Index:
- EC's Election Rule Amendment Controversy
- RBI Bulletin Article - Inflation and Economic Growth
- India Achieves Highest Global Remittance Share in 2024
- Ken-Betwa River Linking Project
- India-Kuwait Relations
- India Funds Sri Lanka
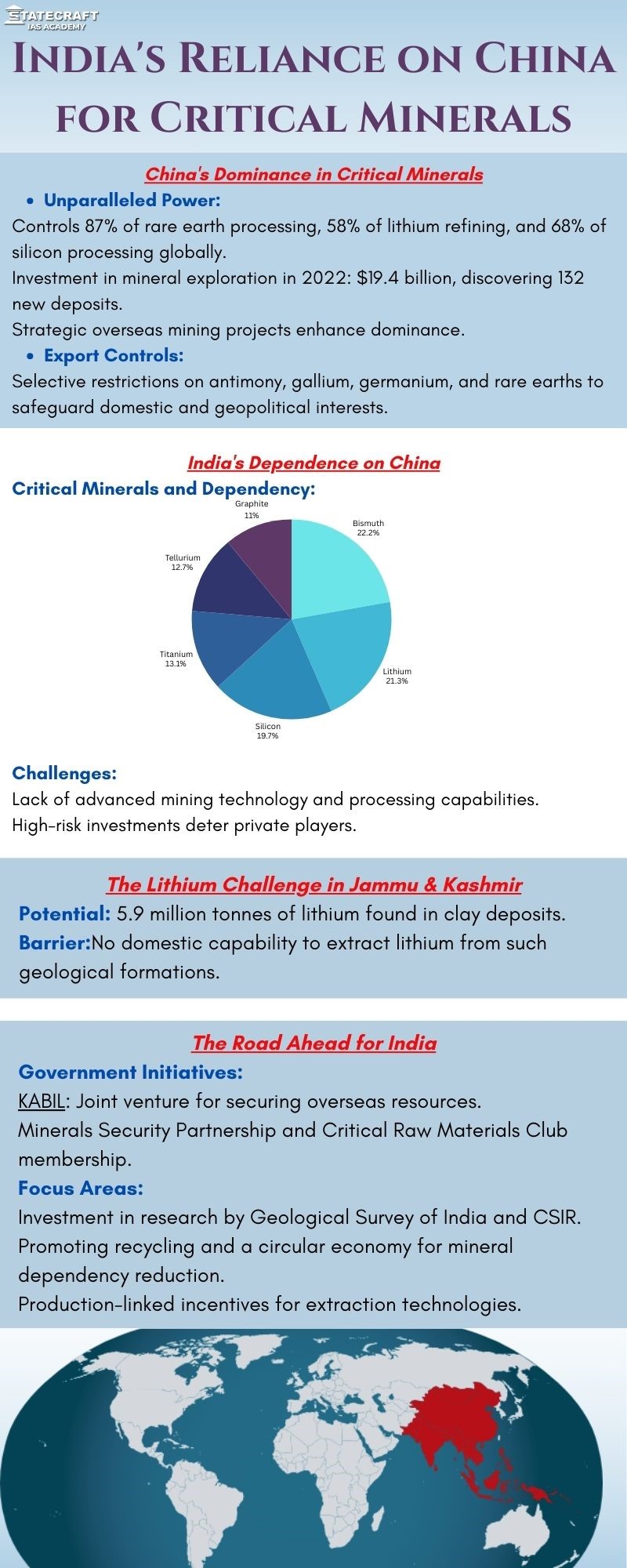
- India's Reliance on China for Critical Minerals - Infographic
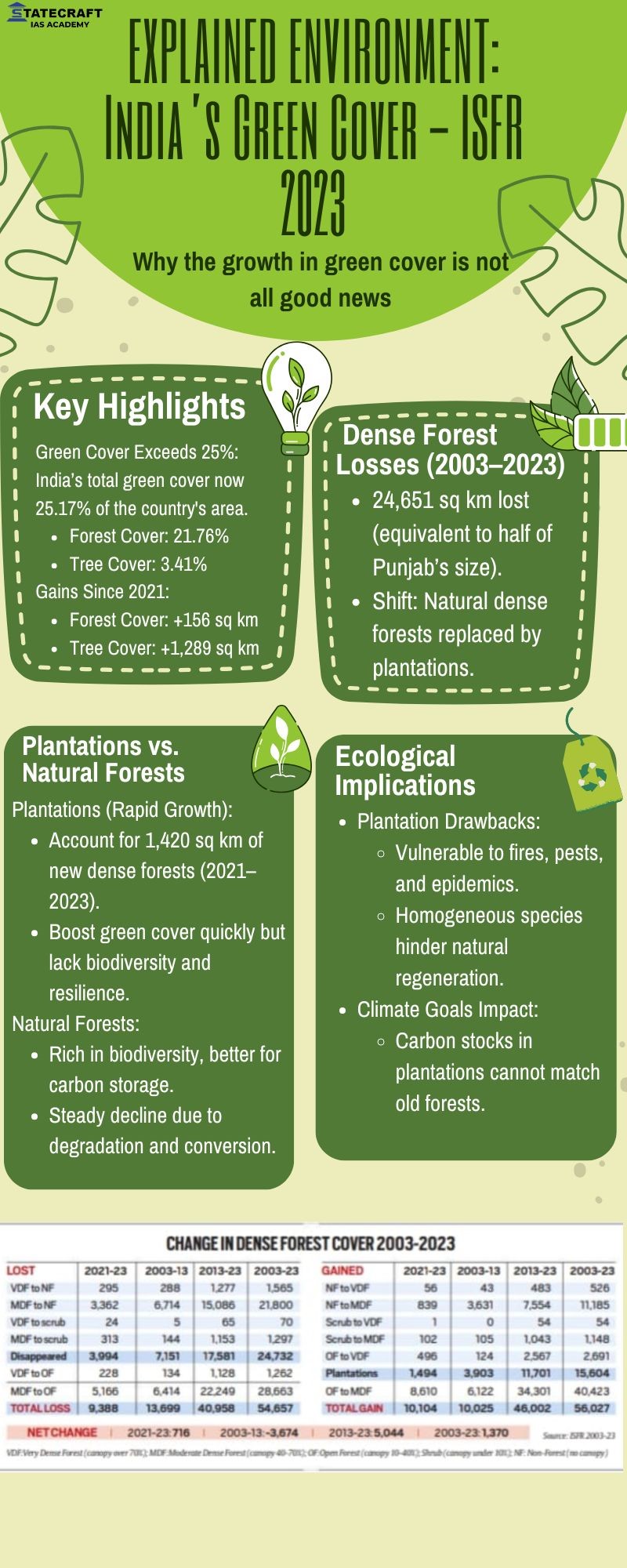
- India’s Green Cover - ISFR 2023- Infographic
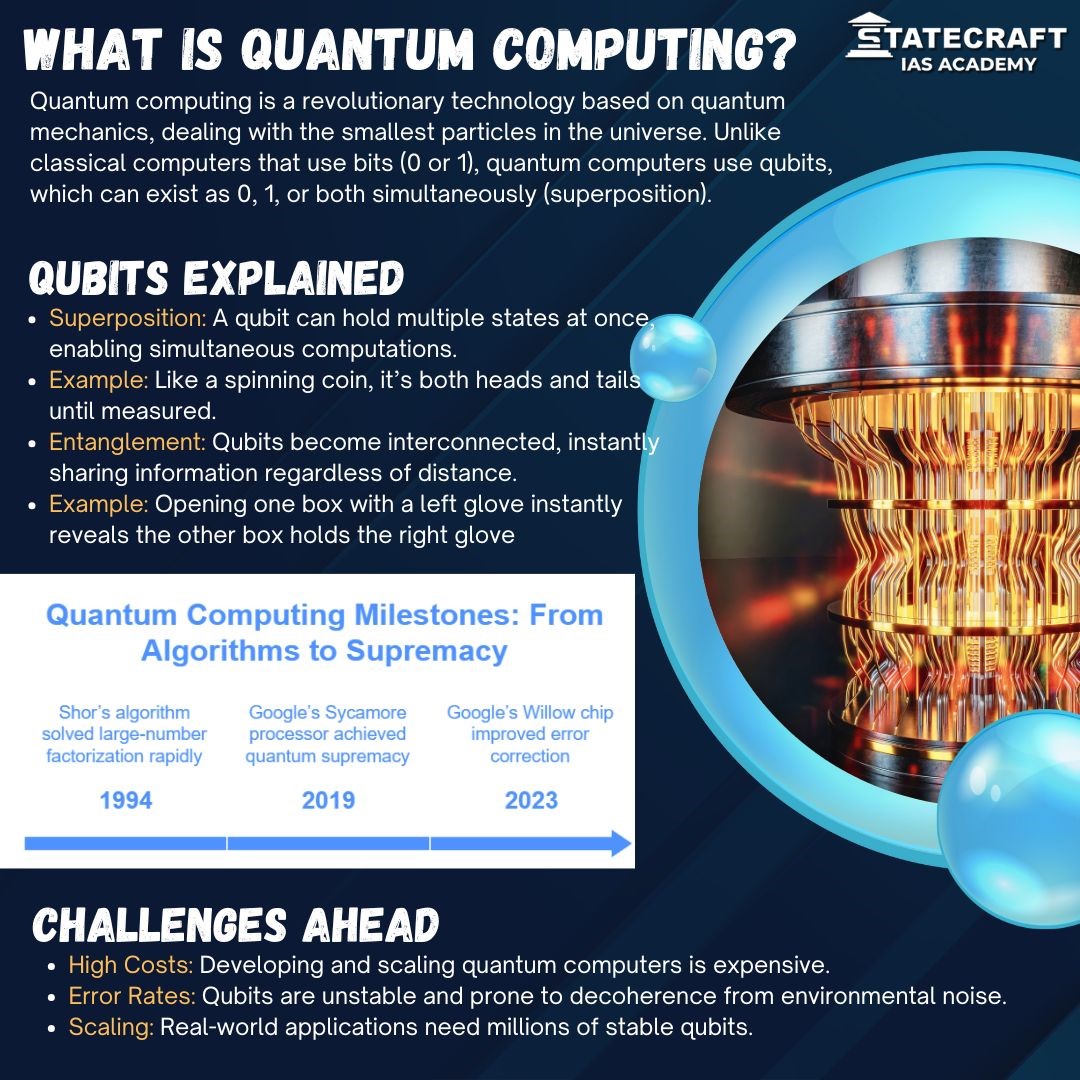
- What is Quantum Computing- Infographic
1. EC's Election Rule Amendment Controversy
Context: The Centre amended the Conduct of Election Rules (December 20, 2023) to restrict public access to certain election-related documents.
- This followed a recommendation by the Election Commission (EC) to the Union Law Ministry.
Key Details:
- Conduct of Election Rules, 1961: Governs provisions on conducting elections under the Representation of People Act.
- Amendment Highlights:
- Revised Rule 93(2)(a) states:
- CCTV footage and some electronic data will not be open for public inspection.
- Other documents remain accessible for inspection.
- Reason for the Amendment:
- To address misuse of CCTV footage via AI manipulation.
- Protects secrecy in sensitive voting areas.
- Opposition and Activist Criticism:
- Transparency concerns:
- Activists argue this curtails citizens’ right to know, conflicting with RTI principles.
- Claims that it undermines free and fair elections.
- Opposition’s stance:
- Congress and other parties label it “unilateral,” alleging it undermines democratic processes.
- Election Commission’s Justification:
- Cited privacy and security concerns over sensitive data.
- Other election-related documents remain accessible.
- Broader Implications:
- Raises questions about electoral transparency vs. data protection and misuse.
Can influence voter trust in democratic institutions.
2. RBI Bulletin Article - Inflation and Economic Growth
Key Highlights:
- Economic Context:
- India’s GDP growth slowed to 4% (July-September 2024) due to:
- Reduced domestic demand.
- Corporate wage stagnation.
- Emerging headwind: Declining nominal GDP growth impacting fiscal spending.
- Inflation Challenges:
- Retail inflation dropped to 5% (November) from 6.2% (October):
- Driven by easing food prices.
- High-frequency data indicates falling rice and wheat prices, stabilizing edible oils and tomatoes.
- RBI’s Recommendation:
- Strongly advocates for immediate action to:
- Tame inflation pressures.
- Revive private investment and consumption.
- Stresses need for targeted capex spending to support economic growth.
- Projected Recovery:
- Growth likely to rebound:
- 8% in Q3 (2024-25).
- 5% in Q4, improving to 7% in 2025-26.
- Disinflationary trends and monetary policy measures will bolster resilience.
- Global Concerns:
- Warned against:
- Persistent inflation shocks eroding purchasing power.
- Geopolitical tensions affecting global trade.
- High public debt posing risks to emerging markets.
- Opportunities for Growth:
- Recovery driven by:
- Sustained rural demand.
- Strong festive-season private consumption.
Supportive factors: Stable labor markets, easing inflation, and robust exports.
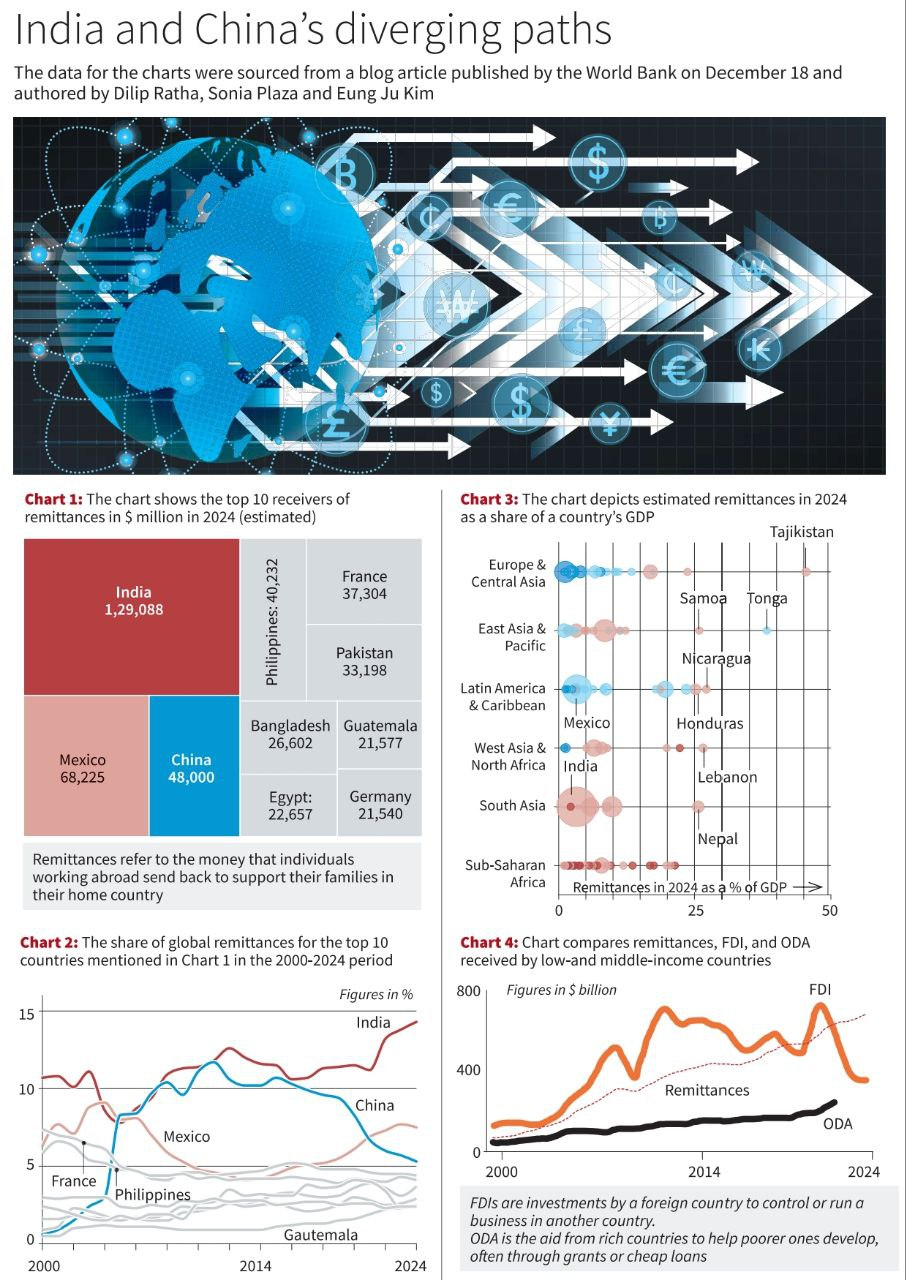
3. India Achieves Highest Global Remittance Share in 2024
Key Highlights:
- India’s Milestone in Remittances:
- India received $129 billion in remittances in 2024, the highest-ever for any country globally.
- Share of global remittances: 3%, marking a significant rise since the turn of the millennium.
- Global Comparison:
- Top countries receiving remittances in 2024:
- India: $129 billion.
- Mexico: $68 billion.
- China: $48 billion (its lowest share in over two decades).
- Nepal, Samoa, Tonga, and other nations’ remittances formed over 25% of their GDP in 2024.
- Significance of Remittances:
- Key contributor to economies: Critical for funding current account deficits and social programs in low-income and middle-income nations.
- For many nations, remittances outweigh FDI and Official Development Assistance (ODA) as financial inflows.
- India vs. China Trends:
- India’s Rise:
- A consistent increase in remittance flows since the early 2000s.
- Contributions from a diverse diaspora working across sectors globally.
- China’s Decline:
- Share fell to 3%, reflecting a reduced dependency on remittances amid an economic shift.
- Regional Patterns:
- South Asia, East Asia, and Africa are significant regions relying on remittances as a percentage of GDP.
- Other nations like Bangladesh, Pakistan, and the Philippines are among top remittance recipients.
- Chart Analysis:
- Chart 1: Top 10 receivers of remittances in 2024.
- Chart 2: Share of global remittances from 2000 to 2024 (notable rise for India, decline for China).
- Chart 3: Percentage of remittances as a share of GDP.
Chart 4: Comparison of remittances, FDI, and ODA for low- and middle-income nations.
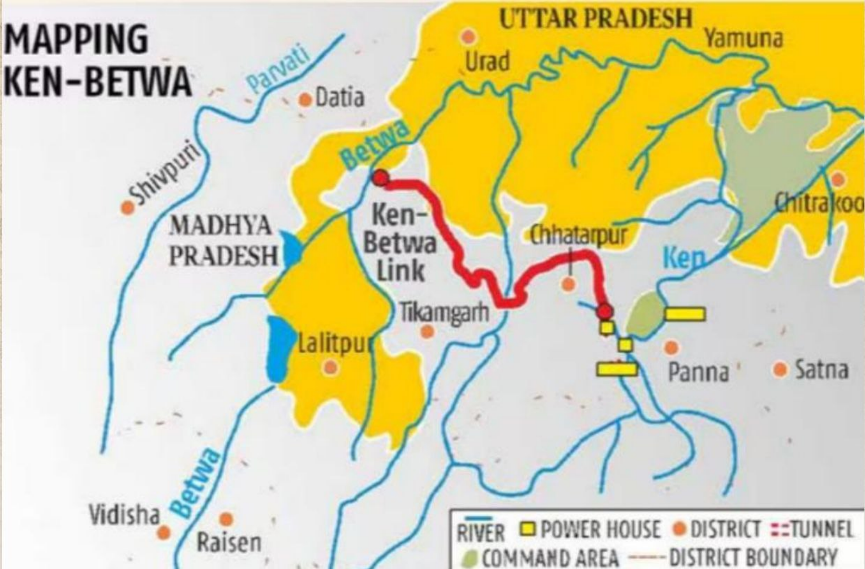
4. Ken-Betwa River Linking Project
Key Highlights:
- Project Overview:
- Foundation Stone Laid: December 2024 by Prime Minister Narendra Modi in Khajuraho, Madhya Pradesh.
- Objective: Address water scarcity in the Bundelkhand region, spread across Uttar Pradesh and Madhya Pradesh.
- Estimated Cost: ₹45,000 crore.
- Significance of the Project:
- Water Distribution:
- Connects the Ken and Betwa
- Aims to provide irrigation, drinking water, and electricity generation.
- Irrigation Benefits:
- Expected to irrigate 62 lakh hectares of agricultural land annually.
- Drinking Water Supply:
- Will supply 49 million cubic meters of drinking water.
- Hydropower Generation:
- Expected to produce 103 MW of hydropower and 27 MW of solar energy.
- Bundelkhand Region:
- Drought-prone area known for water scarcity and agricultural challenges.
- This project is expected to bring economic and agricultural prosperity.
- Historical Context:
- PM Modi credited B.R. Ambedkar for his vision of river valley projects and India’s water management strategies.
Ambedkar’s contributions to the Central Water Commission and water conservation efforts were highlighted.
5. India-Kuwait Relations
Key Highlights:
- Historical Context:
- Trade and Travel Ties:
- Kuwait was a critical entrepôt for India’s trade across West Asia, facilitated by the British East India Company.
- Until 1961, the Indian rupee was legal tender in Kuwait.
- Cultural Connections: The Kuwaiti elite historically maintained ties with Mumbai.
- Economic Relations:
- Bilateral Trade: Tops $10 billion annually.
- Energy Partnership:
- 6th Largest Crude Supplier: Kuwait supplies 3% of India’s energy needs.
- 4th Largest LPG Supplier: Crucial for India’s domestic energy consumption.
- Expatriate Community:
- 500,000 Indians constitute the largest expatriate group in Kuwait, contributing to people-to-people ties and remittances.
- Strategic Partnership:
- Defence Cooperation:
- MOU signed to institutionalize defence collaboration.
- The visit marks a shift to strengthen strategic ties, bridging past hesitations due to India’s close ties with Saddam Hussein’s Iraq.
- Recognition: PM Modi received Kuwait’s highest honor, the Order of Mubarak Al-Kabeer.
Current Geopolitical Context:
- Regional Dynamics:
- West Asia Turmoil:
- Ongoing Israel-Gaza conflict, Lebanon, and Yemen
- Rise in Islamist radicalism post-Assad regime’s ouster in Syria.
- Global Power Shifts:
- The U.S. (domestic focus) and Europe (Russia-Ukraine war) may leave a leadership vacuum in the region.
- India’s Strategic Goals:
- Energy Security: Strengthen ties with Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) nations to secure energy supplies.
- Connectivity Initiatives:
- Projects like IMEC (India-Middle East-Europe Corridor) and I2U2 need stability in the region.
- Diaspora Welfare: Safeguard the rights and welfare of over 8 million Indians working in the Gulf.
Way Forward:
- Leverage Defence MoU: Expand defence and security cooperation with Kuwait to counter regional instability.
- Focus on Energy Security: Diversify energy partnerships to ensure uninterrupted supplies amidst global tensions.
- Diaspora Welfare: Strengthen legal and social frameworks to protect Indian workers’ rights in Gulf countries.
Infrastructure Projects: Push for the realization of initiatives like IMEC and I2U2, critical for India’s global connectivity and trade.