Overview:
The interim Budgets in recent years have been characterized by minimal tax changes and a lack of major policy announcements. However, there is speculation that the Modi government may break this trend, signaling a commitment to continued development. This editorial explores potential areas of focus in the upcoming budget that could impact the common man.
Infrastructure Bonds:
- Infrastructure development has been a priority, with a significant increase in the budget allocation in 2023.
- Despite optimism, data reveals a decline in bank credit to infrastructure, particularly in the power sector.
- The editorial suggests that the government may consider enhancing the attractiveness of infrastructure bonds by extending tax exemptions beyond the current limits.
Housing Tax Incentive:
- With India’s per capita income on the rise, there is a proposal to support the residential housing sector by increasing tax benefits from home loans.
- The editorial suggests raising the deduction limits under Section 80C and Section 24 (b) to encourage investment in housing and boost related industries.
- Additionally, the government could explore incentives for NRIs investing in housing projects in India.
Healthcare Support:
- As life expectancy increases, there is a corresponding surge in medical expenses.
- The note recommends an increase in the deduction limit for medical insurance premiums under Section 80D.
- Alternatively, it proposes a 10% concession in consultation fees for senior citizens across all hospitals in the country.
Child Education:
- The editorial highlights the success of the Sukanya Samriddhi Yojana for girl children and proposes a similar scheme for boys to address the high illiteracy rates in India.
- By widening the scope of the Sukanya Samriddhi Yojana, the government could contribute to improving education levels in the country.
Conclusion:
The upcoming budget could depart from the past trend of lackluster interim budgets.
Focus areas may include infrastructure bonds, housing tax incentives, healthcare support, and expanding child education schemes.
These measures align with the government’s purported commitment to continued development and addressing the needs of the common man.
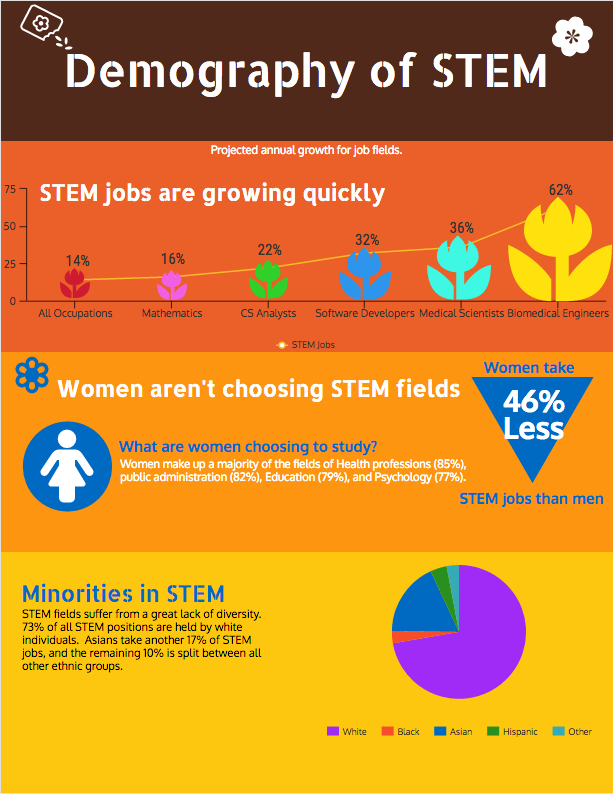
Safeguarding India's Future: The Imperative for Substantial Enhancements in STEM Education
Introduction:
- In the current era of rapid technological advancements, STEM (science, technology, engineering, and mathematics) education emerges as the driving force behind progress.
- Its significance spans across various disciplines, including artificial intelligence, machine learning, quantum computing, and sustainable solutions like green hydrogen.
- STEM education is identified as the bedrock for cultivating critical thinking, problem-solving acumen, and a culture of innovation.
Pivotal Moment for India:
- India finds itself at a pivotal moment, necessitating an immediate enhancement of the quality and modernization of its STEM education system.
- Swift improvements are deemed imperative to equip the youth with essential skills required for the evolving landscape.
Effective Curriculum Design:
- An effective curriculum, according to the editorial, must embody the spirit of inquiry and exploration.
- This involves immersing students in real-world problems to engage their attention and refine analytical skills.
- The integration of theoretical concepts with hands-on experiences is emphasized for a comprehensive understanding of STEM disciplines, fostering genuine appreciation.
Adapting to the 4th Industrial Revolution:
- Acknowledging the significant progress in artificial intelligence, robotics, the internet of things, and biotechnology, the editorial advocates for an educational approach aligned with the accelerated pace of change.
This necessitates not only introducing students to the latest tools and technologies but also immersing them in a product-driven experience that prioritizes practical application over mere consumption.
Global Innovation Economy:
- The document underscores the importance of high-quality STEM education in propelling India to a leading position in the global innovation-based economy.
- It emphasizes that this goes beyond producing STEM graduates, linking success to the country’s ability to harness a STEM-literate workforce.
Teacher Training Initiatives:
- Simultaneously, the note stresses the compelling need to elevate teacher training and development initiatives.
- It highlights the importance of refining teachers’ competencies to stay updated on the latest advancements and teaching techniques in STEM subjects.
- This involves sharpening research skills and embracing innovative approaches to enhance the overall quality of STEM education.
Role of STEM in Technological Transformation:
- The transformative changes driven by AI and ML across industries are seen as reliant on a strong foundation in mathematics and computer science.
- STEM education is deemed crucial for providing individuals with the analytical skills and problem-solving mindset necessary for navigating the intricacies of cutting-edge technologies.
- The potential of quantum computing and breakthroughs in green hydrogen production are cited as examples where STEM disciplines play a pivotal role.
Business Contribution and Collaboration:
- The document concludes by emphasizing the proactive role that Indian businesses must play in cultivating a STEM-literate workforce.
- Collaborations with educational institutions, initiatives promoting STEM diversity, and investments in research and development are deemed essential steps in ensuring a robust talent pipeline prepared to tackle challenges and opportunities in the rapidly evolving technological landscape.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the note strongly advocates for substantial enhancements in India’s STEM education, spanning from K-12 education to the development of post-doctoral scholars engaged in cutting-edge research and innovation.
It frames this imperative as a crucial step in safeguarding India’s future in the face of technological advancements and global competition.
Review of Asean-India Trade in Goods Agreement (AITIGA)
Introduction
- The Asean-India Trade in Goods Agreement (AITIGA) is set to undergo review, responding to long-standing demands from the Indian industry to address trade imbalances.
- Despite concerns raised by the Indian industry over increased imports from Asean, the analysis urges a broader perspective in light of evolving global and regional trade dynamics.
Historical Overview of AITIGA
- AITIGA, initiated in 2009, is criticized for its limited tariff line liberalization, greater advantages to certain Asean economies, and unsuccessful compensatory gains in services liberalization.
- The deficit with Asean is attributed to India’s higher tariffs and limited export competitiveness, prevalent across its Free Trade Agreements (FTAs).
Addressing Trade Imbalances
- To address the trade imbalance, the analysis suggests India reduce its import tariffs before the revision process begins.
- Agriculture and textiles, often cited for high protection by Asean, are highlighted as sectors outside preferential market access in most global FTAs.
Strategic Importance of AITIGA Review
- The broader context emphasizes the strategic advantage of the AITIGA review, positioning India to integrate with regional and global value chains (RVCs/GVCs).
- This becomes crucial following India’s exclusion from the Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership (RCEP), and Asean’s attractiveness as a GVC hub amidst geopolitical shifts.
Key Inputs for AITIGA Review
- Rules of Origin (RoOs): A careful formulation of RoOs, avoiding complexity and dual-criteria, is crucial. Consideration of Asean’s region-wide cumulation formula under the RCEP is recommended to facilitate regional content rules.
- Investment Chapter: The analysis underscores the need for India to evolve its stance on the investment chapter, aligning it with the forward-looking provisions seen in Asean’s FTA with Australia-New Zealand.
- Comprehensive Negotiations: The review process should be simultaneous and comprehensive, covering goods, services, and investment liberalization. This approach enhances bargaining flexibility and trade-offs, maximizing benefits for negotiating parties.
Beyond Mode-4 Liberalization
In liberalizing services, India is encouraged to go beyond mode-4 liberalization, considering sectors like repair and maintenance and digital services to boost export competitiveness.
The Eastward Focus
Emphasizing the importance of looking east, the note suggests India should prioritize negotiations in a region adhering to FTA principles, unlike North America and the EU adopting selective trade protectionism and inward-looking regionalism.
Conclusion
The editorial concludes by stressing the significance of meticulous preparation for negotiations and timely conclusion of the AITIGA review process, positioning India strategically in the dynamic global trade landscape.