2. Minority Institutions need NOT provide Reservations: Madras HC
3. Nobel Prize in Medicine
4. Khadi Mahotsav 2023
5. Asia’s Disputed Waters
6. Operation Kachchhap
7. JuMBO
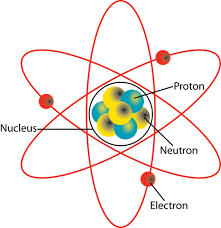
Physics Nobel for Electron Dynamics
Central Idea:
The 2023 Physics Nobel Prize has been awarded to Anne L’Huillier, Pierre Agostini, and Ferenc Krausz for their groundbreaking experiments that have provided humanity with innovative tools to investigate the behavior of electrons within atoms and molecules.
Measuring Rapid Electron Processes:
- Their pioneering work has facilitated the generation of ultra-short pulses of light, lasting only attoseconds (1×10−18 of a second), which has enabled the observation and measurement of the lightning-fast processes through which electrons move and change energy.
Observing Subatomic Motion:
- Electrons, the minuscule particles orbiting the nucleus within atoms, move at incredible speeds, rendering real-time observation impossible.
High-Shutter-Speed Analogy:
- Analogous to a high-shutter-speed camera that freezes motion to capture clear images, the trio’s research has achieved the capability to “freeze” electron movement using ultra-short light pulses.
Their Journey to Success:
- Anne L’Huillier’s discovery in 1987 revealed that laser light waves interacting with noble gases could provide certain electrons with additional energy, which was subsequently emitted as light. She continued to develop this concept.
Pierre Agostini’s Breakthrough:
- In 2001, Pierre Agostini successfully generated consecutive light pulses, each lasting just 250 attoseconds.
Ferenc Krausz’s Contribution:
- Simultaneously, Ferenc Krausz’s experiments isolated single light pulses lasting 650 attoseconds, yielding invaluable insights into atomic processes.
Significance of their Work:
- Their work in atto-second physics has opened doors to understanding mechanisms controlled by electrons.
Eva Olsson’s Insight:
- According to Eva Olsson, Chair of the Nobel Committee for Physics, this breakthrough enables us to comprehend electron-driven phenomena and explore their practical applications.
Potential Medical Application:
- The application of these techniques to study molecular-level changes in blood holds promise for aiding in disease identification.
Advanced Electronics:
A deeper understanding of electrons can contribute to the development of more efficient electronic devices.
India faces a tough battle ahead in protecting its female population from anaemia
Context:
- During the recent International Conference on Maternal & Child Health and Nutrition, several countries, including India, Nepal, Bangladesh, Malaysia, the USA, and the Netherlands, came together with a shared goal: to combat the persistent issues of anemia and malnutrition affecting mothers and children worldwide.
In India, the situation is concerning:
- Stunting: While there has been a slight reduction in stunting rates (35.5% from 38.4% in NFHS4), 13 States or Union Territories have witnessed an increase in stunted children since the National Family Health Survey (NFHS4), including Gujarat, Maharashtra, West Bengal, and Kerala.
- Malnutrition: Malnutrition trends from NFHS surveys indicate that wasting, a severe form of malnutrition, has either increased or remained stagnant over the years.
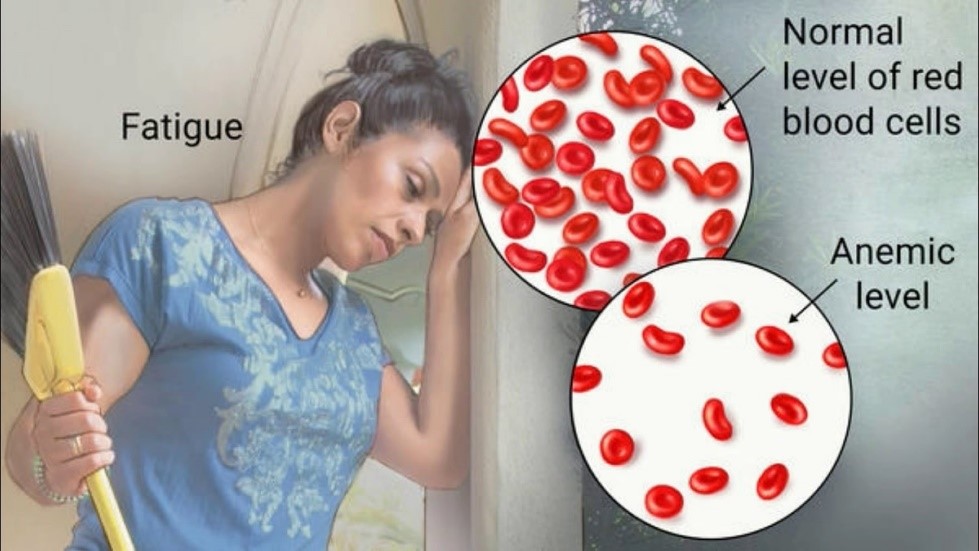
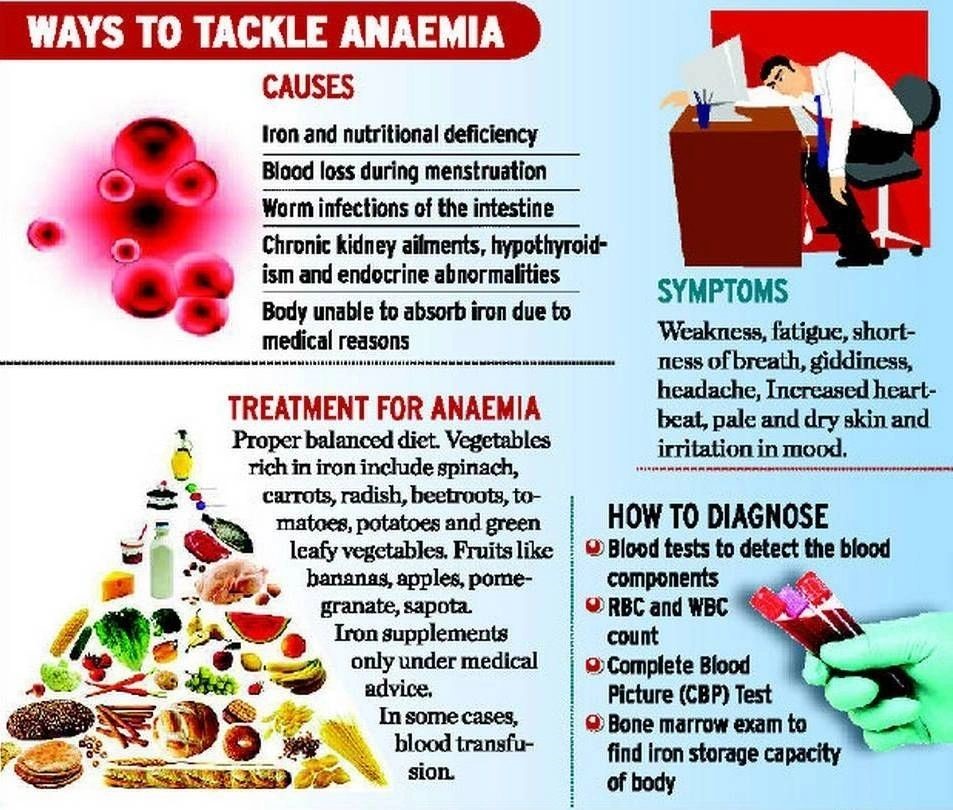
3. Anaemia: India holds the unfortunate title of having the highest prevalence of anaemia globally. The NFHS5 survey reveals that over 57% of women (1549 years) and more than 67% of children (six59 months) suffer from anaemia. Despite the Indian government’s efforts through the Anemia Mukt Bharat program, anaemia remains a significant public health concern across different income groups.
- Anaemia is characterized by a low number of red blood cells, specifically low hemoglobin or hematocrit Hemoglobin, the primary protein in red blood cells, carries and delivers oxygen throughout the body.
- According to the World Health Organization (WHO), anaemia occurs when the number of red blood cells or the concentration of hemoglobin within them falls below normal levels, compromising immunity and hindering cognitive development.
- The symptoms of anaemia include fatigue and shortness of breath. This condition affects individuals of all age groups, leading to reduced physical and cognitive growth, impairing the alertness of children and adolescents, and limiting their potential as productive citizens.
- Anaemia among adolescent girls often progresses to maternal anaemia, contributing to maternal and infant mortality rates and general community health issues.
Several factors contribute to the high prevalence of anaemia in India:
- Imbalanced Diet: Diets centered around cereals with limited consumption of iron-rich foods like meat, fish, eggs, and dark green leafy vegetables are associated with higher anaemia levels.
2. Underlying Factors: Poor water quality and sanitation conditions can negatively impact iron absorption in the body, contributing to anaemia.
- Iron Deficiency: Inadequate intake of iron, folic acid, or vitamin B12 is a common cause of anaemia, along with other conditions such as pregnancy, heavy periods, blood disorders, inherited disorders, and infectious diseases.
Govt. Efforts
- To combat this issue, India has implemented the Anaemia Mukt Bharat scheme, which aims to reduce anaemia prevalence by providing iron and folic acid supplementation to under-five children, along with deworming and advanced research initiatives.
- Additionally, other programs like Surakshit Matritva Aashwasan (SUMAN), Janani Suraksha Yojana (JSY), Pradhan Mantri Surakshit Matritva Abhiyan (PMSMA), LaQshya, Monthly Village Health, Sanitation and Nutrition Day (VHSND), and various delivery point enhancements are in place to improve maternal and child healthcare.
- To address this critical issue effectively, the government must establish strong partnerships with non-profit organizations, invest in nutrition-focused interventions, and consider cultural, social, and economic factors.
- Iron fortification programs, such as fortifying staple foods like wheat flour, can also play a vital role in combating anaemia.
Conclusion
Addressing anaemia is crucial not only for individual health but also for the overall productivity and economy of the country. It is imperative to include anaemia as a priority within the National Health Mission.
UMMEED: Comprehensive School Plan for Suicide Prevention
Context:
The Ministry of Education has introduced a set of draft guidelines called UMMEED (Understand, Motivate, Manage, Empathize, Empower, Develop) aimed at preventing student suicides in schools.
Causes behind increased suicide rates
- The rise in student suicide cases is attributed to a complex interplay of personal and social factors, rather than a single triggering event.
- These factors affect not only the individual but also have repercussions on families, schools, and the wider community.
- Students undergo various transitions during their school years, such as moving from home to school, changing schools, transitioning to college, and coping with personal losses like the loss of a family member or friend.
- Additionally, they face developmental challenges related to physical changes, peer pressure, career choices, academic stress, and pressure to excel in competitive exams.
- Negative aspects of the school environment, such as unhealthy relationships with peers or teachers, discrimination, bullying, harassment, humiliation, and isolation, can also contribute to students’ emotional struggles.
- Family dynamics, including the absence of school-family connections, parental neglect or abuse, lack of acceptance or recognition within the family, family history of suicide, and criticism or bullying by family members, play a significant role in this context.
Initials symptoms of Vulnerable Students
- Identifying students at risk of self-harm or suicide involves recognizing warning signs.
- These signs can manifest in feelings of hopelessness, guilt, shame, self-hatred, and persistent sadness.
- Behaviors such as withdrawal from social interactions, difficulty concentrating, mood swings, changes in appetite or sleeping patterns, lack of participation in school activities, carelessness about safety, and substance use are indicative of distress.
- These students may also become detached from their surroundings.
About UMMEED
- UMMEED guidelines serve as a compass for schools to enhance sensitivity, understanding, and support for students dealing with self-harm tendencies.
- These guidelines are aligned with the National Education Policy (NEP) 2020, which emphasizes holistic education encompassing cognitive and emotional development.
Action Plan for Schools
The action plan for schools includes the formation of a School Wellness Team (SWT) led by the School Principal. When a student exhibiting warning signs is identified, the SWT takes immediate action. The SWT also plays a crucial role in raising awareness about mental well-being and suicide prevention within the school community.
- Promoting a positive school environment involves encouraging peer support through group activities and organizing stress-reduction activities like yoga and meditation.
- Providing channels for expression, such as access to trained counselors and suggestion boxes, is essential. Schools can compile resources like helpline numbers and contact information for counselors and SWT members to facilitate help-seeking.
Integrating mental well-being into daily school interactions and creating a safe physical environment both within and outside the school are also emphasized.
Efforts for endorsing a positive school environment
- Encouraging school-community partnerships among stakeholders like school administrators, teachers, counselors, students, medical staff, support staff, parents, and the broader community is vital.
- Building awareness about mental well-being through various activities like role plays, storytelling, rallies, posters, exhibitions, and annual themes is encouraged.
- To prevent suicides and respond to crises effectively, it is crucial to empower all stakeholders, including teachers, staff, students, and families.
- Immediate action and support for at-risk students are essential, with a focus on maintaining records of at-risk behaviors and connecting with parents after incidents.
- The warning signs are categorized into three areas: feelings, behavior, and actions. Students exhibiting feelings of hopelessness, helplessness, worthlessness, guilt, shame, or a lack of concentration, along with withdrawal from social interactions and sudden mood swings, are at risk.
- Those displaying reckless behavior, discussing self-harm or suicide, and becoming detached are also considered as displaying warning signs.
Schools should regularly assess their suicide prevention efforts, with SWT and other stakeholders meeting periodically to discuss their experiences, gather feedback, and identify areas for improvement.
Nanoparticles from vehicle fumes can cause acute illness
Context:
- In a recent study published in the journal “Urban Climate,” researchers have shed light on the potential health risks posed by vehicular emissions, indicating that these emissions can lead to both chronic and acute illnesses by allowing nanoparticles to travel from the respiratory system to other parts of the human body.
Key Findings of the Study:
- The study investigated nanoparticles ranging in size from 10 to 1090 nanometers during two periods in 2021, from April to June and October to November, in Northwest Delhi.
- It was observed that nanoparticles in road environments have the ability to penetrate deeper into the respiratory system compared to other pollutants.
- The study emphasized that in urban settings, ultrafine particles measuring 1 to 100 nanometers contribute significantly, up to 90%, to the overall particle concentration.
- Researchers noted that the size of these particles varies depending on their sources.
Sources of Nanoparticles:
- The study identified urban road environments as the primary source of nanoparticles, primarily stemming from the combustion processes in automobiles.
- The concentration of these particles in urban roadside areas fluctuates with human activity, particularly vehicular emissions.
Factors Influencing Nanoparticle Dispersion:
- An increase in relative humidity leads to higher concentrations of nanoparticles due to particle coagulation.
- Peak morning and evening hours exhibit elevated concentrations of these pollutants, primarily due to vehicular emissions.
- Higher wind speeds can disperse these particles further.
Significance of the Study:
- The study’s particle number concentration (PNC) estimates offer valuable insights into particle deposition within the human respiratory system, accounting for various inhalation rates and physical activities.
- The quantitative results derived from this research can be instrumental in assessing human health impacts, formulating policies and standards, and implementing pollution mitigation measures with implications for climate change and sustainability.
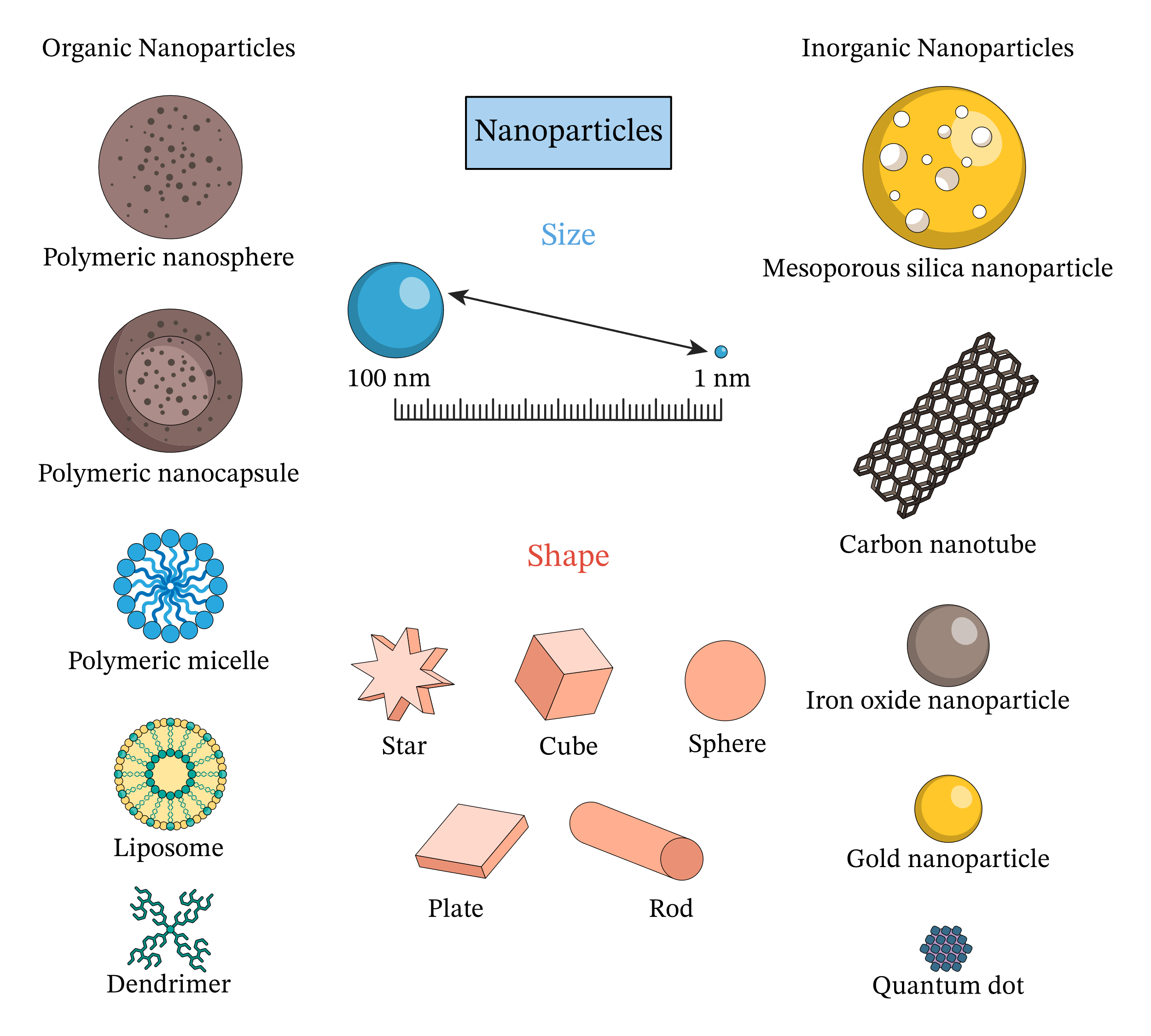
What Are Nanoparticles?
Nanoparticles are minute particles ranging in size from 1 to 100 nanometers. They are imperceptible to the human eye and possess distinct physical and chemical properties compared to their larger counterparts. The European Commission defines nanoparticles as particles in which at least half measure 100 nm or less and are typically composed of only a few hundred atoms.
Concerns Associated with Nanoparticles:
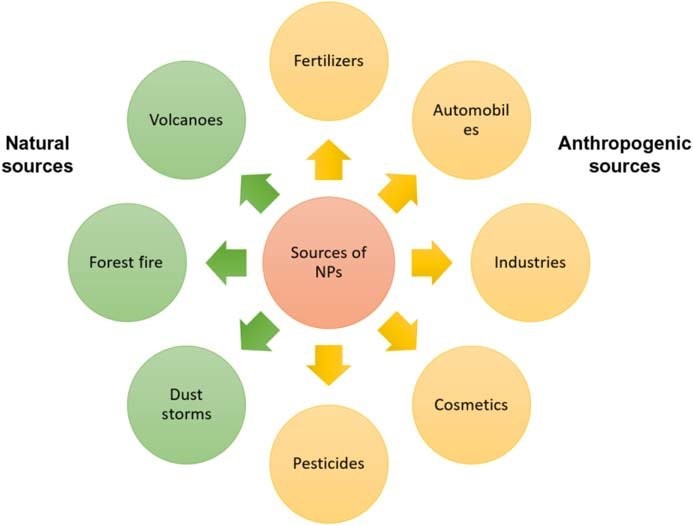
- Natural Sources: Nanoparticles occur naturally in the environment in significant quantities. Examples include salt aerosols from the sea and nanoparticles emitted during volcanic eruptions and fires, some of which can pose health risks
- Human-Made (Anthropogenic) Sources: Man-made nanoparticles are released during large industrial processes, and in modern life, major contributors include power stations, jet aircraft, and vehicles with internal-combustion engines, including car tires. These sources emit various types of nanoparticles, such as partially burned hydrocarbons, ceria, metallic dust, calcium carbonate, and silica.
Can Nanoparticles Interact with Living Organisms?
- Nanoparticles can have dimensions similar to biological molecules like proteins. In living systems, they may readily bind to large molecules as they enter tissues and bodily fluids.
- This interaction depends on nanoparticle surface characteristics and is relevant for drug delivery purposes. Additionally, factors influencing interactions include nanoparticle dose, their ability to distribute within the body, and solubility.
Some nanoparticles dissolve easily and exhibit effects similar to the chemicals they are composed of, while others persist in biological systems, raising concerns about their long-term impact.
Critical Minerals and Clean Energy Summit- 2023
Context:
The inaugural IEA Critical Minerals and Clean Energy Summit, held in Paris on September 28, 2023, aimed to address the challenges and opportunities associated with the increasing demand for minerals crucial for clean energy technologies.
Rapid Growth in Critical Minerals Market
The IEA’s 2023 Critical Minerals Market Review highlighted the remarkable growth in the sector, reaching a market value of $320 billion in 2022.
Global Summit on Critical Minerals
Leaders from 50 countries gathered in Paris for a summit dedicated to discussing the challenges and opportunities presented by critical minerals.
Key Actions Agreed Upon
During the summit, six pivotal actions were agreed upon:
- diversifying mineral supplies,
- optimizing technology and recycling,
- promoting market transparency,
- improving information access,
- incentivizing sustainable production, and
- enhancing international cooperation.
Surge in Critical Mineral Demand
The demand for critical minerals has surged, with notable examples including a tripling of lithium demand and a 70% increase in cobalt demand from 2017 to 2022. Projections suggest that, in a Net Zero scenario by 2050, critical mineral demand could reach 30 million tonnes.
Role of Recycling and Technology
Recycling and innovative technology play vital roles in reducing future supply constraints. New technologies can reduce energy and water requirements in mineral extraction and processing, thus enhancing resource efficiency.
Addressing Pricing Transparency
The lack of pricing transparency in the critical minerals market can hinder investments. The IEA is actively working to strengthen market monitoring.
Upcoming Ministerial Meeting
In February 2024, the IEA will host a Ministerial Meeting to assess global cooperation on energy security and climate change.
Importance of Critical Energy Minerals
- Clean Energy Technologies and Essential Minerals
Clean energy technologies rely heavily on critical minerals such as copper, lithium, nickel, cobalt, and rare earth elements. These minerals are indispensable for various applications, including wind turbines, electric vehicles, and electricity networks.
- Mineral Requirements for Clean Energy Projects
Clean energy projects, such as solar PV plants, wind farms, and electric vehicles, typically require a greater quantity of critical minerals compared to traditional fossil fuel-based counterparts. For example, an electric car requires six times the mineral inputs of a conventional car, and an offshore wind plant requires 13 times more minerals than a similarly sized gas-fired plant.
- Impact of Renewable Energy Investments
The shift toward renewable energy sources has led to a 50% increase in the average amount of mineral resources needed for new power generation capacity since 2010.
- Specific Mineral Requirements
Different clean energy technologies have specific mineral requirements. Lithium, nickel, cobalt, manganese, and graphite are crucial for batteries, while rare earth elements are essential for wind turbines and electric vehicle motors.
- Continued Growth in Mineral Demand
The demand for critical minerals has continued to grow, with a tripling of lithium demand, a 70% rise in cobalt demand, and a 40% increase in nickel demand from 2017 to 2022.
- Investment and Exploration
Investments in critical minerals development have been on the rise, with a 20% increase in 2021 and a subsequent 30% increase in 2022, particularly focusing on lithium projects. Exploration spending also saw a 20% increase in 2022, primarily driven by the exploration of lithium resources.
Top Producing Countries
Key countries in the production of critical minerals include China, Australia, and the Democratic Republic of the Congo.
- Human-Made (Anthropogenic) Sources: Man-made nanoparticles are released during large industrial processes, and in modern life, major contributors include power stations, jet aircraft, and vehicles with internal-combustion engines, including car tires. These sources emit various types of nanoparticles, such as partially burned hydrocarbons, ceria, metallic dust, calcium carbonate, and silica.
Can Nanoparticles Interact with Living Organisms?
- Nanoparticles can have dimensions similar to biological molecules like proteins. In living systems, they may readily bind to large molecules as they enter tissues and bodily fluids.
- This interaction depends on nanoparticle surface characteristics and is relevant for drug delivery purposes. Additionally, factors influencing interactions include nanoparticle dose, their ability to distribute within the body, and solubility.
Some nanoparticles dissolve easily and exhibit effects similar to the chemicals they are composed of, while others persist in biological systems, raising concerns about their long-term impact.
BADIS LIMAAKUMI
Context:
In recent developments, scientists have achieved a significant breakthrough with the identification of a novel fish species, known as Badis limaakumi, residing in the Milak River within Nagaland.
Key Findings:
- This newfound species, located in Nagaland’s Mokokchung district, exhibits a distinctive opercular blotch situated at the base of its opercular spine, which serves both as a facial support structure and protective covering for the gills.
- Unlike other members of its family, Badidae, this species lacks spots on its sides, cleithrum (a membrane bone), and features fewer lateral line scales.
- Badis limaakumi stands as one of the 26 recognized fish species within the Badidae family and is distributed across India, Bangladesh, Nepal, Pakistan, Thailand, and Myanmar.
- Fish from the Badis family are also known as chameleon fish for their ability to change colour. This helps them blend with the surroundings when under stress.
- Notably, this newly discovered fish species differentiates itself from other Badis badis members due to its larger size and distinct physical attributes.
Milak River:
- The Milak River courses through Nagaland’s Mokokchung District.
• Its primary tributary is the Tsurong River.