Topics:
- Agriculture Infrastructure Fund
- Purchasing Managers’ Index
- Himalayan Vulture
- Import Restrictions
- Voyager 2 Spacecraft
- Einstein’s Cross
- Kuril Islands
Agriculture Infrastructure Fund
Context:
In 2020, the Agriculture Infrastructure Fund (AIF) was introduced with a total allocation of Rs 1 lakh crore, aimed at enhancing post-harvest infrastructure. However, it is concerning that only 15 percent of the fund has been utilized during the initial three years.
According to the Union agriculture minister’s disclosure in Parliament, Rs 15,448 crore has been disbursed for 27,748 projects up to this point. Out of this amount, only Rs 9,660 crore (equivalent to 9.66 percent of the total allocation) has been used to complete a total of 19,650 projects.
Introduction
The Agriculture Infrastructure Fund (AIF) is a central sector scheme in India that provides a financing facility of Rs.1 lakh crore for funding agriculture infrastructure projects at farm-gate and aggregation points.
The scheme provides medium to long term debt financing facility for investment in viable projects for post-harvest management infrastructure and community farming assets through interest subvention and financial support/credit guarantee.
The fund has been launched as part of ‘Atmanirbhar Bharat’ to make farmers self-reliant1. The scheme duration is from FY2020 to FY2032 (10 years).
Objectives
- To mobilize a medium – long term debt financing facility for investment in viable projects relating to post-harvest management Infrastructure and community farming assets.
- To improve agriculture infrastructure in the country and reduce post-harvest losses.
- To enhance the income of farmers and create employment opportunities in rural areas.
- To promote value addition and export of agricultural produce.
- To encourage private sector participation and entrepreneurship in the agriculture sector.
Features
- The loans have an interest subvention of 3% per annum and credit guarantee coverage under CGTMSE for loans up to Rs. 2 Crores.
- The eligible community farming assets include organic inputs production, bio stimulant production units, infrastructure for smart and precision agriculture, and projects identified for providing supply chain infrastructure for clusters of crops including export clusters.
- Farmer communities such as PACS, FPOs, SHGs, JLGs, Multipurpose Co-op societies, Marketing Co-op societies and their federations are also eligible to get the benefit under Agri Infra Fund for creation of post-harvest management infrastructures.
- Multiple lending institutions including Commercial Banks, Cooperative Banks, RRBs, Small Finance Banks, NCDC, NBFCs etc. are participating in the scheme.
- A dedicated online portal has been created for the scheme to provide a single window facility for loan applications, approvals, monitoring and grievance redressal.
- A Project Management Unit (PMU) has been set up to provide handholding support for projects including project preparation.
Benefits
- It will help in creating modern infrastructure facilities for storage, processing, grading, packaging and marketing of agricultural produce.
- It will reduce wastage and spoilage of perishable commodities and enhance their shelf life and quality.
- It will increase the income of farmers by providing them better prices and market linkages.
- It will create employment opportunities in rural areas and boost rural economy.
- It will foster innovation and entrepreneurship in the agriculture sector by leveraging new-age technologies such as IoT, AI, etc.
It will improve the competitiveness of Indian agriculture in the global market and boost exports.

Purchasing Managers’ Index
News:
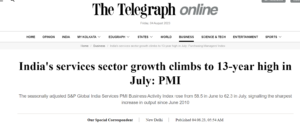
In its latest report, the S&P Global India Services Purchasing Managers’ Index (PMI) revealed a significant recovery in India’s services sector output. After hitting a three-month low in June, the index surged to an impressive 62.3 in July, marking a remarkable 13-year high.
Basics of PMI:
- The Purchasing Managers’ Index, serves as a gauge for business activity in both the manufacturing and services sectors.
- This index relies on surveys, where respondents provide their perceptions of key business variables compared to the previous month.
- Separate calculations are made for manufacturing and services, which are then combined to create a composite index.
- A PMI value above 50 indicates business activity expansion, while a value below 50 signifies contraction.
- The extent of expansion or contraction is determined by the difference from this mid-point.
- Comparing the current PMI with the previous month’s data helps assess the rate of expansion.
- A higher figure suggests faster economic growth, while a lower figure implies slower growth.
By analysing these indicators, the PMI provides valuable insights into the overall economic health of the country or region.
Himalayan Vulture

News:
The initial documentation of captive breeding of the Himalayan vulture (Gyps himalayensis) within India has been successfully achieved at the Assam State Zoo in Guwahati.
This species is classified as ‘Near Threatened’ on the Red List of threatened species by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN).
Basics
- The Himalayan vulture, scientifically known as Gyps himalayensis, is a rare and magnificent bird native to the Himalayas.
- It primarily inhabits the higher regions of the Himalayas and the Tibetan Plateau, usually found at elevations above 1500 meters.
- A wide distribution, spanning from western China, Kazakhstan, Uzbekistan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan, Afghanistan, and Pakistan, all the way east through the Himalayan Mountain range, covering regions in India, Nepal, and Bhutan, extending further to central China and Mongolia.
- Regrettably, the Himalayan vulture is facing threats to its existence, and it is classified as “Near Threatened” by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) Red List of Threatened Species.
- To safeguard its future, conservation efforts have been implemented, including its inclusion in the Multi-species Action Plan (MsAP) for the preservation of African-Eurasian vultures, as well as being subject to national Action Plans in countries such as India, Bangladesh, Nepal, and Cambodia.
- The most significant danger to this vulture species is believed to be mortality resulting from the ingestion of diclofenac and other vulture-toxic non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), which are widely used in livestock, especially in South Asia.
- Addressing this threat is crucial to the survival of the Himalayan vulture and the overall preservation of this magnificent species.
Import Restrictions
News:
In response to security concerns and the desire to boost domestic manufacturing, the government has taken swift action by implementing import restrictions on laptops, tablets, and specific categories of computers. These measures have been put into effect immediately.
Key Points
- This decision will limit the influx of certain goods from countries like China and Korea.
- Importers of these goods will now be required to obtain government permission or a license for their imports.
- The new regulations will enable the government to closely monitor imports, particularly from China, and control the inflow when necessary.
- The notification outlines several cases where licensing requirements are exempted.
- Import restrictions do not apply to goods imported under baggage rules, allowing one old and one new laptop per person.
- Although the import restrictions on laptops, tablets, and computers are not targeted at any specific country, they will likely impact imports from China, given their significant share in the $7 billion annual imports of these items.
● The new notification is effective immediately. However, under the transition provisions of the foreign trade policy, consignments with issued bill of lading and letter of credit before August 3 can be imported without a license until August 31. After that, importers will need the appropriate licenses.
Voyager 2 Spacecraft

News:
After more than a week since the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) lost communication with Voyager 2, the long-running space probe, the space agency has now picked up a signal that can be described as a “heartbeat” from the spacecraft.
The detected signal confirms that Voyager 2, positioned approximately 19.9 billion kilometers away from Earth, is still functional.
The loss of communication occurred on July 21, when a faulty command caused the probe’s antenna to shift 2 degrees away from its Earth-pointing position.
Due to this issue, Voyager 2 is currently unable to receive any commands or send data back to Earth. Despite this setback, the spacecraft continues to operate in space.
Overview
- Voyager 2 is a space probe launched by NASA on August 20, 1977, to study the outer planets and interstellar space beyond the Sun’s heliosphere.
- It is part of the Voyager program, along with its twin, Voyager 1, which was launched 16 days earlier.
- It is the only spacecraft to have visited all four of the solar system’s giant planets: Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune.
- It is also the third of five spacecraft to achieve solar escape velocity, which allowed it to leave the solar system and enter interstellar space.
- It has been operating for 45 years, 11 months and 13 days as of August 3, 2023 UTC; as of July 2023, it has reached a distance of 133.041 AU (19.903 billion km; 12.367 billion mi) from Earth.
Mission Objectives
- The primary mission of Voyager 2 was to explore the Jovian system in 1979, the Saturnian system in 1981, the Uranian system in 1986, and the Neptunian system in 1989.
- The secondary mission of Voyager 2 was to find and study the edge of the solar system, known as the heliosphere, where the solar wind interacts with the interstellar medium.
- The extended mission of Voyager 2 is to study interstellar space, where it can provide direct measurements of the density and temperature of the interstellar plasma.
Major Discoveries
-
- It discovered a 14th moon at Jupiter, named Thebe.
- It observed active volcanoes on Jupiter’s moon Io and geysers on Saturn’s moon Enceladus.
- It revealed complex ring systems around Saturn, Uranus and Neptune.
- It discovered 10 new moons at Uranus, including Miranda, which has a bizarre terrain of ridges and valleys.
- It discovered five new moons at Neptune, including Triton, which has a retrograde orbit and a nitrogen atmosphere.
- It detected a “Great Dark Spot” on Neptune, similar to Jupiter’s Great Red Spot.
- It entered interstellar space on November 5, 2018, becoming the second human-made object to do so after Voyager 1.
Propulsion System: The spacecraft are equipped with compact nuclear reactors, utilizing plutonium pellets as their power source.
Einstein’s Cross
News:
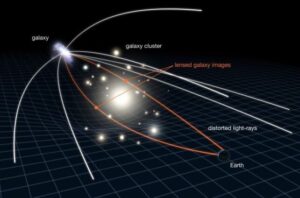
Astronomers made a fascinating discovery of an unusual Einstein cross, where the light from a distant part of the universe undergoes splitting an amplification.
What is it?
- Einstein’s Cross is a phenomenon of gravitational lensing, where the light from a distant object is bent and magnified by the gravity of a massive object in front of it.
- The massive object is a galaxy, which acts as a lens and splits the quasar’s light into four images that form a cross shape around its center.
- The quasar and the galaxy are aligned in such a way that we can see the cross from Earth.
How was it discovered?
- The first Einstein’s Cross was discovered in 1985 by John Huchra and his colleagues, who noticed that there was a quasar behind a galaxy with different redshifts.
- They used the 1.5-meter telescope at Kitt Peak National Observatory to resolve the four images of the quasar, which they named Q2237+0305.
- The galaxy was named ZW 2237+030 or Huchra’s Lens, after the discoverer.
- The quasar is located about 8 billion light-years away from Earth, while the galaxy is about 400 million light-years away.
Why is it important?
- Einstein’s Cross is a rare and spectacular example of gravitational lensing, which confirms Einstein’s theory of general relativity.
- Gravitational lensing can help us study distant and faint objects that would otherwise be invisible or too dim to see.
- It can also reveal information about the mass and structure of the lensing object, such as its dark matter distribution.
- Moreover, Einstein’s Cross can show variations in brightness due to the gravitational microlensing effect of individual stars in the galaxy, which can help us measure their masses and distances.
Kuril Islands
Location:
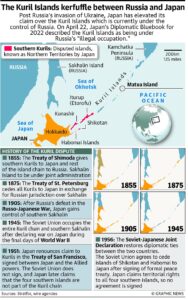
The Kuril Islands constitute a cluster of four land masses situated between the Sea of Okhotsk and the Pacific Ocean, in close proximity to Japan’s northernmost prefecture, Hokkaido.
Names:
These islands are referred to by different names by various countries.
Japan calls them the “Northern Territories,” Russia identifies them as the “Kuril Islands,” and South Korea designates them as the “Dokdo Islands.”
Geological Characteristics:
- The Kuril Islands are part of the Pacific Ring of Fire belt and boast a remarkable geological landscape.
- With over 100 volcanoes, 35 of which remain active, the islands are abundant in hot springs.
Historical Background:
- Following World War II, the Soviet Union took control of the islands and forcibly expelled their Japanese inhabitants by 1949.
- Japan asserts its historical claim to the islands, dating back to the early 19th century, citing treaties such as the Shimoda Treaty (1855), Treaty of St. Petersburg (1875), and Portsmouth Treaty (1905) after the Russo-Japanese War.

