiency
- The unique blend of “Urea Gold” facilitates a controlled and gradual release of nitrogen, promoting sustained plant health.
- This controlled release mechanism has the potential to reduce the frequency of fertilizer application, leading to more efficient resource utilization.
Challenges in Urea Consumption and Agricultural Efficiency
- Surge in Urea Consumption
- Over the years spanning from 2009-10 to 2022-23, urea consumption in India has surged from 26.7 million tonnes to 35.7 million tonnes.
- This considerable increase has solidified urea’s position as the dominant choice among fertilizers in the country.
- Dependency on Imports
- India heavily relies on imported natural gas for domestic urea production.
- The country’s annual urea consumption ranks second globally, trailing behind China, which predominantly employs coal-based production methods.
- Decline in Nitrogen Use Efficiency
- Approximately 35% of nitrogen applied through conventional urea fertilizers actually benefits crops, highlighting concerns regarding resource wastage and the need for increased fertilizer application.
The Fortified Fertilizer Solution
- Incorporating Coating Strategies
- Fortified fertilizers follow a strategy of coating primary nutrients (nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium) with secondary nutrients (sulfur, calcium, magnesium) as well as micronutrients (zinc, boron, manganese, etc.).
- Enhanced Benefits and Innovative Technology
- These coated fertilizers act as carriers for secondary and micronutrients, leading to increased efficiency in the utilization of nitrogen and phosphorus.
- Innovative technologies, such as the “Procote” technology developed by Yara International, facilitate the micronutrient coating process, resulting in improved fertilizer efficacy.
- Validation of Efficacy
- Trials have confirmed that the use of micronutrient-coated fertilizers can lead to amplified yields of crops like paddy and wheat.
- This holds the potential to mitigate concerns surrounding NUE.
Challenges in Pricing and Distribution
- Complexities in Pricing
The existing subsidies provided for other coated fertilizers, such as zincated urea and boronated DAP, may not serve as adequate incentives for companies to actively promote fortified products like “Urea Gold.”
- Hurdles in Farmer Adoption
Price disparities between fortified and non-fortified fertilizers have discouraged farmers from adopting the coated options, posing a hurdle in the widespread adoption of these innovative fertilizers.
Optimal Implementation and Balancing Pricing
Advocating for Uniform Coating
To ensure consistent nutrient distribution and user convenience, proponents of fortified fertilizers recommend implementing the coating process at the factory level.
Liberating Maximum Retail Prices (MRPs)
Allowing flexibility in maximum retail prices (MRPs) for coated fertilizers could play a crucial role in encouraging their adoption among farmers.
Striking a Pricing Balance
Given the significant subsidies offered for traditional fertilizers, maintaining reasonable premium prices for fortified products becomes essential to ensure affordability.
Conclusion
Promising Prospects of Urea Gold and Fortified Fertilizers
Amidst the challenges posed by declining NUE and increasing urea consumption, the introduction of “Urea Gold” and fortified fertilizers holds great potential in enhancing agricultural efficiency.
Addressing Pricing and Distribution Challenges
The journey towards successful implementation requires careful consideration of pricing disparities and distribution intricacies, in order to fully unlock the benefits of these innovative fertilizers.