 |
||
| 12 April 2024 | ||
|
- NGT Intervention to Prevent Stubble Burning
- Microbial Innovations for Agricultural Enhancement
- Developed in Indian laboratories, NexCAR19 marks a significant advancement in cancer care within the country.
- Doctrine of Harmonious Construction
- Corporate Climate Responsibility Monitor (CCRM) 2024
- Ural Mountain
- Global Trade Outlook & Statistics Report
NGT Intervention to Prevent Stubble Burning

Context;
The National Green Tribunal (NGT) has mandated that the Punjab government develop a thorough plan for managing the anticipated 19.52 million tonnes of paddy stubble within the state.
Regulatory framework;
- Under the Air (Prevention and Control of Pollution) Act of 1981, the National Green Tribunal (NGT) oversees measures to prevent stubble burning in Punjab.
- This legislation enforces bans and actions against individuals engaged in burning crop residue, aiming to curb air pollution.
Reporting Obligations
- Punjab is obligated to provide comprehensive details on its strategies for utilizing paddy straw from the previous year.
- These reports must cover the mode and manner of removal, transportation, and utilization of crop residue across various sectors.
Projected Increase in Paddy Straw Generation
- Punjab anticipates a substantial increase in paddy straw generation, reaching 52 million tonnes in 2024.
- However, the state aims to counter this by utilizing an estimated 18.66 million tonnes of paddy straw, thereby reducing the need for burning.
Off-Site Utilization
- A noteworthy aspect is the projected 60% increase in off-site utilization, with industrial and energy plants expected to utilize 5.96 million tonnes of paddy straw, contributing to environmental sustainability.
Alternatives to Stubble Burning
1. In-Situ Treatment;This approach involves managing crop residue directly within the field. Techniques such as zero-tiller machines and bio-decomposers are utilized to break down stubble, eliminating the need for burning.
2. Ex-Situ Treatment;Crop residue is treated outside the field. For instance, rice straw can be repurposed as cattle fodder, providing a sustainable alternative to burning.
3. Turbo Happy Seeder (THS) Technique;An innovative technique that enables the simultaneous uprooting of stubble and sowing of seeds while leaving the stubble as mulch, benefiting soil health and reducing the need for burning.
4. Pusa-Biodecomposer;Developed by the Indian Council of Agricultural Research (ICAR), this fungi-based liquid solution softens hard stubble, facilitating its integration into soil as compost.
Moreover, it produces enzymes that digest cellulose, lignin, and pectin in paddy straw, swiftly converting crop residues and other waste into organic manure.
Microbial Innovations for Agricultural Enhancement
Introduction;
The Indian Institute of Spices Research (IISR) based in Kozhikode has introduced and validated three novel microbial formulations with the aim of enhancing agricultural productivity.
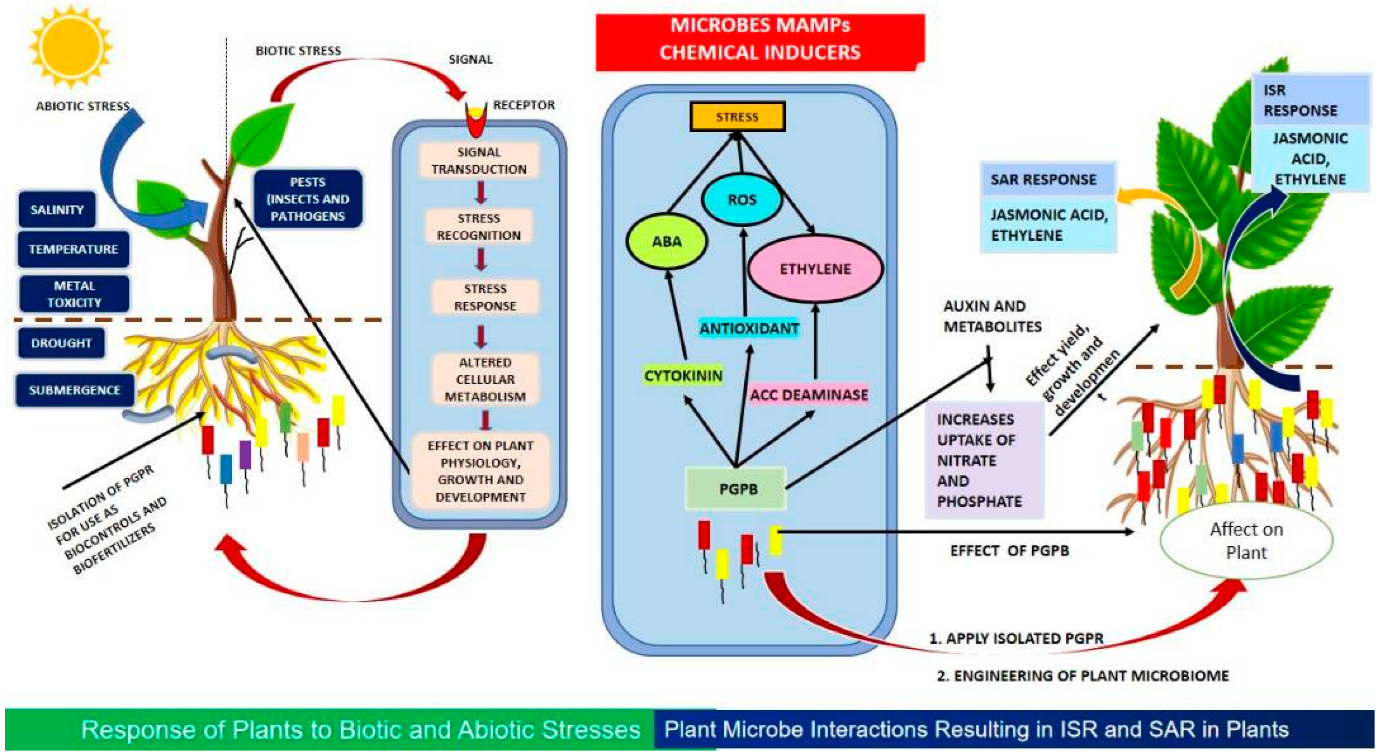
IISR Microbial Solutions
- These formulations utilize granular lime and gypsum to tackle soil pH imbalances while concurrently introducing beneficial microorganisms.
- Developed using exclusive patent-pending technology from IISR, these formulations consist of:
Bactolime:
- The flagship product, Bactolime, combines plant growth-promoting Rhizobacteria with lime material in a singular formulation.
- This unique blend not only rectifies soil acidity but also provides essential nutrients to plants.
Bactogypsum and Trichogypsum:
- The other two formulations, Bactogypsum and Trichogypsum, utilize gypsum as their base material to adjust soil pH levels to near-neutrality.
- By creating an optimal habitat for beneficial microbes, these formulations enhance soil structure, increase the availability of secondary nutrients, and stimulate overall microbial activity.
Fundamentals of Soil Microorganisms
- Soil microbes encompass a diverse array of microorganisms inhabiting the soil environment, crucial for soil health, nutrient cycling, and plant development.
- This microbial community includes bacteria, fungi, archaea, protozoa, and algae.
Developed in Indian laboratories, NexCAR19 marks a significant advancement in cancer care within the country.
Overview;
President Droupadi Murmu unveiled India’s inaugural CAR T-cell therapy, a groundbreaking development in the fight against cancer. Named ‘NexCAR19 CAR T-cell therapy’, this innovation is a collaborative effort between the Indian Institute of Technology (IIT) Bombay and the Tata Memorial Centre.
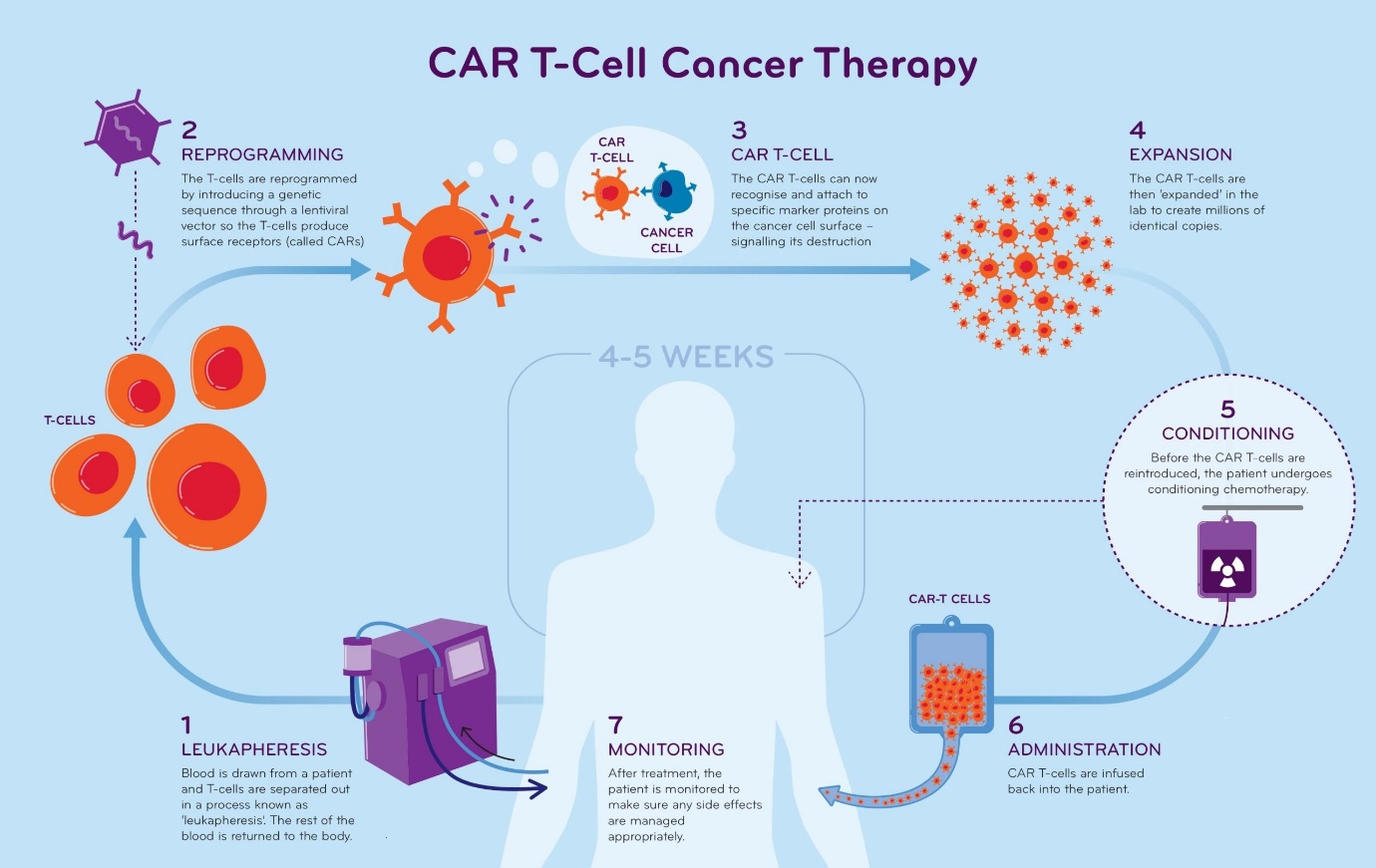
Significance of CAR-T Therapy:
- Promising Outcomes: This therapy has demonstrated encouraging results in treating certain types of blood cancers, including specific lymphomas, pediatric leukemia, and adult leukemia. Approximately 70% of patients have responded positively to the treatment.
- Reduced Treatment Duration: CAR T-cell therapies typically involve a single infusion and less than 2 weeks of inpatient care, contrasting with the prolonged durations associated with stem cell transplants and chemotherapy.
Limitations of CAR-T Therapy:
1.Varied Efficacy: The effectiveness of CAR-T therapy varies among individuals, and it is premature to deem it a definitive cure. While it has shown remarkable progress in challenging cases, its efficacy is not uniform.
2.Cost Considerations: Despite being priced significantly lower than its US counterpart, NexCAR19 remains relatively expensive for many Indians, ranging from ₹40 to 45 lakh.
Side Effects:
1.Cytokine Release Syndrome (CRS): The most common side effect of CAR-T therapy, CRS induces an inflammatory response that can lead to hyperactivity of the immune system.
2.Neurotoxicity: Though not observed in initial clinical trials, neurotoxicity is a potential side effect that can manifest as confusion, seizures, or impaired motor skills.
3.Infections and Hematological Complications: Patients undergoing CAR-T therapy may experience infections and decreased blood cell counts as expected side effects.
Conclusion:
India is poised to achieve a significant breakthrough in cancer care with advancements like NexCAR19. Despite challenges related to affordability, governmental initiatives aim to improve accessibility and outcomes in the healthcare sector.
Doctrine of Harmonious Construction
Overview;
In a recent case, the Supreme Court declined to condone a delay of 5659 days in filing an appeal. Instead, it outlined eight guiding principles by interpreting Sections 3 and 5 of the Limitation Act, 1963, under the doctrine of ‘Harmonious Construction’.

Understanding the Doctrine:
- The doctrine of harmonious construction involves reconciling conflicting provisions within a law to maintain consistency and coherence in legal interpretation.
- It ensures that legislative intent is upheld while resolving apparent conflicts within statutes.
Origin:
- 1.The origin of the Doctrine of Harmonious Construction can be traced back to the landmark judgment of Sri Shankari Prasad Singh Deo v. Union of India (1951).
- This doctrine emerged in response to conflicts between Fundamental Rights and Directive Principles of State Policy (DPSP).
- In the present case, the Supreme Court applied the doctrine to reconcile Sections 3 and 5 of the Limitation Act, balancing the strict interpretation of limitation periods under Section 3 with the liberal approach to condonation of delay under Section 5.
Principles for Condonation of Delay:
A bench comprising Justices Bela M Trivedi and Pankaj Mithal articulated the following principles:
- Public Policy Basis: Limitation laws prioritize concluding litigation by forfeiting remedies rather than rights.
- Temporal Limitation: Rights or remedies unexercised for an extended period should cease to exist.
- Strict vs. Liberal Construction: Section 3 (limitation period) requires strict interpretation, while Section 5 (condonation of delay) demands a liberal approach.
- Substantial Justice: The core of limitation law (Section 3) must not undermine the promotion of substantial justice.
- Discretionary Power: Courts may condone delay if sufficient cause is explained but may refrain due to factors like inordinate delay and negligence.
- Individual Justification: Relief granted to some does not mandate the same for others if the justification for delay is unsatisfactory.
- Merit Irrelevance: The merits of the case should not influence decisions on delay condonation.
- Condonation Parameters: Applications for delay condonation must adhere to statutory provisions; disregarding conditions amounts to disregarding the law.
Corporate Climate Responsibility Monitor (CCRM) 2024
Context:
The CCRM 2024 report, compiled by the New Climate Institute, scrutinized the climate objectives of 51 prominent global corporations.
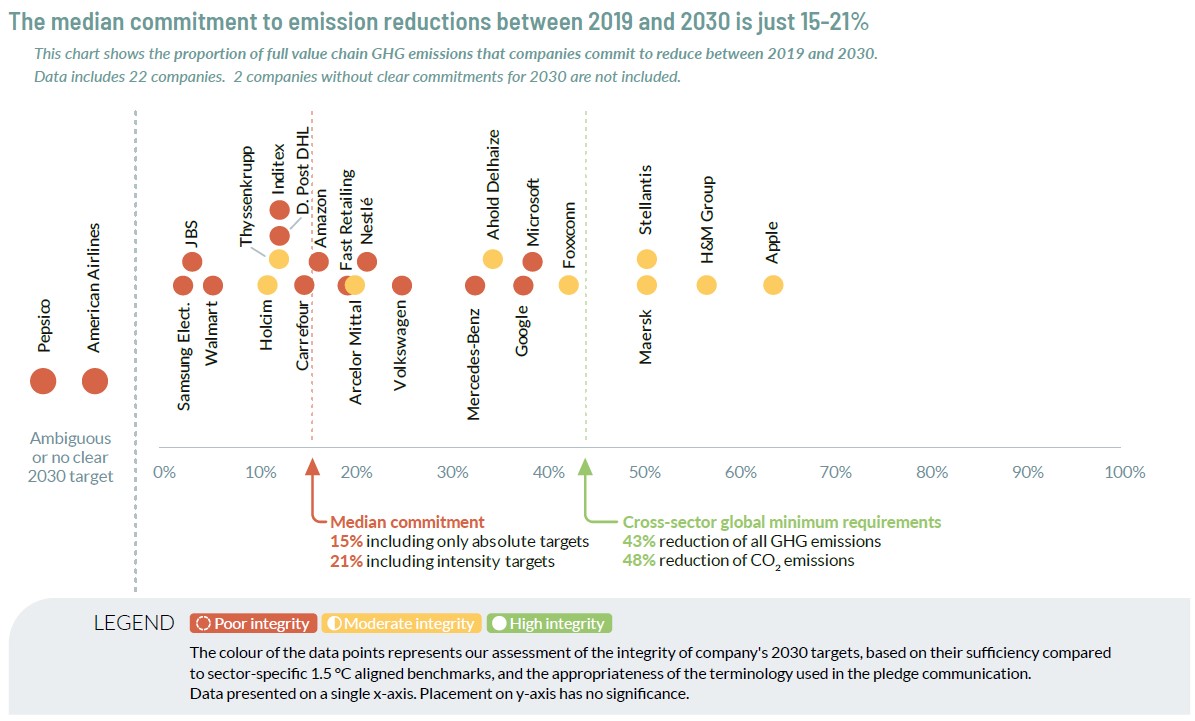
Assessment of Climate Targets:
– The CCRM 2024 examined the climate targets established by 51 major companies, which collectively generated $6.1 trillion in revenue in 2022.
– These companies self-reported greenhouse gas emissions totaling 8.8 gigatonnes of CO2 equivalent in 2022, approximately equivalent to the combined annual emissions of India, Russia, and Brazil.
– Their emissions accounted for approximately 16% of global greenhouse gas emissions in 2022.
Progress in Emissions Reduction:
– The collective emissions reduction target for 2030 is a mere 30% compared to 2019 levels.
– Only 7 companies have set targets to reduce emissions by more than 50% by 2030.
– Some companies, such as Walmart and Volkswagen, lack updated or clear emission reduction plans.
– Conversely, companies like Danone, Iberdrola, Mars, and Volvo Group have relatively robust emission reduction plans.
Loopholes and Accountability:
1.Companies may resort to contentious solutions and carbon offsets to achieve their targets.
2. Initiatives like the Voluntary Carbon Market Initiative and Science Based Targets initiative may create loopholes for companies to evade accountability for Scope 3 emissions.
3.Testing flexible offsetting mechanisms has revealed the potential for erasing accountability for Scope 3 emissions.
Overreliance on Voluntary Reporting:
A. Climate targets established by companies are voluntary and evaluated by validation frameworks such as SBTi, Transition Pathways Initiative, and MSCI Net Zero Tracker.
B. While voluntary reporting encourages target setting, it lacks robust accountability mechanisms.
C.There is a pressing need for a more stringent accountability system to ensure genuine emissions reduction by private corporations.
Ural Mountains
Overview;
Recent severe flooding in the Ural Mountains, situated on the continental divide between Asia and Europe, has raised questions regarding its association with climate change.
- The Ural Mountains act as a natural boundary between Europe and Asia, stretching from the Arctic Ocean to the Ural River and extending into Kazakhstan.
- Renowned as one of the oldest mountain ranges globally, the Urals hold significant geological and cultural significance.
- They boast abundant mineral resources, including gold, platinum, and coal, making them a vital mineral base for Russia since the 18th century.
- The region is a prominent center for metallurgy and heavy industry production in Russia.
- The Ural Mountains are categorized into five sections: Southern, Middle, Northern, Pre-Polar (the tallest), and Polar.
- With average elevations ranging from 1,000 to 1,300 meters (3,300 to 4,300 feet), the highest peak is Mount Narodnaya, reaching 1,894 meters (6,214 feet).
- The Ural River ranks as the third-largest river in Europe, following the Volga and the Danube.
- The Tobol River is a tributary of the Irtysh, which ultimately joins the Ob River.
- The Ob-Irtysh river system is the seventh-longest in the world.
Global Trade Outlook & Statistics Report
Overview;
The World Trade Organization’s (WTO) “Global Trade Outlook and Statistics” evaluates recent global trade trends up to Q4 2023 and provides forecasts for 2024 and 2025. It offers detailed breakdowns of merchandise and commercial services trade by sector and region, including insights into top traders.
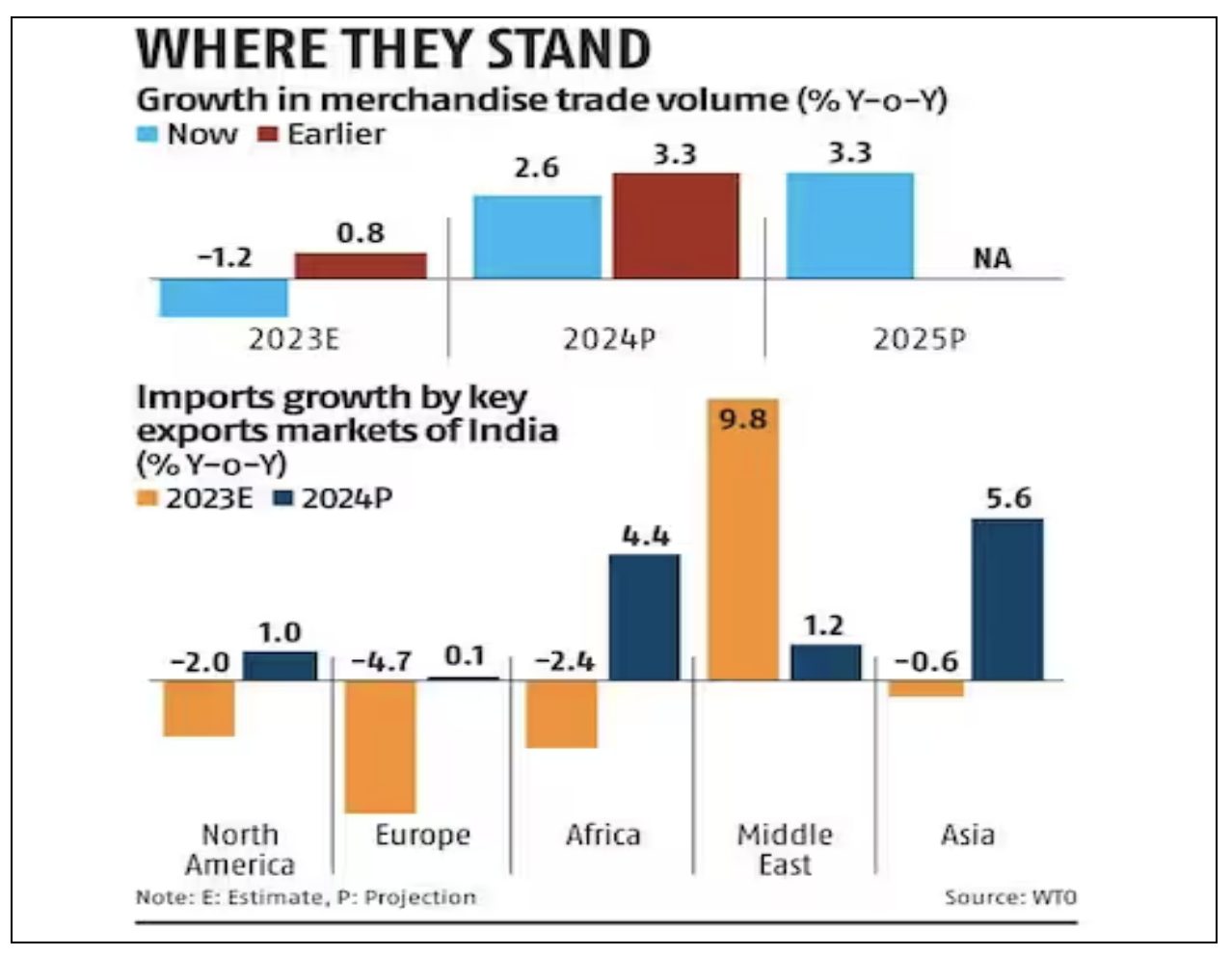
1.Key Forecasts
– Projections anticipate a 2.6% increase in world merchandise trade volume in 2024, followed by a 3.3% rise in 2025, rebounding from a 1.2% decline in 2023.
2.Import Trends
– In 2023, weak import demand was prevalent across various regions, particularly in Europe, North America, and Asia. However, notable exceptions were observed in the Middle East and the Commonwealth of Independent States (CIS), where imports experienced significant growth.
3.Global GDP Growth
– Global real GDP growth slowed from 3.1% in 2022 to 2.7% in 2023. Projections indicate stabilization at 2.6% in 2024, followed by a continuation at 2.7% in 2025.
-The discrepancy between GDP growth and merchandise trade volume deceleration is attributed to inflationary pressures affecting the consumption of trade-intensive goods.
4.Trade Value
– The US dollar value of world merchandise trade declined by 5% in 2023, amounting to US$ 24.01 trillion.
-Conversely, commercial services trade witnessed a 9% increase, reaching US$ 7.54 trillion.
-The decrease in merchandise exports was influenced by declining commodity prices, while the rise in commercial services trade was driven by the recovery of international travel and the surge in digitally delivered services.
5.Resilience of Global Trade
– Despite significant economic shocks, global trade has demonstrated resilience in recent years.
-Merchandise trade volume increased by 6.3% by the end of 2023 compared to 2019, while commercial services trade also grew, with the annual US dollar value rising by 21% between 2019 and 2023.
6.Inflation and Income Growth
– Inflation is anticipated to gradually decrease in 2024 and 2025, leading to rising real incomes in advanced economies and boosting the consumption of manufactured goods.
-Increased demand for tradable goods in 2024 is expected due to improved income prospects and increased household consumption.
7.Risks and Uncertainties
– Downside risks to the forecast persist due to geopolitical tensions and policy uncertainty.
-Conflict in the Middle East has disrupted sea shipments between Europe and Asia, while tensions in other regions could result in trade fragmentation.

