1. National Judicial Data Grid (NJDG)
2. PMMSY
The Significance of Saudi Arabia to India
Vagus Nerve
Data-driven Innovations in Agriculture
6. National Logistics Policy 2022
National Judicial Data Grid (NJDG)
Context
- In a recent announcement by Chief Justice of India D Y Chandrachud, it was revealed that the Supreme Court has officially integrated with the National Judicial Data Grid (NJDG) portal.
- The NJDG serves as a comprehensive national repository, housing data related to cases, including those that are instituted, pending, and disposed of, across various courts in the country.
- The NJDG, a product of the eCourts Project, stands as a database encompassing orders, judgments, and case particulars from District & Subordinate Courts as well as High Courts.
- This online platform was developed through a collaborative effort between the National Informatics Centre and the Supreme Court’s in-house software development team.
- It is designed with an interactive user interface and an analytics dashboard to facilitate data analysis and reporting.
Key Features of NJDG include:
- Real-time Data Updates: The NJDG constantly updates its data, thanks to the connected District and Taluka courts.
- Comprehensive Judicial Data: It offers insights into judicial proceedings and decisions from all computerized district and subordinate courts nationwide.
- High Court Integration: All High Courts have joined the NJDG through web services, making case data easily accessible to the public.
- Detailed Case Analysis: NJDG provides information on civil and criminal cases, allowing users to perform in-depth analysis based on case age, state, and district.
Benefits of NJDG:
- Case Pendency Management: NJDG serves as a monitoring tool to identify and manage case pendency, aiding in reducing delays in case disposal.
- Policy Inputs: It offers timely inputs for policy decisions aimed at expediting case resolutions and decreasing case backlog.
- Performance Monitoring: NJDG enables efficient monitoring of court performance and helps identify systemic bottlenecks, making it a valuable resource management tool.
- Business-Friendly: The World Bank has recognized NJDG in its Ease of Doing Business report for 2018, as it facilitates the generation of case management reports, making contract enforcement more straightforward.
- Government Access: Open Application Programming Interfaces (APIs) are provided to Central and State Governments, ensuring easy access to NJDG data for policy purposes.
- Future Expansion: Plans are in place to expand NJDG access to non-institutional litigants in the future.
- Reason for Delay: NJDG now includes a feature specifying the reasons for case delays, helping address judicial issues and improving transparency.
- The eCourts Integrated Mission Mode Project, initiated by the government, focuses on the computerization of District and subordinate courts, enhancing access to justice through technology.
- It aligns with the National Policy and Action Plan for Implementation of Information and Communication Technology in the Indian Judiciary and is implemented in collaboration with the e-Committee Supreme Court of India and the Department of Justice.
- The project unfolds in three phases: Phase I (2011-2015), Phase II (2015-2023), and Phase III, which involves migrating the system to cloud technology, with an estimated cost of ₹1,205.20 crore for providing 25 petabytes of cloud storage.
The integration of the Supreme Court with NJDG brings several advantages:
- Real-Time Case Data: NJDG now offers real-time data on Supreme Court case filings and dispositions, accessible to the public for tracking case status and accessing relevant information.
- Open Data Policy: This integration aligns with an ‘open data policy,’ promoting transparency and accessibility of judicial information.
- Enhanced Coordination: Onboarding the NJDG improves coordination within the judiciary and facilitates informed decision-making.
- Resource Optimization: NJDG assists in deploying judicial resources more efficiently to address case backlog and manage workload.
- Centralized Data Source: NJDG serves as a single repository for case-related data, streamlining access and ensuring data consistency.
- Research Opportunities: Legal scholars and researchers can utilize NJDG data for in-depth analysis, studying trends and case outcomes within the Indian judicial system.
- Pendency and Case Statistics: The NJDG-SCI portal provides insights into Supreme Court case pendency, filings, and disposals, as well as the number of judges on each bench.
- Access for All: Real-time data accessibility empowers the public to track Supreme Court case proceedings, enhancing their understanding of the legal system.
With the Supreme Court’s integration, NJDG now encompasses all three tiers of the Indian judiciary, marking a significant milestone in the e-courts project and aligning with the government’s “ease of doing business” initiative.
Pradhan Mantri Matsya Sampada Yojana PMMSY
Context
In 2020, the Indian government introduced the Pradhan Mantri Matsya Sampada Yojana (PMMSY) with the aim of fostering sustainable, economically prosperous, and socially inclusive growth in the country’s fisheries sector.
Current State of India’s Fisheries Sector
(Information sourced from the Economic Survey of 2022-23)
- The fishing industry remains a vital and rapidly expanding sector closely associated with agriculture in India.
- It sustains the livelihoods of over 8 crore fishermen and fish farmers at the grassroots level, with numerous others benefiting throughout the fisheries value chain.
- Since 2016-17, the fisheries sector has achieved an annual average growth rate of approximately 7%, contributing to about 6.7% of the total agricultural Gross Value Added (GVA).
- Notably, fish and fish products account for around 17% of India’s agricultural exports.
Furthermore, India has secured its position among the top three countries globally in fish and aquaculture production, establishing itself as a prominent exporter of shrimp.
Overview of the Pradhan Mantri Matsya Sampada Yojana (PMMSY)
- The Pradhan Mantri Matsya Sampada Yojana is administered by the Department of Fisheries under the Ministry of Fisheries, Animal Husbandry, and Dairying.
- PMMSY is strategically designed to address critical gaps within the fisheries value chain, spanning fish production, productivity, quality, technology, post-harvest infrastructure, and marketing.
- Its overarching objectives include the modernization and fortification of this value chain, enhancing traceability, and establishing a robust framework for fisheries management while concurrently safeguarding the socio-economic welfare of fishermen and fish farmers.
- The scheme places a strong emphasis on doubling the income of fishermen through various interventions, fostering meaningful employment opportunities, boosting the fisheries sector’s contribution to agricultural GVA and exports, and enhancing regulatory mechanisms for effective sector management.
Advantages of PMMSY
- PMMSY extends financial support for the development of fishing infrastructure, encompassing facilities such as fishing harbors, fish landing centers, fish markets, fish feed plants, and fish processing units.
- It also offers assistance for marketing and exporting fish products, encouraging the establishment of cold chains, fish processing facilities, and packaging units to enhance India’s competitiveness in the global seafood market.
- For instance, individuals involved in aquaculture in Nellore have successfully become exporters with the cultivation of biofloc shrimps.
- The scheme is a catalyst for generating employment opportunities, particularly in rural and coastal areas, benefiting fishermen, fisherwomen, and related sectors like processing, marketing, and transportation.
- Additionally, PMMSY promotes the adoption of modern technology and equipment in fishing and aquaculture, including advanced fishing vessels, fish-finding technology, and fish processing machinery.
- Furthermore, PMMSY encourages diversification in fisheries by supporting activities such as ornamental fish farming, seaweed cultivation, and mariculture, thereby expanding the sector’s scope.
- Importantly, the scheme focuses on empowering women in the fisheries sector by providing training and financial support, facilitating their active participation in various activities.
- Notable examples include women entrepreneurs from the Kashmir Valley efficiently rearing cold water rainbow trout using recirculatory aquaculture systems.
Conclusion
PMMSY has ushered in a realm of opportunities, and its successful implementation will play a pivotal role in shaping the destiny of India’s fisheries and aquaculture industry for generations to come.
The Significance of Saudi Arabia to India
Introduction:
Saudi Arabia holds immense significance in India’s foreign relations, primarily due to its strategic, economic, and cultural ties. This note outlines the multifaceted importance of Saudi Arabia to India.
- Economic Partnership:
- Bilateral Trade: Saudi Arabia is India’s fourth-largest trade partner, with a bilateral trade value of $52.76 billion in FY2022-23. It accounts for a significant portion of India’s total trade.
- Indian Investment: Indian companies, including L&T, Tata, and Wipro, have made substantial investments in Saudi Arabia, further deepening economic relations.
- Saudi Investments in India: Saudi Arabia has invested billions of dollars in India, with investments in startups, energy projects, and infrastructure development, enhancing economic cooperation.
- Energy Security:
- Crude Oil Imports: Saudi Arabia is a vital source of crude oil for India, providing about 16.7% of India’s total crude imports. Ensuring a stable supply of energy resources is critical for India’s energy security.
- Defence and Security Cooperation:
- Growing Defence Ties: India and Saudi Arabia have witnessed significant growth in their defence partnership, marked by high-level visits, joint exercises, and discussions on joint development and production of defence equipment.
- Security Cooperation: Both countries emphasize the importance of security cooperation in combating terrorism and ensuring stability in the region. They share concerns about the threat of terrorism and its financing.
- Cultural and People-to-People Ties:
- Large Indian Diaspora: Saudi Arabia is home to a substantial Indian community of more than 2.4 million people. This diaspora is highly respected for its contributions to Saudi Arabia’s development and serves as a cultural bridge between the two nations.
- Hajj and Umrah: Saudi Arabia plays a crucial role in facilitating the pilgrimage of Indian Muslims for Hajj and Umrah, fostering cultural and religious ties.
- Strategic Partnerships and Diplomacy:
- Strategic Partnership Council: The establishment of the India-Saudi Arabia Strategic Partnership Council has further elevated diplomatic relations, allowing for comprehensive discussions and cooperation in various sectors.
- Geopolitical Alignment: India and Saudi Arabia share interests in regional stability and security, contributing to their alignment on various global and regional issues.
- Energy Cooperation Beyond Oil:
- Renewable Energy: Besides crude oil, the two countries are exploring opportunities in renewable energy, emphasizing the transition to cleaner sources of energy.
Conclusion:
Saudi Arabia holds a multifaceted and crucial role in India’s foreign policy. Their relationship encompasses economic, energy, defence, cultural, and diplomatic dimensions, making Saudi Arabia one of India’s most important strategic partners in the Middle East and beyond. Both nations are committed to strengthening their ties and exploring new avenues for cooperation in the years to come.
Recent Developments: IMEC + West Coast Mega Refinery Project
West Coast Mega Refinery Project
Core Message
India and Saudi Arabia are actively revitalizing efforts to accelerate the long-pending West Coast Mega Refinery Project, aimed at processing 60 million tonnes of oil annually. This project has faced various obstacles in its development.
The West Coast Mega Refinery Project
- First proposed in 2015, this ambitious endeavor involves the construction of an extensive oil refinery and petrochemical complex in Maharashtra’s Konkan region, with the involvement of Saudi Arabia and the UAE.
- The designated location for this project is Barsu village in Maharashtra’s Ratnagiri district.
- To implement the project, Indian Oil Corporation (IOC), Bharat Petroleum Corporation Limited (BPCL), and Hindustan Petroleum Corporation Limited (HPCL) established a joint venture known as Ratnagiri Refinery & Petrochemicals (RRPCL).
- However, the project encountered resistance from local communities due to environmental concerns and shifting political dynamics within the state.
- Despite initial agreements and an estimated cost of Rs 3 lakh crore, the project failed to progress as foreign partners had not acquired stakes in the joint venture.
Recent Developments
- The acquisition of approximately 15,000 acres of land across 17 villages became a prerequisite for the project’s execution.
- A joint monitoring committee has been instituted to oversee the project’s progress, reflecting renewed commitment from both India and Saudi Arabia.
- A substantial fund of $50 billion has been earmarked for the project.
Significance of the Project
- India is a significant consumer of crude oil, and its demand for petroleum products and petrochemicals is projected to experience substantial growth.
- India’s objective is to increase its refining capacity from 250 million tonnes per annum (mtpa) to 450 mtpa, establishing itself as a key player in the global oil market.
- For companies such as Aramco and ADNOC, this project presents opportunities for diversification, global expansion, risk mitigation, and access to a substantial oil market.
Future Possibilities
Feasible alternatives include exploring alternative coastal sites within Maharashtra or considering other coastal states. Another, more radical option is to divide the proposed mega refinery into smaller units.
Vagus Nerve
Context:
- The topic of the vagus nerve has gained significant attention online due to its potential health benefits, ranging from anxiety relief to addressing obesity.
- A variety of videos and devices are available, offering methods for stimulating the vagus nerve. Recent research has also associated vagus nerve dysfunction with long COVID.
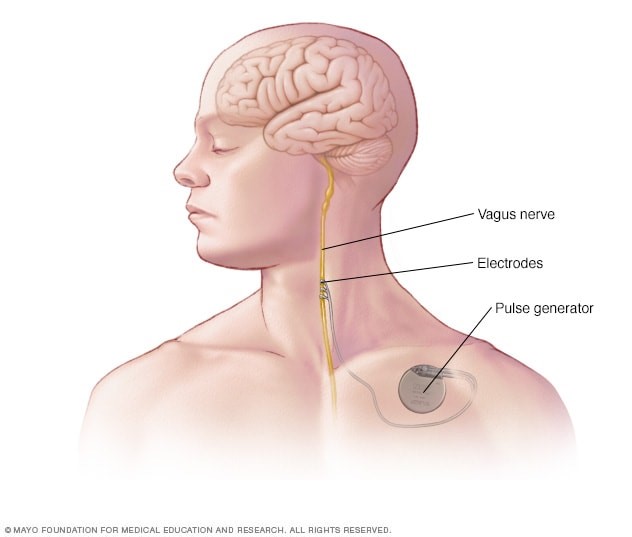
- Understanding the Vagus Nerve A Pair of Nerves: Comprising two nerves, one on each side of the body, the vagus nerve extends from the brainstem through the neck, chest, and stomach.
- Part of the Parasympathetic Nervous System: These nerves are integral components of the parasympathetic nervous system, responsible for inducing relaxation and rest in the body while regulating functions such as heart rate, blood pressure, digestion, and contributing to immune system responses.
Why Researchers are Focusing on the Vagus Nerve Several factors contribute to the intensive research surrounding the vagus nerve:
- Extensive Reach: The vagal nerves are the longest cranial nerves, establishing connections between the brain and the large intestine, as well as interacting with critical regions in the neck, heart, lungs, abdomen, and digestive tract.
- Communication Hub: These nerves encompass 75% of the nerve fibers within the parasympathetic nervous system, enabling two-way communication between the brain and the body.
- Health Implications: Scientists are exploring how stimulating these “sensory superhighways” might activate the parasympathetic nervous system and potentially provide therapeutic benefits for various health conditions.
- Medical Applications of Vagus Nerve Stimulation Epilepsy and Depression: Implantable vagus nerve stimulators are employed to treat epilepsy and depression, particularly when standard treatments prove ineffective. These devices stimulate specific brain areas associated with seizure control and mood regulation.
- Inflammation Regulation: The vagus nerve plays a significant role in regulating inflammation, with potential implications for treating various conditions by modulating post-infection inflammation.
- Vagus Nerve and Long COVID Research indicates a potential link between vagus nerve dysfunction and post-COVID-19 conditions (PCC), commonly referred to as long COVID.
- Patients experiencing PCC exhibit symptoms indicative of vagus nerve dysfunction, suggesting a potential role in the underlying mechanisms of PCC.
- Additional research is exploring impaired vagal activity in long COVID patients and potential therapeutic strategies involving vagus nerve stimulation.
Natural Approaches to Stimulate the Vagus Nerve Numerous natural methods are believed to stimulate the vagus nerve, including:
- Meditation: Emphasizing longer exhalations compared to inhalations.
- Exercise: Engaging in physical activity.
- Massage: Utilizing techniques such as reflexology.
- Music: Incorporating humming and singing.
- Cold Exposure: Applying a cold pack to the face or engaging in icy water immersion.
Limitations and Considerations
- It’s important to note that implanted vagus nerve stimulation is not a universal solution and should not replace conventional treatments.
- Instead, it serves as an adjunctive therapy for most conditions and necessitates further research to comprehensively understand its potential therapeutic effects.
- The use of vagus nerve stimulation devices should be carried out under medical supervision due to their influence on heart rate and blood pressure.
Adherence to specific protocols, typically in a clinical setting, is essential for safe usage.
Data-driven Innovations in Agriculture
Context
- In an auspicious development, the National Bank for Agriculture and Rural Development (Nabard) has forged a strategic alliance with the United Nations Development Programme (UNDP) in India.
- Their joint mission: to co-create innovative solutions harnessing the power of data, all in the service of smallholder farmers.
A Path to Improved Livelihoods
Fostering Prosperity in India’s Agricultural Heartland
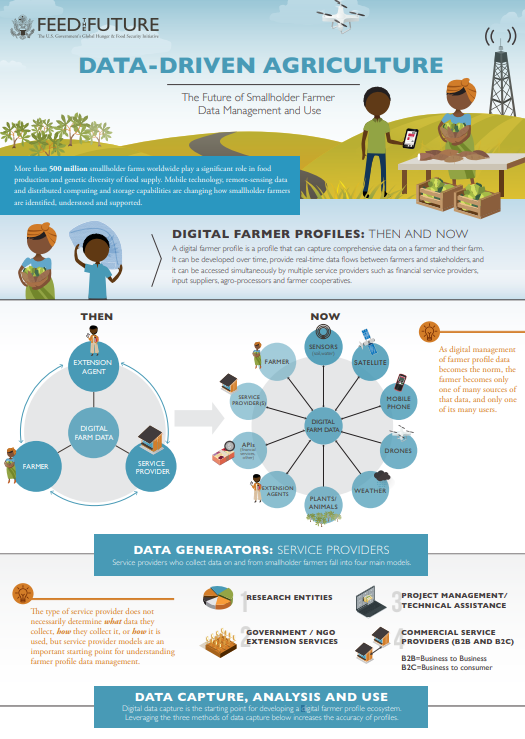
This landmark partnership has set its sights on the transformation of the lives and livelihoods of smallholder farmers. Their shared vision involves the seamless exchange of open-source data, a catalyst for product development, technology transfer, and the formulation of forward-thinking policies.
Bolstering Climate Resilience in Agriculture
A Crucial Focus for Sustainable Farming: At the core of this collaboration lies an unwavering commitment to enhancing climate resilience within the agricultural sector. The cornerstone of their efforts is the dissemination of collaborative digital public assets, epitomized by DiCRA (Data in Climate Resilient Agriculture).
DiCRA: A Gateway to Climate-Resilient Agriculture
Unlocking Geospatial Insights for Sustainable Farming: DiCRA, meticulously curated by UNDP in partnership with other esteemed organizations, offers unfettered access to critical geospatial datasets that hold the key to climate-resilient agriculture.
A Digital Public Infrastructure for Rural India
Elevating Smallholder Farming through Data: This pioneering collaboration signifies a significant opportunity to harness the untapped potential of data, positioning it as a digital public resource to benefit India’s rural farming community.
Promoting Best Practices and Resilience
Unlocking the Potential of Open Data Innovation: Open data innovations, such as this initiative, hold the promise of advocating for best practices, optimizing agricultural investments, and fortifying the resilience of smallholders—particularly women—against a wide spectrum of risks.
National Logistics Policy 2022
Context:
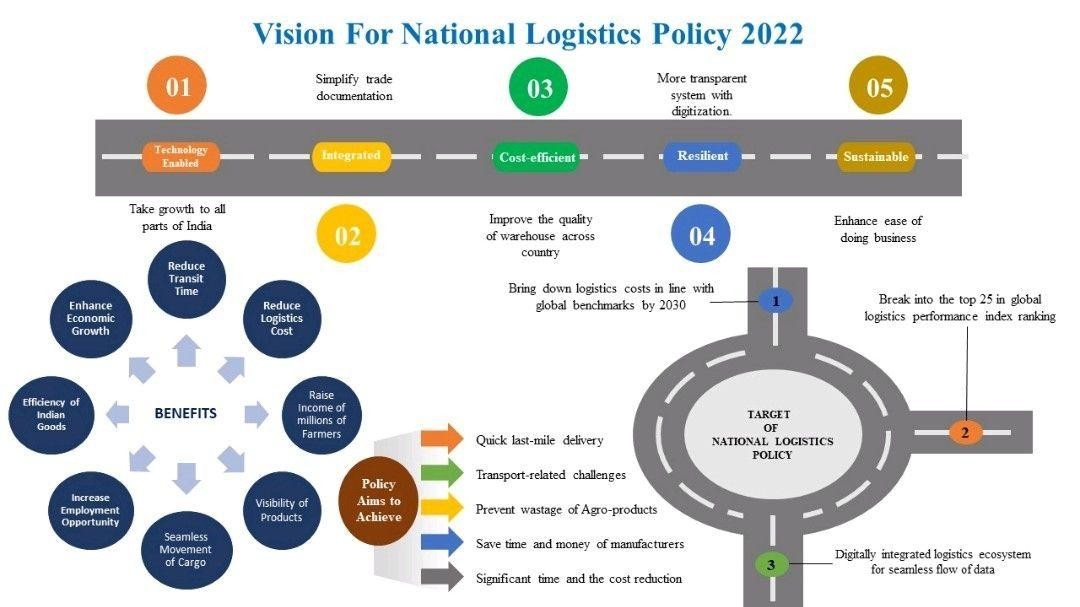
- In the context of India marking the one-year anniversary of the National Logistics Policy on September 17, 2023, the policy envisions fostering economic growth and enhancing business competitiveness in the country.
- This vision is underpinned by the establishment of an efficient, environmentally friendly, and cost-effective logistics network achieved through the utilization of technology and a skilled workforce.
- The overarching goal is to reduce operational costs while improving overall logistics performance.
The key objectives of the National Logistics Policy (NLP) :
- Reducing the overall logistics costs within India.
- Elevating India’s ranking on the Logistics Performance Index to be among the top 25 nations by 2030.
- Creating a data-driven decision-making framework to support an efficient logistics ecosystem.
The Comprehensive Logistics Action Plan (CLAP) has been devised as a strategic roadmap to realize these objectives. The CLAP comprises various action areas, including:
- Integrated Digital Logistics Systems
- Standardization of Physical Assets and Service Quality Benchmarking
- Logistics Human Resource Development and Capacity Building
- State Engagement
- Enhancement of Export-Import (EXIM) Logistics
- Development of a Services Improvement Framework
- Sectoral Plans for Efficient Logistics (SPEL)
- Facilitation of the Development of Logistics Parks
Progress in implementing the NLP can be summarized as follows:
- Unified Logistics Interface Platform (ULIP):
- Introduction of ULIP to enable digital integration in logistics, offering a single sign-on for users.
- Integration of 34 logistics-related digital systems/portals across various Ministries and Departments.
- Integration of GST data with ULIP.
- Private sector involvement, with over 614 industry players registered.
- 106 private companies have signed non-disclosure agreements, and 142 have submitted 382 use cases.
- 2. Export-Import (EXIM) Logistics:
- Measures taken to promote trade facilitation and streamline EXIM logistics.
- Addressing infrastructure gaps.
- Development of a comprehensive port connectivity plan.
- Efforts to enhance port productivity and reduce logistics costs.
- Implementation of the Logistics Data Bank (LDB) for tracking EXIM cargo.
- Human Resource Development:
- Development of qualification packs for various job roles in the logistics sector.
- Capacity-building webinars conducted.
- Development of syllabi and training modules.
- Sectoral Plan for Efficient Logistics (SPEL):
- Formulation of plans to address sector-specific needs.
- Emphasis on the movement of bulk and break-bulk cargo.
- Development of the Comprehensive Port Connectivity Plan (CPCP).
- Ongoing plans for efficient coal evacuation and improvements in the steel sector.
- State Engagement:
- States and Union Territories (UTs) are developing State Logistics Plans (SLPs) aligned with the NLP.
- Monitoring logistics performance through the Logistics Ease Across Different States (LEADS) index.
- Notification of State Logistics policies by 22 States.
Efforts to estimate logistics costs as a percentage of GDP.
Conclusion:
The National Logistics Policy of India, on its one-year anniversary, is aimed at transforming the logistics landscape by leveraging technology, human resources, and strategic planning to reduce costs and improve efficiency, ultimately enhancing the nation’s economic growth and global competitiveness.