Adapting the criminal justice system to current needs.
Context
In order to have a criminal justice system that is fair, just, and effective, the new bills that will replace the IPC, the CrPC, and the IEA need to be subjected to the appropriate level of scrutiny by the legislature.
Reformulation of Legislation Regarding Fundamental Laws
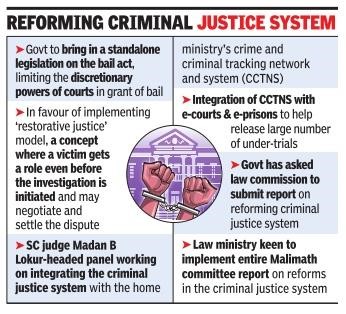
- Legislative Overhaul: The government promotes three legislation as a comprehensive replacement for basic criminal justice laws. These bills are the International Penal Code, the Criminal Procedure Code, and the International Environmental Act. This action provides some evidence that the legal basis is about to undergo a substantial overhaul.
- Parliamentary Scrutiny These measures are now being scrutinised by the Parliamentary Standing Committee, which is conducting an in-depth analysis of them. This is a reflection of the rigorous procedure that was used to pass this legislation, which ensured full analysis and potential changes.
The legislation, once passed into law, carry the promise of reshaping the legal environment in a manner that is more favourable to the authors’ goals. Their relevance in legal governance is shown by the fact that they have the ability to have an impact on and reimagine the criminal justice system.
Obstacles to Confront When Attempting to Modernise Jurisprudence
- Legal Reach and Methodology: Important doubts have been raised about the way in which the laws address civil law, which may indicate a move away from retributive justice towards restorative justice. The influence on a wide variety of legal concerns requires close examination.
- Achieving a Balance in Public Order :There are several challenges that arise when attempting to maintain public order while working within the framework of criminal prosecution. Because the legislation keep the structures in place, there has to be a careful equilibrium for successful governance.
- Modernization and Consistency: Critical concerns include age provisions, gender-related offences, and the consistent application of punishment rules. Modernization is also important. The laws ought to traverse contemporary values, conform with directives from the Supreme Court, and guarantee that sentence is consistent across the board.
Concerns Regarding Duplication as Well as Drafting
- Exceptions for Mental Illness: The successor for the IPC is in line with the Mental Healthcare Act and includes provisions for those suffering from mental illness. By taking into account issues pertaining to mental health, this addresses an essential component of the criminal justice system.
- Persistent issues: Entail duplications and discrepancies among legislation, which run the danger of misunderstanding and legal conflicts. These problems have been there for a long time. The legal environment is made even more complicated by the fact that specific regulations are ignored and outdated drawings are kept.
Insist on a Meticulous Examination by Parliament: Parliamentary examination to guarantee that these measures would result in a criminal justice system that is fair, just, and effective, while avoiding potential traps.
The Delhi government is planning to use "cloud seeding" to create rain in the face of pollution
Context
In the past, cloud seeding was only done to bring rain to places that were in danger of drought, not to reduce pollution.
Background:
- To clean up the air, the Delhi government had planned “artificial rain” or “cloud seeding.”
- India has tried this idea before, but only during the monsoon season (when clouds with water are present) and the months before the rainfall.
- Also, this has only been done in the country before to help places that are prone to drought get rain, not to cut down on pollution.
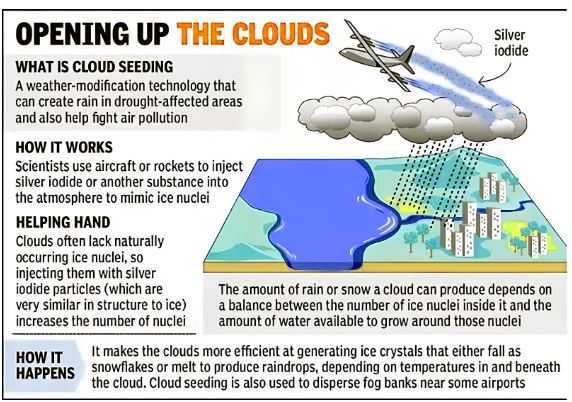
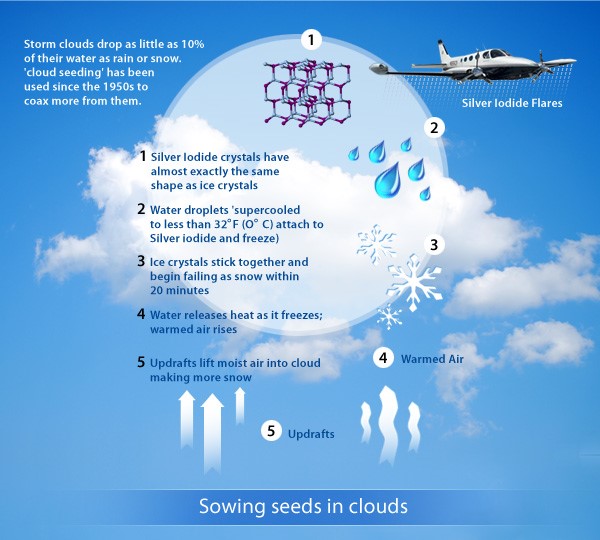
What cloud seeding is:
- As water vapour cools down around tiny particles, it forms drops that make up a cloud. It starts to rain when these drops hit each other and get heavier. When the cloud is full, it starts to rain.
- As part of cloud seeding, salts like silver iodide, potassium iodide, or sodium chloride are generally introduced into the clouds.
- These salts are called “seeds.” It is predicted that these salts will add more centres around which more cloud droplets can form. To get them into the cloud, either planes or engines on the ground are used.
Microphysical process:
- Seeding speeds up the microphysical processes in clouds. Enough big drops must form so that they can reach the earth’s surface without evaporating.
- Ice nuclei and cloud condensation nuclei: The stuff that goes into the cloud needs to have ice nuclei and cloud condensation nuclei, which are made from two different salts.
- Nodes of cloud condensation help make cloud drops, and nodes of ice condensation help make ice crystals. Crumbs of ice get bigger faster than drops of water, then fall.
Explanation Video: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=OddSiiiBtXE
Rural Business Sustainability: Prospects and Pitfalls
Context:
- In the context of rural enterprise development, rural entrepreneurship is crucial to India’s economic success and prosperity.
- These businesses facilitate societal transformation at the grass-roots level while simultaneously generating cash.
- With approximately 63 million MSMEs in India, the vast majority of which are micro-enterprises, the status of rural entrepreneurship is promising.
- Many obstacles, such as sexism and a lack of business education and training, stand in the way of rural entrepreneurs’ success.
In order to create prosperity and economic progress, which in turn leads to improved employment possibilities and less migration, it is necessary to exploit local resources effectively. Manpower, cash, materials, machinery, and knowledge of the market are only some of the resources that need to be made accessible in order to successfully support rural businesses.
Self-Help Groups (SHGs), cooperatives, and producer companies are all examples of rural enterprises that fall under the umbrella of group entrepreneurship and, when successful, can bring in capital, generate new jobs, forge new relationships, access previously unavailable resources, and put idle savings to good use.
The Value of Entrepreneurship in Rural Areas
Utilisation of Resources:
The increased output of rural enterprises can be attributed to their efficient use of local resources like labour and materials.
They help to boost rural resources by encouraging savings in rural areas.
Creation of Job Opportunities:
Many people find work in rural areas because of the industries that thrive there.
They address the frequent issue of large-scale unemployment and underemployment in rural regions.
Reducing City-to-Country Moves:
Rural entrepreneurship helps give employment prospects, deterring rural populations from migrating to metropolitan regions in pursuit of work and, subsequently, eliminating rural-urban imbalances.
Support for Creative Endeavours:
Small business owners in rural areas play an important role in promoting and preserving India’s cultural heritage.
Combating Social Ills:
Poverty the spread of slums, and pollution in major cities may all be mitigated by an increase in rural entrepreneurship.
Motivating Teens in the Country:
Entrepreneurship in rural areas shows young people from these areas that starting their own business is possible and validates their interest in this field.
Inspiring Growth in the Economy:
To reduce rural-urban migration and problems such as uneven urban growth, slum expansion, social conflicts, and environmental pollution, rural industrialization is essential.
Improvements in Rural Life:
The agricultural community now has a better understanding of the need of conserving our planet’s natural resources.
The emergence of the agricultural sector.
Handloom and other traditional handicraft industries are being revitalised as a result of the rise of specialised markets.
Challenges
- Entrepreneurs in rural areas may face sexism and other forms of prejudice stemming from entrenched gender roles and cultural expectations. For inclusive entrepreneurship to succeed, these prejudices must be overcome.
- Many rural company owners struggle to properly manage and expand their operations because they lack a solid grounding in basic business fundamentals. Because of this information deficiency, their judgement and strategy may suffer.
- Inadequate Skillsets Some rural company owners may be missing key business management and operational abilities. Improving their talents necessitates the acquisition of new skills.
- It is essential for rural business owners to have a solid grasp of market conditions, client tastes, and demand. It might be difficult to develop commercially successful goods or services without an in-depth understanding of these elements.
- Market links It can be difficult for rural business owners to make and keep links to larger markets. Having easy access to markets is crucial for driving sales and expanding operations.
- Businesses in rural areas face competition not just from their neighbours, but also from those in larger cities. Finding a way to differentiate yourself from the competition is crucial to achieving any level of success.
- Difficulties in Production and Distribution Caused by Poor Infrastructure and Logistics Poor infrastructure, transportation, and logistics can impede the effective production and distribution of goods.
- Many startups fail because their founders don’t know about government funding opportunities. Learning about and using these tools may help their companies succeed.
- It might be difficult for rural business owners to find and keep qualified workers. Issues with labour must be resolved for efficient delivery of goods or services.
- Inadequate working capital limits a company’s capacity to run day-to-day operations, which in turn reduces profitability and threatens its ability to expand.
- Businesses in rural areas may have trouble keeping up with the competition due to a lack of up-to-date technology. Adapting to technological changes is crucial for survival.
- It might be difficult to diversify one’s product or service offers. Companies can better meet customer needs and reduce risk by diversifying their operations.
Methods to Improve Rural Entrepreneurship and Employment
- Selecting participants for a project-based skilling and entrepreneurship development programme depends on their existing talents, where they live, and other demographic characteristics. After selection, participants get skill training and continuing assistance.
- Cluster development takes a comprehensive strategy, incorporating both forward and backward links to facilitate effect. Its primary goal is to strengthen support systems for businesses in rural areas.
- Entrepreneurial incubation in rural areas involves selecting and training prospective entrepreneurs, then providing them with support for anything from six months to a year. Training in product completion, promotion, and credit links are provided during incubation to encourage long-term potential for self-employment.
Rural Business Development Programmes and Policies
- Initiated by the Government of India, the Start-up Village Entrepreneurship Programme (SVEP) helps new and existing businesses in India’s rural areas. Financial aid is provided, and a group of Community Resource Persons-Enterprise Promotion (CRP-EP) is formed to give services to businesses in rural areas.
- The government plays a crucial role in bolstering and expanding rural businesses. Through programmes like SVEP, the government encourages the development of rural firms and the creation of self-employed individuals.
- Businesses in rural areas are crucial to the development of the Indian economy. Rural entrepreneurship, job creation, and economic growth face constraints such as insufficient infrastructure and restricted access to money; nevertheless, these issues may be addressed with coordinated and continuous efforts, coupled with government support.
Conclusion:
Promoting rural entrepreneurship is crucial to India’s development since it will lead to economic expansion and more job openings. Government programmes like Pradhan Mantri-YUVA and other similar initiatives have played a critical role in educating and training rural young to become entrepreneurs.
Mentoring and filling knowledge gaps are crucial to fostering rural entrepreneurship, and here is where civil society organisations, NGOs, and specialists in the field come in. Entrepreneurial spirit and originality may be encouraged by setting up incubation centres and holding ideation workshops and hackathons in Tier 2 and Tier 3 cities.
In partnership with organisations like TATA trusts, the government fosters rural entrepreneurship through the ‘Foundation for Development of Rural Value Chain’ (FDRVC), which promotes value chain projects and large-sized producer firms. Empowering rural businesses by giving them access to resources and information is crucial to their growth and prosperity.
The Constitution: An Evolving Text
Context
There has been a rising desire to modify the Constitution to reflect the current state of affairs as we move into the new Parliament building and away from the old one that gave us the Constitution.
Some more news:
- The 299 members of the Constituent Assembly of India worked tirelessly for 2 years, 11 months, and 18 days in the historic old edifice to write the Constitution of India.
- Important parts are asking fundamental topics like: Is India a country or merely a “Union of States”?
- Should we keep calling ourselves India, or should we switch to Bharat?
- Is it still important to have the word “socialist” in the Preamble?
- Is there any validity left in the “Basic Structure” argument?
About the Constitution as a Living Record:
- Constitution: It sets the rules and limits that politicians must follow when making decisions.
- Living paper: This paper responds to new situations and events all the time, almost like a living thing.
- Flexibility: A constitution shouldn’t stay the same; it should be able to adapt to changes in society over time through things like constitutional revisions.
- Evolution: A law that protects democracy while also letting new ideas grow is not only long-lasting, but also respected by the people who live in it.
- Important examples that show the Constitution is a live document: The Act of the 42nd Amendment: People often call it the “Mini Constitution” because it changed many parts of the Indian Constitution, such as the Preamble, the Directive Principles, the Judicial Review, the Emergency Provision, the Anti-Defection Law, the Election Commission, and more.
- The constitution’s basic framework and how it has changed over time: it came about through judicial analysis. In the 1973 case of Kesavananda Bharati, the judiciary put this idea forward.
- “Fundamental Rights”: People have different ideas about what these rights mean over time.The Supreme Court said that the right to privacy is a basic right in the case of K.S. Puttaswamy v. Union of India (2017).
- Reservations: The rules for making reservations have been changed so that more groups can use them.As an example, the Mandal Commission’s suggestions led to seats for people from Other Backward Classes (OBCs).
- Article 370 was taken away because it gave the state of Jammu and Kashmir extra autonomy. This was done by changing the constitution in 2019.
- There have been many talks and arguments about different parts of the Indian Constitution and the need for constitutional changes. One idea that is being talked about a lot is replacing the current constitution with a new one.
Arguments for a new constitution:
- It has been changed so many times: Considering how hard it is to change the Constitution, the number of changes seems pretty high.
- For example, ten changes were made in just three years, from 1974 to 1976. In contrast, the US Constitution has only been changed 27 times in 230 years.
- Calling India, a Nation: The constitution’s general description of India as a nation-state committed to democracy, equality, social justice, and unity in diversity shows that India is a nation. The new constitution can make this official by calling India a nation.
- The word “socialist” is used in the preamble. Thanks to the LPG changes of 1991, socialist ideas have become less strong in Indian politics wide range.
- R. Ambedkar said that the way society should be set up in terms of its social and economic aspects must be the people themselves make the choice.
- Biggest and Most Unread: It gives the government a lot of power to take advantage of people politically and economically.
- A Legacy of Colonialism: The Indian Constitution makes the government the boss and the people its slaves, which is a that the British government had.
- After 1947, Indian governments, like the British government before them, became the master and set rules on Indians’ rights to vote and do business.
- Reflecting modern values and goals: The Constitution is innovative in many ways, but it may not fully address Problems we face today include new technologies, climate change, environmental issues, LGBTQ+ rights, and changing ideas about what is fair and just.
Counterarguments
- The Indian Supreme Court (SC) has played a vital role in interpreting and enlarging the scope of the current constitution to suit contemporary concerns, thus there’s no need to rewrite it.
- A new constitution may not automatically result in more consistent legal interpretation. Consensual gay behaviour, for instance, was decriminalised by the Supreme Court of India (SC) in the case of Navtej Singh Johar v. Union of India (2018).
- The Constitution has been revised multiple times to address different problems, including reservation policies, anti-defection legislation, and the introduction of additional basic rights, since it allows for ample freedom to adapt.
- According to India’s Chief Justice, the Constitution’s core framework should be protected because it acts as a north star, pointing interpreters and implementers in the right way even when the road ahead is unclear.
- The existing Indian constitution is a reflection of the principles and ideals of the people who fought for India’s freedom in the past, and as such, it should be preserved for future generations.
- It would be more efficient to use these funds to combat challenges like poverty, provide access to quality education and healthcare, and improve the nation’s ageing infrastructure.
Way Forward:
- India or Bharat? Article 1 of the Constitution starts with both “India” and “Bharat” and sets the tone for the whole constitution. To change the name of the country, all that needs to be done is change Article 1.
- Expert Committee: Put together a group of people from different backgrounds to look over the current law and figure out what works and what doesn’t.
- For example, the National Commission to Review the Working of the Constitution looks at how the Constitution can best adapt to new needs and suggests changes that need to be made.
- Specific Areas of Concern: List the parts of the constitution that aren’t working right or are out of date and need to be changed. For example, the IPC, the CrPC, and the Evidence Act need to be changed.
- Strengthening Existing Provisions: To deal with modern issues like protecting the environment, equal rights for women, and technology progress, you might want to think about strengthening existing constitutional provisions.
Conclusion:
Extreme views may be right in theory and appealing from a moral point of view, but everyone should be ready to soften their extreme ideas and find a middle ground.
The Missteps of Start-ups: Insights Derived from the WeWork Case Study
The key notion
- The ascent and decline of WeWork serves as a notable case study that underscores the perils associated with market ambiguity, faulty business strategy, and inadequate capital management for aspiring entrepreneurs.
- The primary objective of this lesson is to emphasise the need of learning from past errors, aligning strategy with the prevailing demands of the business, and effectively managing and utilising capital in order to achieve enduring succes
- Developing enterprises with a comprehensive comprehension of the market, deliberate tactics, and judicious financial administration.
Quotations and pivotal expressions for enhancing the core value
- The present discourse serves as a cautionary narrative illustrating the antithesis of entrepreneurship.
- Entrepreneurship may be defined as the endeavour to achieve ambitious goals that may appear unattainable, often in the face of significant challenges and obstacles.
- WeWork’s strategy involved conflating a broad market with a market that could be effectively targeted and penetrated.
- The concept of blitzscaling, which emphasises prioritising rapid expansion over minimising losses, was created by Reid Hoffman.
- The significance of the amount of money expended in relation to the amount of money earned is of considerable importance.
- Boards that function as auditory assistance devices, reflective surfaces, and safety restraints.
- Society derives advantages from the process of innovation, although remains uncertain regarding the outcomes and success of specific entrepreneurial endeavours.
- The majority of new ventures experience failure, with just a select minority achieving success, which is sufficient for societal advantages.
- The WeWork phenomenon, characterised by its rapid ascent and subsequent decline, serves as a cautionary tale for entrepreneurs on the potential pitfalls of presentism.
- It is vital to acquire knowledge from one’s experiences, rather than only relying on the act of experiencing itself.
Important Points:
- The trajectory of WeWork: From an initial valuation of $47 billion, WeWork had a significant decline leading to its eventual bankruptcy, so highlighting the need of avoiding presentism within the realm of entrepreneurship.
- The entrepreneurial landscape is characterised by a high rate of failure among startups.
- However, it is important to recognise that successful businesses contribute to societal advancement through their innovation, enhanced productivity, and job creation.
One of the primary issues that need to be addressed are the challenges that arise in this context
- Market Misunderstanding: WeWork’s misinterpretation of its market resulted in a conflation of traditional office space with the potential market for co-working spaces, ultimately leading to a faulty strategic approach.
- The misapplication of blitzscaling is seen in WeWork’s disastrous foray into property leasing, highlighting the limited applicability of prioritising growth above preventing losses.
- The mismanagement of capital: WeWork shown proficiency in fundraising but exhibited a lack of proficiency in efficiently allocating and using cash, hence neglecting the significance of return on equity.
- Governance concerns arose inside WeWork when the board exhibited a tolerance for dubious behaviour by its creator, Adam Neumann.
- This leniency compromised the organization’s credibility, as the board failed to critically evaluate and challenge Neumann’s decisions, instead offering unwavering support.
- The failure to prioritise sustainability: WeWork’s organisational culture hindered the expression of opposing viewpoints, so impeding the establishment of a harmonious equilibrium between immediate profits and the long-term well-being of the corporation.
The present text will be subjected to an academic analysis.
- The misrepresentation of WeWork as a “tech-enabled physical, social network” resulted in the company setting unattainable goals and adopting unsustainable business strategies, causing confusion over its addressable market.
- The use of blitzscaling, while beneficial in certain markets, was shown to be unsuitable for property leasing, thereby emphasising the significance of aligning tactics with the unique dynamics of the business.
- The lesson in capital management highlights that the mere accumulation of money is insufficient to offset the absence of a robust plan, underscoring the need of prudent expenditure.
- The presence of inadequate governance facilitated unregulated acts by the founder, hence highlighting the important role of watchful boards in ensuring the implementation of ethical practises.
- The cultural influence of WeWork is characterised by a stifling of dissent, which has hindered the healthy interchange of ideas amongst those involved in both conceptualization and execution. This has therefore had an effect on the long-term survival of the organisation.
Potential Strategies for Progress:
- The acquisition of knowledge from errors is a crucial aspect of entrepreneurship, and the case of WeWork serves as a notable illustration of the significance of introspection in achieving future accomplishments.
- The strategic alignment of entrepreneurs necessitates the harmonisation of their strategies with the inherent characteristics of their respective industries. It is important for entrepreneurs to exercise caution and refrain from implementing methods, such as blitzscaling, in markets that are not conducive to such approaches.
- cash Respect: Fundraising is critical, but appreciating and employing cash intelligently is also important for continued success.
- Enhanced Governance: The implementation of robust governance practises, characterised by diligent oversight from boards, is vital in mitigating unethical behaviour and safeguarding the sustained well-being of corporations.
- Cultural adaptation entails fostering a business environment that places significance on the expression of differing viewpoints and cultivates a harmonious equilibrium between immediate advantages and enduring organisational viability.
In conclusion, the demise of WeWork serves as a valuable lesson in the realm of entrepreneurship, highlighting the need of avoiding presentism. This underscores the significance of strategic alignment, efficient capital management, diligent governance, and fostering a culture that promotes multiple opinions.