1. Understanding the Delimitation Exercise
Introduction:
The upcoming delimitation process for Lok Sabha and State Legislative Assemblies, slated to be based on the initial Census data post-2026, has sparked considerable discourse and raised significant queries.
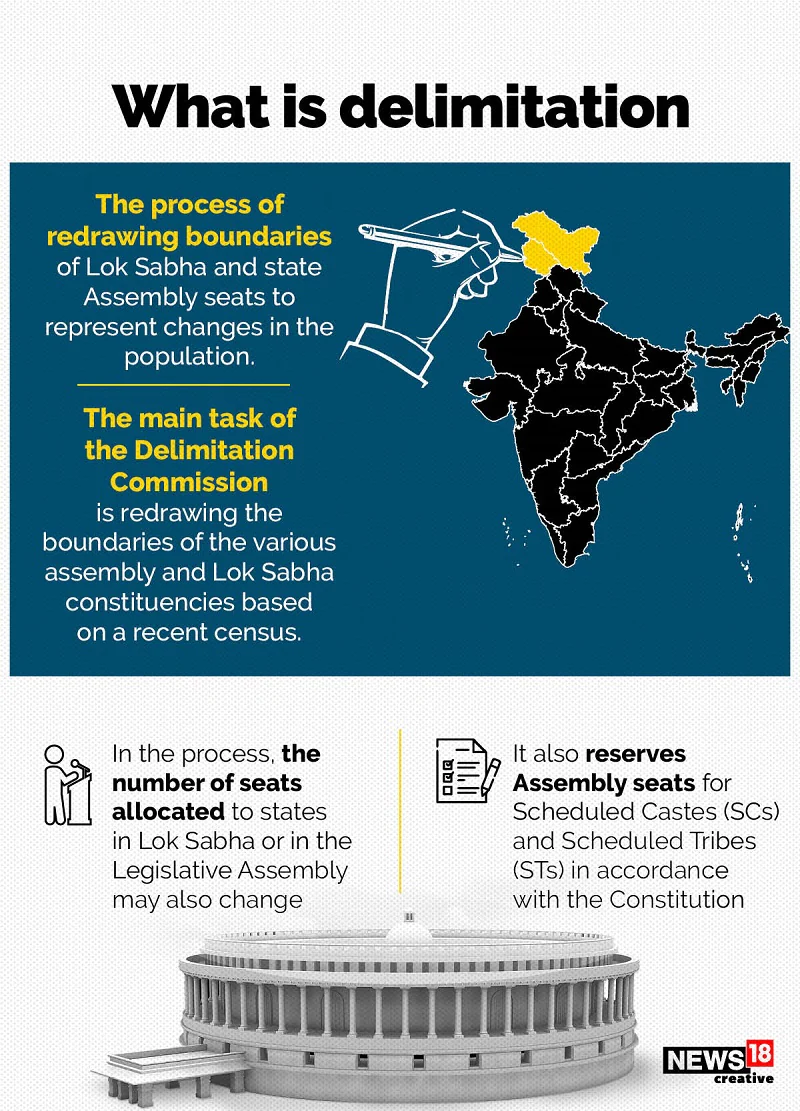
Understanding Delimitation:
Delimitation involves the delineation of the number of seats and boundaries of territorial constituencies, incorporating provisions for the reservation of seats for Scheduled Castes (SC) and Scheduled Tribes (ST) based on census figures.
Constitutional Mandate:
The necessity for seat readjustment following each Census is stipulated by Article 82 (pertaining to Lok Sabha) and Article 170 (pertaining to State Legislative Assemblies), carried out by the Delimitation Commission.
Historical Context:
Delimitation exercises were previously conducted subsequent to the 1951, 1961, and 1971 Censuses, underlining its periodic nature.
About the Delimitation Commission:
The Delimitation Commission, constituted to delineate and redraw constituency boundaries for state assembly and Lok Sabha elections, comprises a distinguished panel appointed by the President in collaboration with the Election Commission.
The commission includes:
- A retired or incumbent Supreme Court Judge as chairperson
- An Election Commissioner
- Relevant State Election Commissioners
The directives issued by the Delimitation Commission possess legal validity and are not subject to judicial review. Although presented before the Lok Sabha and respective legislative assemblies, these directives cannot be altered by them.
Need for Delimitation:
Essential to the democratic process is the principle of ‘one citizen-one vote-one value,’ necessitating periodic seat adjustments to mirror population shifts.
Seat Freeze:
Since 1971, seats have remained static to encourage population control, a measure extended until 2026 via the 84th Amendment Act.
Challenges Encountered:
- Disparities in population growth among states present challenges, with some experiencing rapid growth while others stagnate.
- Proposed solutions include redistributing existing seats or augmenting total seats to reflect population changes.
- Additionally, the merging of constituencies can result in the diminishment of electoral representation.
International Perspectives:
- The United States redistributes seats among states post-Census to maintain proportionality, minimizing disruption.
- The European Union Parliament utilizes a principle of ‘degressive proportionality,’ allotting seats based on population ratios.
The Way Forward:
- Balancing democratic representation with federal principles is paramount. While capping Lok Sabha seats at the current 543 ensures continuity, augmenting State Legislative Assembly seats aligns with democratic representation.
- Strengthening grassroots institutions like panchayats and municipalities is vital for enhancing citizen engagement and governance.
Conclusion:
The delimitation process necessitates a delicate equilibrium between democratic representation and federal principles. By embracing a nuanced approach that upholds constitutional mandates while empowering local governance, India can adeptly navigate the intricacies of delimitation, ensuring comprehensive and effective representation for its diverse populace.
2. Kerala is one of most financially unhealthy States: Centre
Introduction:
The ongoing disagreement between the central government and the administration of Kerala concerning fiscal policies has initiated discussions on matters of financial stability, resource allocation, and federal governance.
Financial Mismanagement in Kerala:
- Challenges in Fiscal Health: The central government asserts that Kerala’s fiscal condition is fragile due to inadequate management of public funds.
- Financial Assistance Concerns: Despite substantial financial aid from the central government, which includes additional funds beyond the recommendations of the 15th Finance Commission, Kerala continues to grapple with financial pressures.
- Issues of Mismanagement: Kerala is accused of imprudent borrowing practices, financing unproductive expenditures, and poorly targeted subsidies, exacerbating its financial difficulties, which have ramifications for both the state and national economies.
Data Analysis:
- Escalating Liabilities: Kerala’s outstanding liabilities, relative to its Gross State Domestic Product (GSDP), have shown a consistent increase from 31% in 2018-19 to 39% in 2021-22, surpassing the national average.
- Impact of High Liability Ratio: The central government warns that the elevated outstanding liability ratio leads to increased interest payments, worsening fiscal deficits, and the risk of falling into a debt trap.
- Growing Committed Expenditure: Kerala’s committed expenditure as a percentage of revenue receipts has climbed from 74% in 2018-19 to 82.40% in 2021-22, surpassing that of any other state. This trend limits the state’s ability for effective government spending, negatively impacting long-term growth prospects.
Kerala’s Defense:
- Asserting Federal Structure: Kerala emphasizes its rights within the federal system to independently manage its finances, highlighting concerns about the central government’s encroachment on its fiscal autonomy.
- Economic Impacts: The state argues that actions by the central government, such as imposing arbitrary borrowing limits, endanger Kerala’s economic stability, jeopardizing its ability to achieve developmental objectives.
Legal Response:
- Judicial Proceedings: Kerala’s legal challenge against the central government’s alleged interference in state finances includes submissions to the Supreme Court by the Attorney General.
- Preservation of Federalism: Kerala seeks judicial intervention to uphold the federal structure, asserting the state’s prerogative over budgetary management and borrowing decisions.
- FRBM Consideration: While the FRBM Act of 2023 primarily applies to the central government, certain states have enacted their own FRBM legislation to ensure fiscal discipline at the state level. Kerala, however, has yet to enact its own version.
Implications:
- Broader National Impact: The resolution of this dispute extends beyond Kerala, influencing the broader framework of fiscal federalism and intergovernmental relations.
- Developmental Challenges: Prolonged legal proceedings could hinder Kerala’s development agenda and exacerbate financial strains, impacting the well-being of its populace.
Conclusion:
The ongoing fiscal dispute between the central and state governments underscores the complexities inherent in federal governance and fiscal management.
As legal proceedings unfold, the resolution of this conflict will shape the landscape of intergovernmental relations and delineate the boundaries of fiscal autonomy within India’s federal structure.
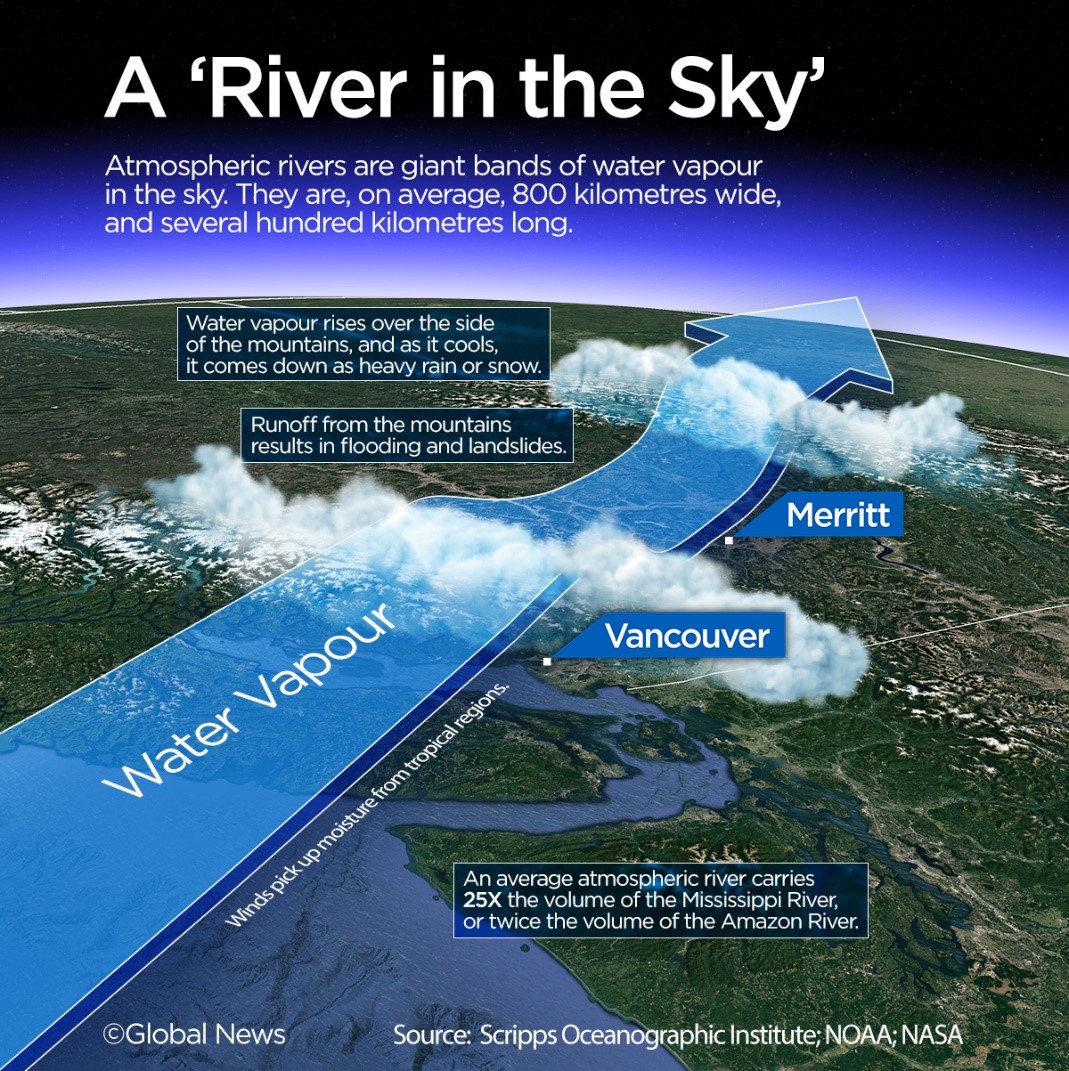
3. Atmospheric River
Overview of Atmospheric Rivers
Atmospheric rivers, often described as ‘rivers in the sky,’ recently impacted parts of Los Angeles, showcasing their significant role in weather patterns.
Characteristics of Atmospheric Rivers
- Atmospheric rivers, resembling elongated aerial corridors, transport vast amounts of water vapor outside tropical regions.
- They exhibit considerable dimensions, spanning up to 800 kilometers in width and extending over 1,600 kilometers in length.
Magnitude of Atmospheric Rivers
According to the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, atmospheric rivers can transport up to 15 times the volume of the Mississippi River, highlighting their substantial impact.
Formation of Atmospheric Rivers
- Atmospheric rivers originate in tropical regions, where warm temperatures trigger seawater evaporation, lifting moisture-laden air into the atmosphere.
- Driven by strong winds, this moist air embarks on a journey across the sky.
Impact of Atmospheric Rivers
- Upon reaching land, atmospheric rivers undergo a transformative process, leading to intense precipitation.
This precipitation can result in flooding, landslides, mudslides, disruptions in water supply, and the onset of drought-like conditions, emphasizing the need for comprehensive understanding and effective management strategies.
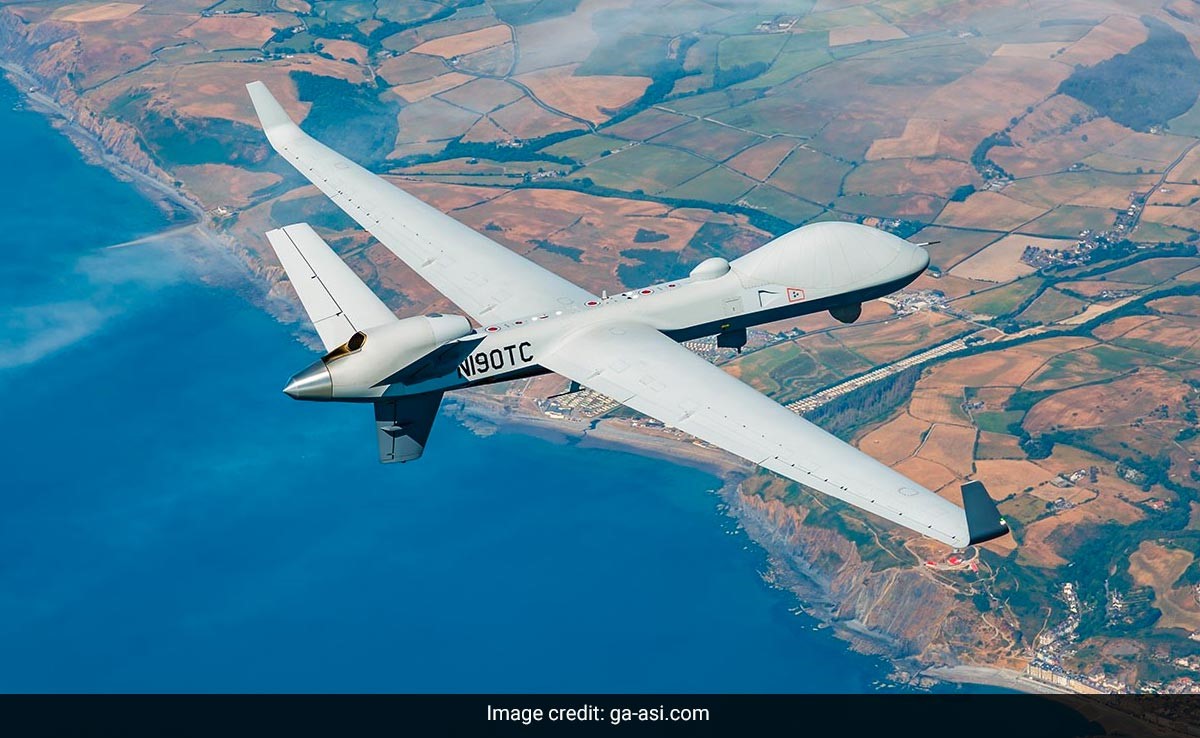
4. MQ-9B Drones
Context:
- Recently, the United States government disclosed a significant development regarding the proposed sale of 31 MQ-9B armed drones to India, valued at approximately $4 billion.
- This transaction is anticipated to significantly bolster India’s maritime security capabilities and enhance its domain awareness. Moreover, the acquisition would confer India complete ownership of these advanced aircraft.
Key features of the MQ-9B drones include:
- The MQ-9B, also recognized as the Predator drone, comes in two variants: SkyGuardian and SeaGuardian.
- It boasts a substantial payload capacity of 3,850 pounds (1,746 kg).
- Equipped with nine hardpoints, the MQ-9B can accommodate various payloads such as sensors, laser-guided bombs, and air-to-ground missiles.
- The Indian Navy has been utilizing the SeaGuardian variant of the MQ-9B since 2020.
Capable of operating at altitudes exceeding 40,000 feet, the SeaGuardian version can carry payloads weighing up to 5,670 kg, while accommodating a fuel capacity of 2,721 kg.
5. Halal Certification
Understanding Halal Certification
Halal certification assures consumers that products and services comply with Islamic dietary and ethical guidelines.
What does “Halal” mean?
- The Arabic word “halal” translates to “permissible” or “lawful” according to Islamic law (Sharia).
- In the context of food, halal refers to items considered fit for consumption based on specific Islamic dietary rules.
- Conversely, “haram” signifies anything prohibited or unlawful in Islam, including certain foods, substances, and actions.
What products require Halal certification?
- Primarily, halal certification applies to food and beverage products to assure adherance to Islamic dietary guidelines.
- This includes meat, poultry, seafood, processed foods, and even food additives and ingredients.
- However, halal certification can extend beyond food to encompass cosmetics, pharmaceuticals, personal care products, and even financial services and tourism facilities.
What are the core principles of Halal certification?
- Permissible ingredients: Products must not contain any ingredients deemed haram, such as pork, alcohol, blood, or animals not slaughtered according to Islamic rites.
- Sourcing and processing: The entire production process, from sourcing ingredients to manufacturing and packaging, must comply with Islamic guidelines.
- Hygiene and cleanliness: Halal-certified facilities must maintain high standards of hygiene and sanitation to ensure product purity and safety.
- Animal welfare: Islamic slaughter methods emphasize minimizing animal suffering, requiring a swift and humane process with a sharp blade.
Who issues Halal certificates?
- In many countries, government bodies regulate halal certification.
However, private halal certification bodies also play a significant role, accredited by government agencies or recognized by Muslim communities, In India there is no such Govt. body for the same.