 |
||
| 13 April 2024 | ||
|
- India’s Position in the World Cybercrime Index
- India and the US have jointly agreed to reinvigorate the Indian Ocean Observing System (IndOOS).
- Adjudication Process under the Prevention of Money Laundering Act (PMLA)
- Mount Etna’s Volcanic Vortex Rings: A Rare Natural Phenomenon
- Innovative Solution: IISc’s Sustainable Hydrogel for Microplastic Removal
- The Great barrier reef
- Understanding the Science Based Targets Initiative (SBTi)
India’s Position in the World Cybercrime Index
Context;
India stands at the 10th position in the World Cybercrime Index, according to recent research findings.

About the World Cybercrime Index
Developed through a collaboration between the University of Oxford and the University of New South Wales, Sydney, the World Cybercrime Index receives funding from CRIMGOV, a European Union-supported project. It aims to illuminate global cybercrime patterns and hotspots.
Key Aspects of the Study
Published in the journal PLOS ONE, the study titled ‘Mapping the global geography of cybercrime with the World Cybercrime Index’ categorizes cybercrimes into five main types:
1. Technical Products/Services: Involving activities such as malware coding, botnet access, and compromised system access.
2. Attacks and Extortion: Including denial-of-service attacks and ransomware.
3. Data/Identity Theft: Encompassing hacking, phishing, and account compromises.
4. Scams: Involving advance fee fraud, business email compromise, and online auction fraud.
5. Cashing Out/Money Laundering: Covering credit card fraud, money mules, and illicit virtual currency platforms.
Key Findings of the Report;
- India’s ranking at 10th is attributed to prevalent scams involving advance fee payments.
- The top spots are occupied by Russia, Ukraine, China, the US, Nigeria, and Romania.
- Russia and Ukraine are identified as major technical cybercrime hubs, while Nigerian cybercriminals are more involved in less technical cybercrimes.
India and the US have jointly agreed to reinvigorate the Indian Ocean Observing System (IndOOS).
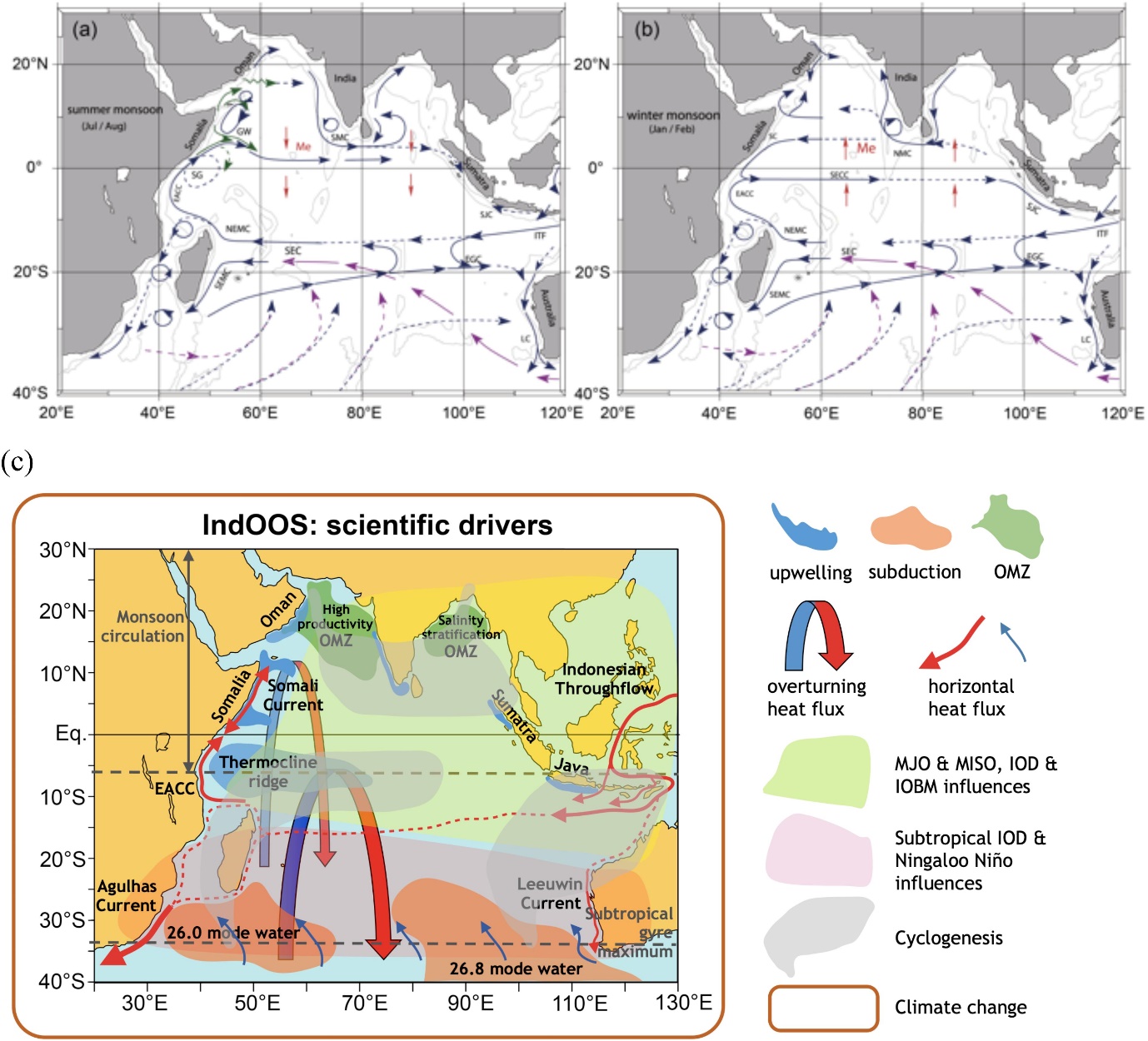
Overview;
IndOOS, established in 2006, consists of strategically positioned moored buoys across the Indian Ocean. This network comprises 36 buoys in high-seas locations, gathering detailed oceanic and atmospheric data for weather forecasts.
Parameters measured include seawater temperature, salinity, ocean currents, atmospheric humidity, and wind speed. Initially focused on understanding and forecasting the monsoon, IndOOS now aids in climate modeling and prediction of extreme weather events like floods, droughts, and cyclones.
Objectives:
- The primary aim of IndOOS is to furnish continuous, high-quality oceanographic and meteorological data, supporting informed decision-making and advancing scientific comprehension of weather and climate.
- It seeks to foster collaborations among Indian Ocean nations and beyond to bolster long-term monitoring and forecasting capabilities.
Rationale for IndOOS:
- The Indian Ocean region, home to nearly one-third of the global populace, confronts substantial vulnerabilities due to climate change and extreme weather phenomena.
- Sectors such as fisheries and rain-dependent agriculture, heavily reliant on the monsoon, rely on accurate weather forecasts to mitigate potential damage to crops and livelihoods.
- Furthermore, the Indian Ocean’s influence extends globally, redistributing heat and modulating climate in distant regions.
Observing Networks:
IndOOS comprises five observing networks:
1. Research Moored Array for African-Asian-Australian Monsoon Analysis and Prediction (RAMA)
2. Profiling floats (part of the global Argo array)
3. Surface drifters (Global Drifter Program, GDP)
4. Repeat temperature lines (eXpendable Bathy Thermograph (XBT) network)
5. Tide gauges
These networks are augmented by satellite observations of surface wind, sea level, temperature, salinity, rainfall, and ocean color.
Partnerships and Support:
- IndOOS originated from deliberations among scientists during the First International Conference on the Ocean Observing System for Climate (OceanObs) in 1999.
- An implementation plan for IndOOS was devised by the Indian Ocean Panel, operating under the Climate and Ocean Variability, Predictability, and Change (CLIVAR) and Intergovernmental Oceanographic Commission – Global Ocean Observing System (IOC-GOOS) programs.
Adjudication Process under the Prevention of Money Laundering Act (PMLA)
Introduction;
The Adjudicating Authority operating under the Prevention of Money Laundering Act, 2002 (PMLA) has affirmed the attachment of assets totaling Rs 751.9 crore associated with a political family.
The Enforcement Directorate (ED) had provisionally attached these properties in a PMLA case.
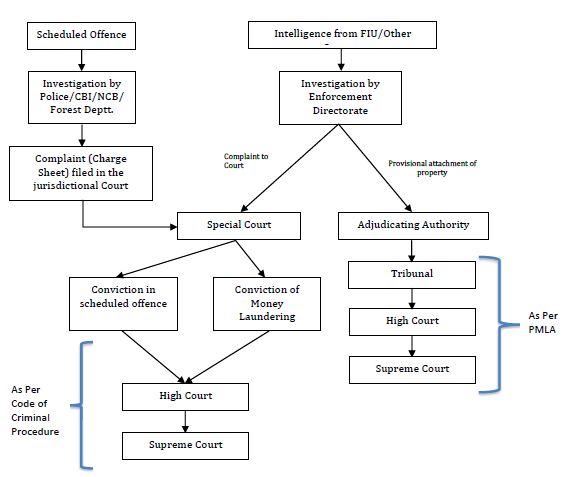
Background on Adjudicating Authority under PMLA;
- Empowered by Section 5 of the PMLA, the ED provisionally attaches assets suspected to be acquired through criminal proceeds.
- These provisional orders, lasting for 180 days, necessitate confirmation by the Adjudicating Authority within the designated timeframe to maintain their legal validity.
Responsibilities of the Adjudicating Authority
- Appointed by the central government, the Adjudicating Authority scrutinizes attachment orders to ensure adherence to legal standards and procedural requirements.
- Failure to confirm the attachment within the prescribed timeline results in the automatic release of the attached property.
Legal Consequences Following Confirmation
- Upon confirmation, the accused retains the right to challenge the order within 45 days at the PMLA’s Appellate Tribunal.
- If the order is upheld, the accused may pursue further legal recourse, while the attached property remains inaccessible until the conclusion of legal proceedings.
Impact on Property Owners and Enforcement Agencies
- Confirmed attachments may prompt the ED to take possession of residential properties, compelling owners to vacate.
- Attached properties, including vehicles, may deteriorate over time as legal battles prolong, posing significant financial implications for both parties.
Mount Etna’s Volcanic Vortex Rings: A Rare Natural Phenomenon
Context;
Mount Etna, situated on the eastern coast of Sicily in Italy, has recently garnered attention for emitting circular rings of vapor, known as volcanic vortex rings, from its summit.
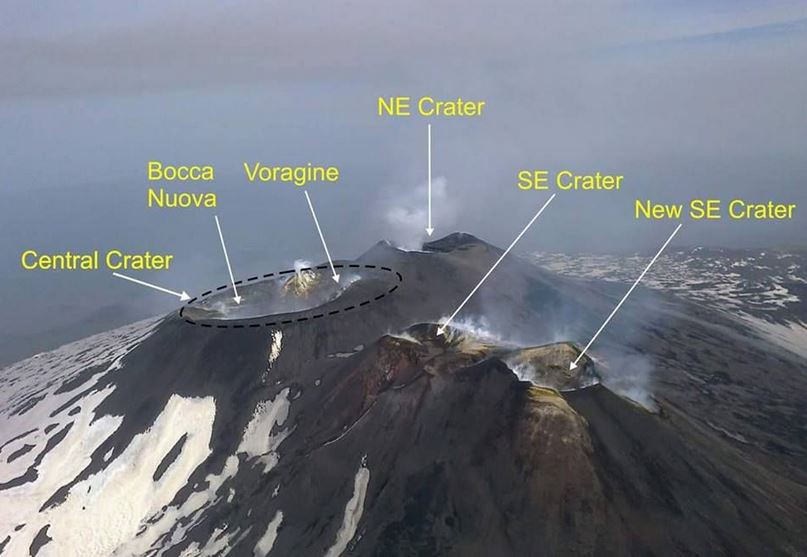

About Mount Etna
- Mount Etna is an active stratovolcano characterized by its conical shape, formed by layers of hardened lava, ash, and volcanic rocks.
- It is Europe’s tallest active volcano, towering approximately 3,329 meters (10,922 feet) above sea level.
- Etna has a rich history of eruptions dating back to around 1500 BCE and has been designated as a UNESCO World Heritage Site since 2013 due to its geological significance and natural beauty.
- The volcano boasts five craters responsible for eruptions, as well as numerous vents along its slopes.
Understanding Volcanic Vortex Rings
- Volcanic vortex rings are a rare phenomenon observed when gas, primarily water vapor, is rapidly released through a vent in the volcano’s crater, forming circular rings of smoke above the mountain.
- This occurrence, akin to smoke rings blown by cigarette smokers, takes place when gas is expelled through a nearly perfect circular vent in the crater.
- These rings can linger in the air for up to 10 minutes but may dissipate rapidly in windy conditions.
Historical and Recent Observations
- Mount Etna produces more vapor rings than any other volcano on Earth, making it a focal point for studying this phenomenon.
- The occurrence of volcanic vortex rings was first documented in 1724 at Mount Etna and Vesuvius in Italy and has since been observed at various volcanoes worldwide.
- Recent sightings of this phenomenon have been reported at volcanoes in Alaska, Ecuador, Guatemala, Iceland, Italy, Japan, Vanuatu, New Zealand, and Nicaragua.

Recent Volcanic Eruptions in the News
Numerous active volcanoes worldwide, particularly those clustered in the Pacific Ring of Fire, continue to capture headlines due to their ongoing volcanic activity. Notable examples include:
- Kilauea, Hawaii: Kilauea volcano has been erupting nearly continuously since 1983, with a notable eruption lasting until 2018 and rekindling in 2021.
2. Dukono, Indonesia: The Dukono volcano in Indonesia has been erupting since August 1933, demonstrating sustained volcanic activity over the decades.
3. Santa Maria, Guatemala: Santa Maria volcano in Guatemala has been erupting since June 1922, highlighting the enduring nature of certain volcanic phenomena.
4. Yasur, Vanuatu: Yasur volcano in Vanuatu has been erupting since around 1270 and remains active as of June 9, 2023.
Understanding Volcanoes
- Volcanoes are geological features characterized by openings or vents through which lava, tephra (small rocks), and steam erupt onto the Earth’s surface.
- They are the result of both their own eruptions and broader tectonic plate movement. Volcanic eruptions occur when magma, or molten rock, beneath the Earth’s surface rises, bubbles, and overflows, much like boiling milk spilling from a pot on a stove.
- This magma seeks pathways to vents within the volcano, where it erupts and is expelled across the land and into the atmosphere, a phenomenon referred to as lava.
Innovative Solution: IISc’s Sustainable Hydrogel for Microplastic Removal
Introduction:
Researchers at the Indian Institute of Science (IISc) have developed a groundbreaking hydrogel aimed at tackling the pervasive issue of microplastic pollution in water.
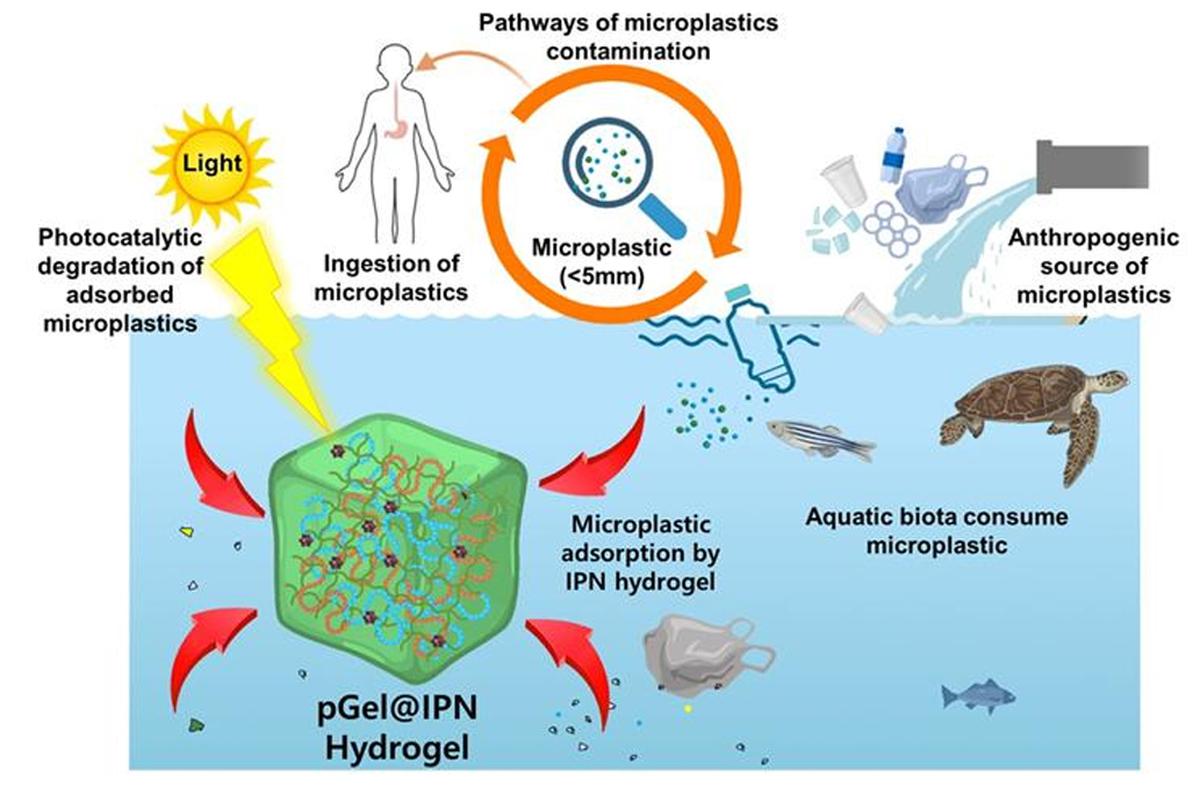
Understanding the Hydrogel:
- Hydrogel, also known as aqua gel, is a network of polymer chains with the ability to absorb and retain large quantities of water.
- This newly devised hydrogel boasts a unique polymer structure adept at binding and breaking down microplastic contaminants upon exposure to UV light.
- Unlike conventional filtration methods prone to clogging, the hydrogel offers a sustainable solution for microplastic removal
Composition and Architecture:
- The hydrogel is composed of chitosan, polyvinyl alcohol, and polyaniline layers intricately intertwined to form an interpenetrating polymer network (IPN) architecture.
- Within the hydrogel matrix are embedded nanoclusters of a substance called copper-substituted polyoxometalate (Cu-POM), which serve as catalysts for microplastic degradation under UV light.
Efficiency and Effectiveness:
– Demonstrating remarkable efficacy, the hydrogel is capable of removing approximately 95% and 93% of two distinct types of microplastics from water sources.
Implications and Future Prospects:
- This eco-friendly hydrogel represents a significant step towards combating microplastic pollution, offering a promising solution for environmental preservation.
- Further research and development may lead to widespread implementation of this technology for mitigating microplastic contamination in aquatic ecosystems.
The Great Barrier Reef
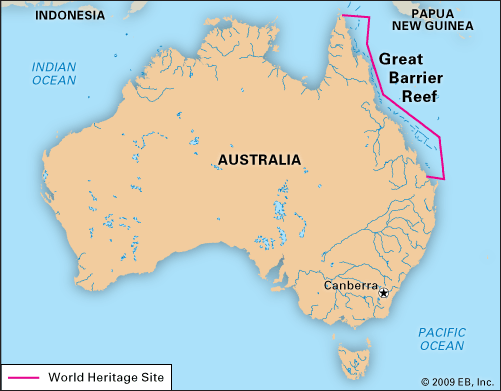
Introduction;
Recent findings by the Australian Marine Conservation Society have revealed that the coral bleaching event witnessed earlier this year in the southern sector of the Great Barrier Reef has exceeded initial expectations.
About the Great Barrier Reef:
- The Great Barrier Reef is an intricate system of coral reefs, shoals, and islets situated in the Pacific Ocean.
- Located off the northeastern coast of Australia in the Coral Sea, it stands as the longest and largest reef system globally and is recognized as the largest living structure on Earth.
- Spanning over 2,300 km in a northwest-southeast direction, with a width varying from 60 to 250 km, and covering an area of approximately 350,000 square km, the reef is a monumental natural wonder.
- Comprising nearly 3,000 individual reefs and over 900 islands, the Great Barrier Reef is visible from space and holds the distinction of being declared a World Heritage Site by UNESCO in 1981.
- A significant portion of the reef is designated as a marine protected area, overseen by the Great Barrier Reef Marine Park Authority of Australia.
Biodiversity:
– The reef ecosystem hosts an impressive array of marine life, including around 2,000 species of fish and approximately 600 species of coral.
– Additionally, the reef provides habitat for over 4,000 species of mollusks, more than 250 species of shrimp, six out of seven known species of sea turtles, numerous sea snakes, and nearly two dozen species of birds.
Understanding the Science Based Targets Initiative (SBTi)
Overview:
A recent decision by the Science Based Targets Initiative (SBTi) to allow carbon offsetting for Scope 3 emissions among businesses with SBTi-based climate targets has sparked controversy and raised doubts.
About the Science Based Targets Initiative (SBTi):
- The Science Based Targets Initiative (SBTi) is a global initiative established in 2015.
- The objective of encouraging and assisting companies in setting science-based targets (SBTs) to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and constrain global warming to well below 2°C above pre-industrial levels.
- The SBTi operates as a collaboration between CDP, the United Nations Global Compact, the World Resources Institute (WRI), and the World Wide Fund for Nature (WWF).
- It furnishes a framework and guidelines for companies to establish targets that align with the most recent climate science, including the objectives of the Paris Agreement.
- This entails setting targets consistent with limiting warming to 1.5°C above pre-industrial levels, which represents the more ambitious aim of the Paris Agreement.
- Companies can have their targets independently verified and endorsed by the SBTi, ensuring alignment with the latest scientific findings and Paris Agreement objectives.
- Through the adoption of science-based targets, companies can showcase their dedication to combating climate change and reducing their carbon emissions.
- The SBTi differentiates between near-term and long-term objectives and commitments.
- Near-term targets outline how organizations plan to reduce emissions over the next 5-10 years, crucial for significant progress by 2030 and a prerequisite for achieving net zero targets.
- Long-term targets detail how organizations must decrease emissions to attain net zero status, according to the criteria outlined in the SBTi Corporate Net-Zero Standard, by 2050 at the latest (2040 for the energy sector).
- The SBTi oversees the SBTi Net-Zero Standard, a pioneering framework for establishing corporate net-zero targets.
Conclusion;
It stands as the sole framework globally for setting corporate net-zero targets aligned with climate science, offering companies the necessary guidance and resources to establish science-based net-zero objectives.
Parivartan Chintan
Context:
The Tri-service Conference, known as ‘Parivartan Chintan’, convened in New Delhi to address crucial military strategies and operational restructuring.
About:
- ‘Chintan’ was orchestrated as a collaborative brainstorming session to foster innovative ideas, initiatives, and reforms aimed at advancing Jointness and Integration within the Armed Forces.
- Jointness and Integration serve as foundational elements in the transition toward unified Joint Structures, aligning the Indian Armed Forces with the vision of being “Future Ready”.
Theatre Command:
- A Theatre Command integrates elements of the Indian Army, Indian Navy, and Indian Air Force under a unified command structure.
- Each command is designated a specific geographic region, consolidating resources from all three services for operational effectiveness.
- The initial setup includes two land-based commands, focusing on Pakistan and China respectively, alongside a maritime command responsible for overseeing the Indian Ocean Region.
- The first three theatre commands are likely to be established in Jaipur, Lucknow, and Karwar, with discussions on their formation ongoing for three years.
Need for Theatre Command:
1. Hostile Neighborhood: With China and Pakistan posing significant threats, the possibility of a two-front conflict necessitates swift and dynamic responses.
2. Resource Optimization: Pooling resources enables efficient utilization of platforms, weapon systems, and assets, eliminating redundancy.
3.Logistics Improvement: Theatre commands offer potential enhancements in logistics management within the forces.
4. Enhanced Coordination: Unified command structures facilitate streamlined communication processes during joint operations and exercises.
5. International Practice: Major military powers like the US, UK, Russia, China, and France already operate under theatre commands, demonstrating their effectiveness.
6. Efficient Planning: A unified command structure promotes more efficient planning for both peacetime and wartime strategies.
Challenges in Implementation:
- Inter-Service Differences: Variances in perspectives among the three forces regarding scope, structure, and control of commands.
- Resource Transfer: Uncertainty regarding the deployment of war-fighting equipment and the transfer of resources between theatre commands.
- Curriculum Development: Insufficient preparation in educational frameworks for military personnel serving in theatre commands.
4. Lack of National Security Strategy (NSS): Implementing theatre commands without a coherent NSS may lead to ambiguity in objectives and policies.
Conclusion:
As India embarks on its significant military restructuring, integrating theatre commands will be pivotal in bolstering its defense capabilities.
However, addressing institutional and ideological challenges is imperative to ensure a balanced and effective transformation, especially given the threats posed along India’s northern and western borders.

