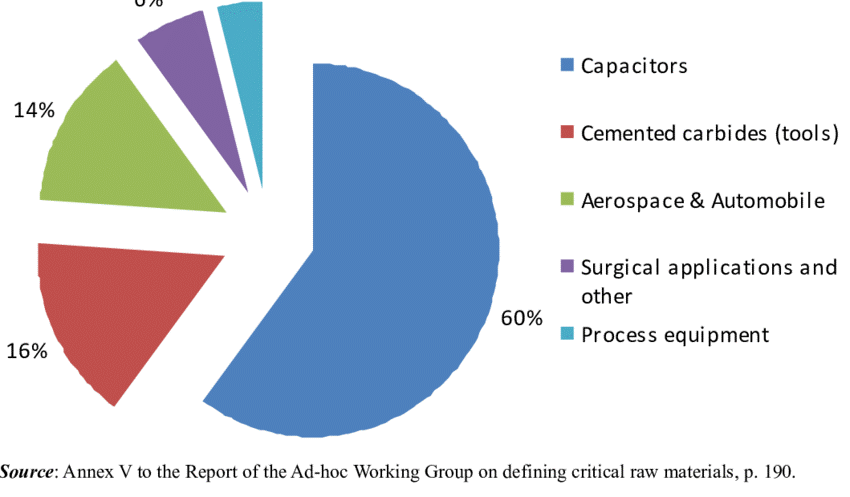
Tantalum Reserves found in Sutlej River
Context:
IIT-Ropar researchers have identified the presence of tantalum in the soil of Punjab’s Sutlej River Basin. While the origin of tantalum in the Sutlej is uncertain, it may be linked to tectonic plate movement in the Himalayan region, a probable source of this rare metal.
Tantalum Overview
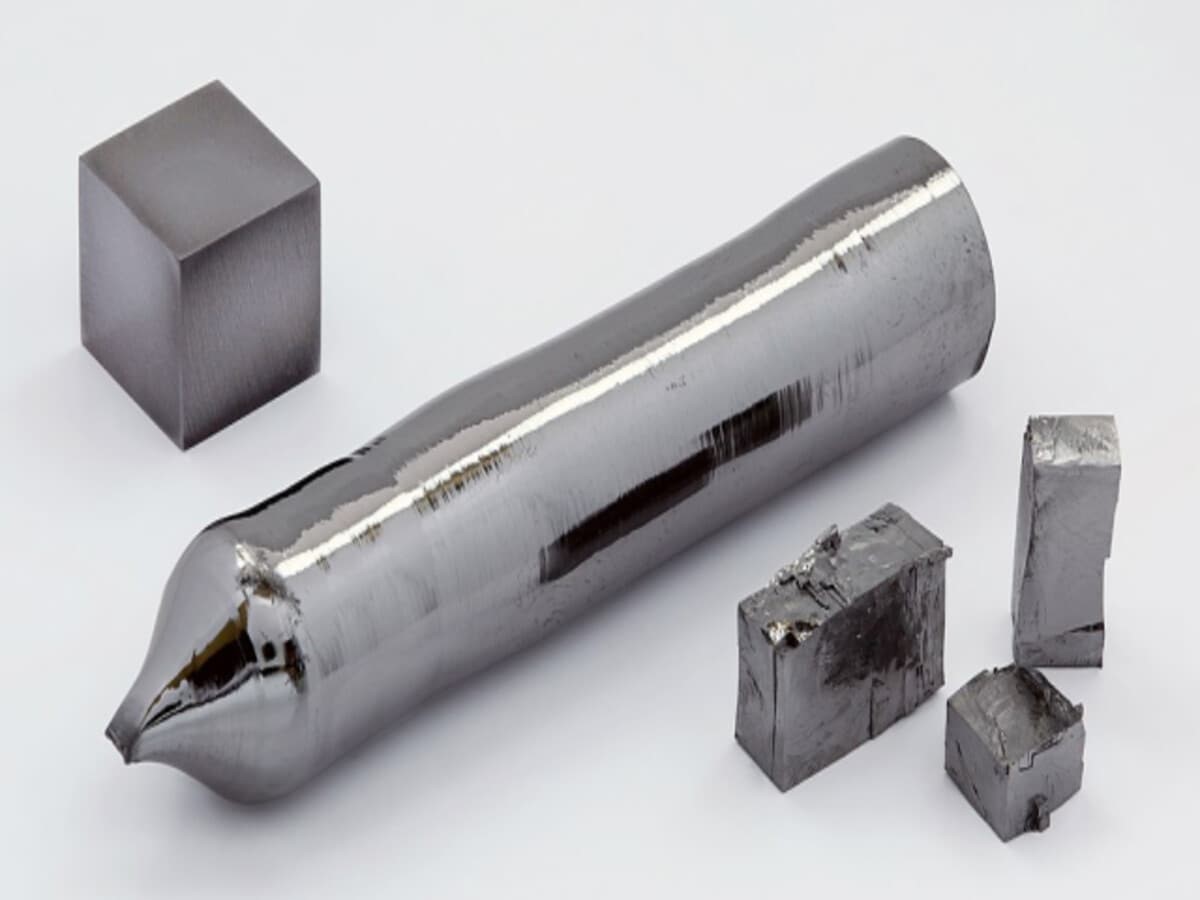
- An Uncommon and Valuable Element: Tantalum, characterized by its atomic number 73, is a rare and crucial metal in the realm of electronics and semiconductors.
- This dense, hard, gray metal is renowned for its exceptional resistance to corrosion.
- Outstanding Corrosion Resistance: Tantalum’s ability to create a protective oxide layer when exposed to air contributes to its resistance to corrosion, even in highly acidic environments.
- Versatile and Robust: Pure tantalum is ductile, allowing it to be stretched into thin wires without breaking. It withstands chemical damage below 150°C but is susceptible to hydrofluoric acid and certain other substances.
Historical Context
Swedish Origins: Initially confused with niobium, tantalum was first discovered by Swedish chemist Anders Gustaf Ekenberg in 1802 in Ytterby, Sweden.
Distinguishing Tantalum and Niobium: In 1866, Swiss chemist Jean Charles Galissard de Marignac clarified that tantalum and niobium are distinct elements.
Origin of the Name: Named after Tantalus, a figure from Greek mythology enduring eternal punishment, the metal’s name reflects its intriguing property of being insoluble in acids.
Applications of Tantalum
- Critical in Electronics: Tantalum capacitors, known for their efficient electricity storage in a compact space with minimal leakage, play a crucial role in smartphones, laptops, and cameras.
- Substitute for Platinum: Tantalum’s high melting point positions it as a substitute for platinum in various industries, including chemical and nuclear plants, aerospace, and missile systems.
- Ideal for Medical Tools: Its non-reactive nature makes tantalum suitable for surgical tools and implants, such as artificial joints.
- Hard Material Formation: Tantalum carbide, when combined with graphite, creates one of the hardest materials, enhancing the cutting edges of high-speed machine tools.
SUTLEJ RIVER
Origin: Lake Rakshastal in Tibet, near Mount Kailash.
Length: 1,500 km (930 miles) Punjab’s Longest River
Path of the River: – Tibet – India (Himachal Pradesh, Punjab) – Pakistan
Tributaries: Beas River in India
Indus River System: Confluence with Chenab River in Pakistan
Economic Role: Importance in Irrigation and Hydroelectric Power
International River: Treaty Governance The Indus Water Treaty: India and Pakistan
Gujarat declares ‘Ghol’ as State Fish
Context
The uniqueness and economic significance of the ‘Ghol’ fish are highlighted by the Gujarat government’s decision to designate it as the state fish.
About the Ghol Fish
- The Ghol fish, also known as the Blackspotted Croaker, holds considerable importance in marine fisheries.
- Scientifically classified as Protonibea diacanthus and belonging to the Sciaenidae family, it is commonly found in the Indo-Pacific region, spanning from the Persian Gulf to Indonesia and north to Japan.
- Recognizable by its robust body, brownish hue, and distinctive black spots on its sides, the Ghol fish possesses a large mouth and a slightly protruding lower jaw.
- Some individuals can attain significant size, reaching up to one meter in length and weighing approximately 25 kilograms.
Economic Significance of the Ghol
- The Ghol fish is highly prized, particularly for its fish maw, the dried swim bladder, which is considered a delicacy and is utilized in traditional medicines, especially in East Asian markets.
- Valued for its perceived health benefits, the fish maw is commonly incorporated into soups and stews, commanding high prices in the market, at times reaching Rs 25,000 per kilogram.
Rescuing Trapped Workers of Uttarkashi Tunnel
Context:
The core focus revolves around the rescue mission at Silkyara Tunnel in Uttarakhand, underscoring the diverse representation of workers and the challenges posed by Himalayan geology.
The strategic deployment of auger and drift technology emerges as a pivotal factor in executing an efficient rescue. The primary objective remains the secure retrieval of 41 trapped workers through a unified and adaptive strategy.
Noteworthy Points:
- The incident at Silkyara Tunnel in Uttarkashi, Uttarakhand prompts a joint effort by both governmental and private entities.
- A group of 41 workers, hailing from different states, find themselves trapped in a section of the tunnel that has partially collapsed.
- The rescue operation capitalizes on technological advancements, emphasizing communication and transportation.
- Multiple government bodies, including the Prime Minister’s Office and various ministries, are actively involved.
Primary Challenges:
- The rescue operation encounters risks and challenges, notably the unpredictable nature of Himalayan geology.
- Balancing urgency with caution becomes imperative in the face of varying levels of difficulty in deploying machinery due to risk factors and geological intricacies.
Key Concepts for Added Insight:
- Silkyara Tunnel
- An all-encompassing governmental approach
- Himalayan geology intricacies
- Simultaneity principle
- Auger technology application
- Drift technology implementation
- Convergence of capability
Auger Technology Insights:
Definition: Auger technology utilizes a rotating metal shaft with a blade to cut through debris and earth.
Rescue Application: In the Silkyara Tunnel rescue, auger technology is instrumental in clearing debris, creating a pathway for rescuers.
Success Milestone: A 22-meter section has been effectively negotiated, demonstrating the efficacy of auger technology.
Challenges Faced: Geological obstacles present challenges, necessitating the restart of the auger technology efforts.
Drift Technology Insights:
Definition: Drift technology involves scraping tunnel sides to increase size and enhance access.
Rescue Application: Employed to widen the tunnel, facilitating easier access and maneuverability during the rescue.
Timing: Top and side boring attacks on tunnel alignment are set to commence in the coming stages.
Redundancy Factor: Provides a backup approach to ensure the success of the rescue mission.
Crucial Facts and Data:
- 41 workers are trapped in a partially collapsed tunnel.
- Initiatives spearheaded by the Prime Minister’s Office, Ministry of Road Transport and Highways, Ministry of Home Affairs, NDMA, and Uttarakhand SDMA.
- Five rescue strategies with time frames ranging from five-six days to eight weeks.
Critical Evaluation:
- Emphasis on collaborative efforts involving diverse governmental bodies and private sectors.
- Recognition of the unpredictable Himalayan geology and its associated challenges.
- Utilization of advanced technologies, including auger and drift technology, to navigate the complexities.
- Highlighting psychological and social impacts on workers, with provisions for psycho-social specialists.
- Acknowledgment of the significance of enabling convergence of capability among competent agencies.
Future Course of Action:
- Sustained emphasis on simultaneous approaches to expedite the rescue mission.
- Priority given to the horizontal approach utilizing auger and drift technology.
- Recognition of leadership from New Delhi as a pivotal factor in ensuring effective coordination.
Stressing the paramount importance of the safe return of the trapped workers as the primary goal.
India and Australia hold 2+2 Ministerial Dialogue
Context:
In a recent development, the Indian Defence Minister and External Affairs Minister, S. Jaishankar, engaged in discussions with Australian Deputy Prime Minister and Defence Minister Richard Marles and Foreign Minister Penny Wong during the second India-Australia 2+2 Ministerial Dialogue.
Key Points:
- In the context of strengthening strategic ties between India and Australia, both parties underscored the importance of advancing cooperation in information exchange and Indo-Pacific Maritime Domain Awareness.
- Maritime domain awareness (MDA) was defined by the International Maritime Organization as the effective understanding of anything associated with the maritime domain that could impact security, safety, economy, or the environment.
- Discussions also centered on collaboration in air-to-air refueling and hydrography.
- Hydrography, defined as the science measuring and describing the physical features of the navigable portion of the Earth’s surface and adjoining coastal areas, was a topic of consideration. Hydrographic surveyors analyze bodies of water to understand their physical characteristics.
- Both nations acknowledged the potential for deepening cooperation in the defense industry and research to further strengthen their existing relationship.
- Identified areas of potential collaboration included shipbuilding, ship repair and maintenance, as well as aircraft maintenance, repair, and overhaul.
- The shared vision between the countries would facilitate collaboration in specialized training areas such as Artificial Intelligence (AI), Anti-Submarine Warfare, anti-drone warfare, and the cyber domain, reflecting a commitment to developing advanced defense capabilities.
- Discussions also encompassed joint research in underwater technologies and collaboration between defense start-ups, signaling a commitment to innovation and technological advancement in defense strategies.
- Both sides reiterated their commitment to strengthening bilateral defense relations, expressing satisfaction with the increasing military-to-military cooperation, joint exercises, exchanges, and institutional dialogues.
China Factor in India-Australia Relations:
- Both Australia and India advocate for a rules-based international order and are working towards establishing inclusive regional institutions in the Indo-Pacific to promote further economic integration.
- Their participation in the Quad (India, Australia, US, Japan) exemplifies their alignment of interests based on shared concerns.
Public Good vs. Freebies
Context:
Each vote in an election is interchangeable, yet equally important. A political mandate can legitimately be constructed through the provision of direct benefits.
Voting and Budgetary Restraint
- Academics criticise “reckless” and “financially irresponsible” welfare-state candidates running in current state elections.
- The Supreme Court and the RBI are worried about the potential consequences for the economy if government money are given away irrationally.
Public good against giveaways and the need for extensive budgetary evaluations are at the centre of the discussion.
- When trying to attract a wide audience, political parties need to keep their statements as straightforward as possible.
- The electorate may see the good effects of direct benefits like cash transfers immediately.
Complexities and uncertainties in governance make it difficult to highlight progress, which is why infrastructure and immediate benefits often receive more attention.
Impacts
- When voters are just concerned with immediate gains, the party’s platform and ideology suffer.
- Transactional relationships between parties and voters enhance rewards, signalling a depletion of party ideology.
By prioritising personal gain over the party’s programme, political leaders undermine their own principles.