Index:
- Strife-hit Manipur put under President’s Rule
- Pilgrims Meet Climate Change on an Island
- Engaging Russia – Trump's Overtures to Putin
- Removal of High Court Judge – Statement by Jagdeep Dhankhar
- Retail Inflation Eases to 4.31% (January 2025)
- SC to Hear Pleas on CEC Appointment Law
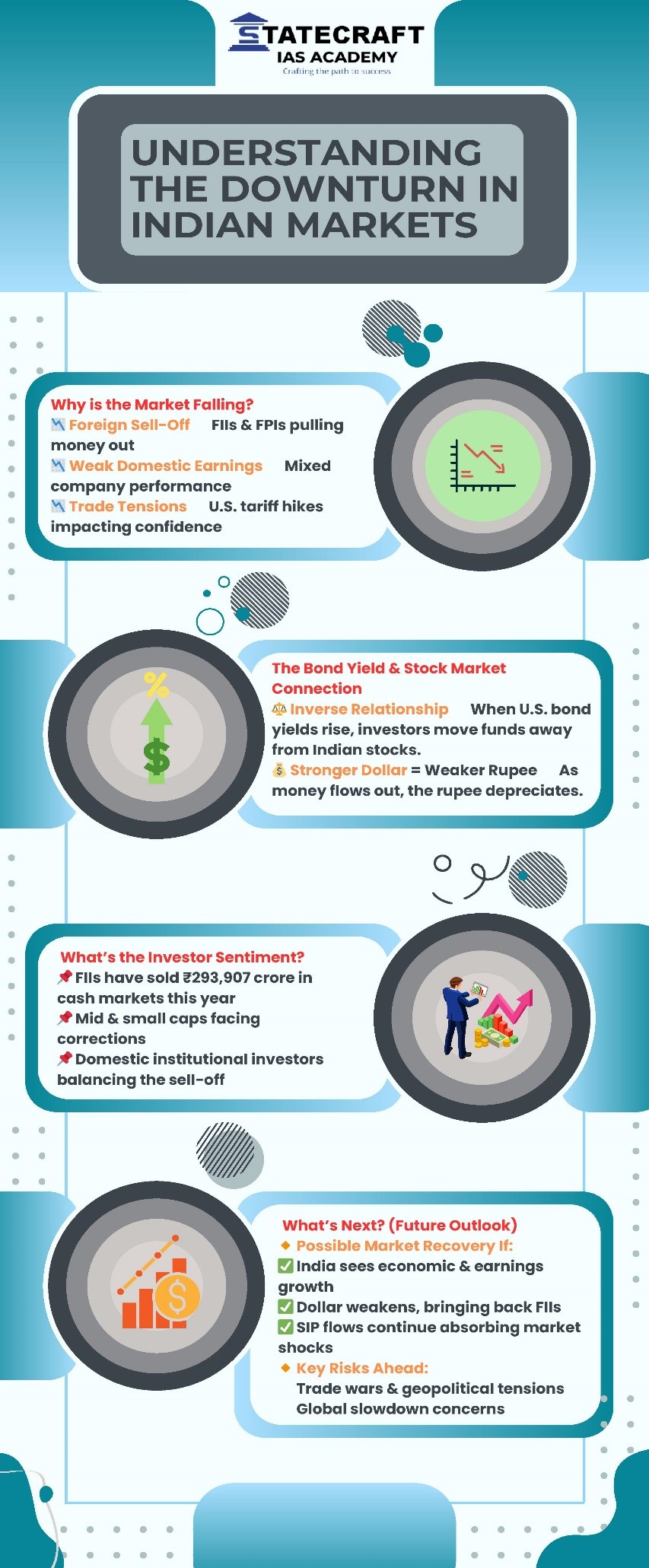
- Understanding the Downturn in Indian Markets-Infografic
- SHOULD CONVICTED PERSONS CONTEST ELECTIONS-Infografic
1. Strife-hit Manipur put under President’s Rule
Context:
- President Droupadi Murmu imposed President’s Rule in Manipur under Article 356 after receiving a report from Governor Ajay Kumar Bhalla.
- The move follows the resignation of Chief Minister N. Biren Singh and ongoing ethnic violence.
President’s Rule in Manipur (2024)
- Invoked under Article 356 of the Constitution.
- Manipur Legislative Assembly is under “suspended animation” (not dissolved).
- Governor Ajay Kumar Bhalla to handle administrative and security-related decisions.
Background of Political Crisis
- Ethnic conflict between tribal Kuki-Zo and Meitei communities since May 3, 2023.
- Over 250 people killed and 60,000 displaced due to violence.
- CM N. Biren Singh resigned on February 9, 2024, after meeting with Home Minister Amit Shah.
- BJP leadership failed to agree on an alternative CM.
Historical Context: President’s Rule in Manipur
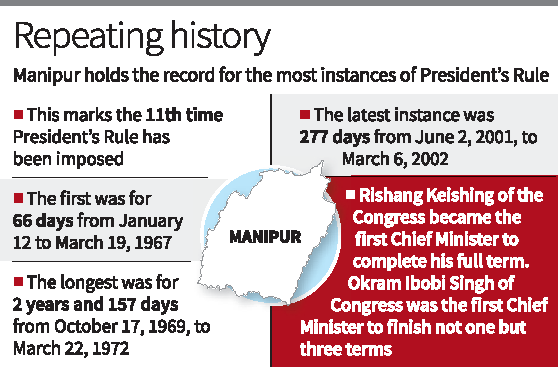
- 11th instance of President’s Rule in the state.
- First imposition: 1967 (for 66 days).
- Longest duration: 2 years and 157 days (1969-1972).
- Latest before 2024: 277 days (June 2, 2001 – March 6, 2002).
- Rishang Keishing (Congress) was the first CM to complete a full term.
- Okram Ibobi Singh (Congress) was the first CM to complete three terms.
Constitutional Provisions Involved
- Article 356: Allows President’s Rule if a state government cannot function as per the Constitution.
- Article 356(3): Proclamation must be laid before Parliament for approval within two months.
- If not approved, the rule ceases to operate.
2. Pilgrims Meet Climate Change on an Island
Context:
- The Gangasagar Mela on Sagar Island (West Bengal) is facing severe climate change impacts, especially rising sea levels and soil erosion.
- The Kapil Muni temple is threatened as the sea is creeping inland.
- The West Bengal government accuses the Centre of non-cooperation in funding protection measures.
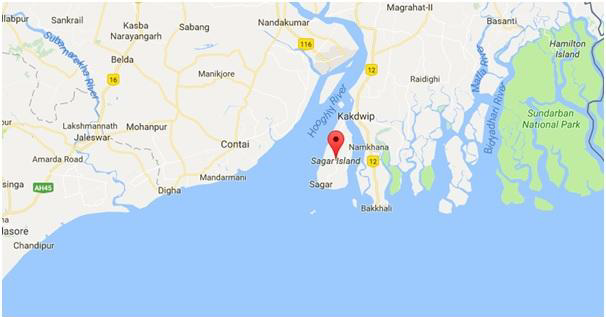
Geographical Significance of Sagar Island
- Located in the Sundarbans delta, South 24 Parganas district, West Bengal.
- Situated at the confluence of the Ganga and the Bay of Bengal.
- Hosts the Gangasagar Mela, India’s second-largest religious gathering after the Kumbh Mela.
- Home to fragile coastal ecosystems, including mangroves.
Climate Change Impact on Sagar Island
- Rising Sea Levels & Coastal Erosion
- The Kapil Muni temple is now just 40 meters from the sea.
- The coastline has receded by 1.2 km over 25 years.
- Encroachment by seawater is reducing available land.
- Threats to Infrastructure & Livelihoods
- Pilgrim shelters and houses have been damaged or submerged.
- Fishermen and locals are losing homes and facing reduced fish catch due to saltwater intrusion.
- Impact on Pilgrimage & Tourism
- Pilgrims face difficulty accessing the Kapil Muni temple due to encroaching waters.
- Authorities built embankments, but these have collapsed due to erosion.
- Biodiversity Loss & Deforestation
- Mangrove forests are declining, increasing the risk of storm surges and cyclones.
- Local deforestation for infrastructure worsens soil erosion.
Centre-State Conflict
- West Bengal government claims that the Centre is not providing adequate funds for coastal protection.
- The state requested ₹500 crore for embankment projects, but there is no agreement on funding.
- National Disaster Management Authority (NDMA) and West Bengal Irrigation Department involved in tackling erosion issues.
Key Environmental Concerns
- Sea Level Rise: Affects coastal communities and heritage sites.
- Erosion & Land Loss: Reduces habitable land and agricultural space.
- Saltwater Intrusion: Affects freshwater resources and agriculture.
- Displacement: Threatens local livelihoods and forces migration.
Government Initiatives & Possible Solutions
- Mangrove Restoration Projects to reduce coastal erosion.
- Construction of Stronger Embankments using geotextile and concrete.
- Relocation of Vulnerable Communities to safer inland areas.
- Centre-State Coordination for climate adaptation funding.
Promotion of Sustainable Tourism to protect fragile coastal ecosystems.
3. Engaging Russia – Trump's Overtures to Putin
Context:
- Former U.S. President Donald Trump has indicated a willingness to negotiate with Russian President Vladimir Putin to end the Russia-Ukraine war.
- The move has raised both hopes and fears—hopes for peace but fears of Moscow leveraging negotiations to its advantage.
Key Highlights of Trump’s Negotiations with Putin
- Trump-Putin Call (90 minutes)
- Trump stated both leaders agreed on stopping the war.
- Russia’s stance: Expressed readiness to receive American officials for discussions, including on Ukrainian settlement.
- Possible Meeting in Saudi Arabia
- A significant shift from the current U.S. stance of isolating Russia through NATO and sanctions.
- Breaks from Biden’s hardline approach, where he labeled Putin a “murderous dictator” and “pure thug”.
- Trump’s Position on the War
- Pledged to end the war within 24 hours if elected.
- Likely to push for a settlement unfavorable to Ukraine.
- No U.S. troop commitment to Ukraine under Trump’s administration.
- Ukraine’s NATO membership unlikely under Trump.
- Pre-2014 borders (before Crimea annexation) ruled out as a settlement option.
Implications of Trump’s Approach
- Geopolitical Consequences
- S. shifts responsibility to Europe → NATO and the EU would bear the brunt of Russian aggression.
- Russia strengthens its position → Negotiations may lead to a deal that legitimizes Russian territorial gains.
- Ukraine faces an unfavorable outcome → Would be forced to accept territorial losses without NATO membership.
- Impact on U.S. Foreign Policy
- Contradicts Biden’s strong anti-Russia stance.
- Could lead to fractures within NATO over policy on Ukraine.
- Reduces U.S. strategic influence in European security.
- Global Security & Economic Effects
- Weakening of Ukraine’s defense without U.S. and NATO backing.
- Potential loss of confidence in U.S. commitments to allies.
Energy and trade disruptions if Europe faces further instability.
4. Removal of High Court Judge – Statement by Jagdeep Dhankhar
Context:
- Rajya Sabha Chairman Jagdeep Dhankhar asserted that only Parliament has the jurisdiction to constitutionally remove a High Court judge.
- The statement was made in the context of Justice Shekhar Yadav (Allahabad HC) facing an impeachment motion over alleged controversial remark.
Key Constitutional Provisions
- Article 124(4) & Article 217 of the Indian Constitution govern the removal of Supreme Court & High Court judges, respectively.
- Impeachment Process:
- Initiated in either House of Parliament with a signed notice from at least 50 Rajya Sabha members or 100 Lok Sabha members.
- The motion is investigated by a committee.
- If found guilty, both Houses must pass the motion by a special majority.
- Finally, the President gives assent, leading to removal.
Events Leading to the Issue
- Justice Shekhar Yadav summoned by the Supreme Court over his controversial communal remarks.
- Opposition parties moved an impeachment notice on December 13, 2024, with 55 Rajya Sabha members signing the motion.
- Chairman Dhankhar reaffirmed that only Parliament can remove a High Court judge, not the Supreme Court.
Implications & Analysis
- Separation of Powers & Judicial Independence
- Ensures checks and balances in the removal process.
- Prevents judicial overreach by limiting the role of the Supreme Court in removal procedures.
- Political and Legal Impact
- The impeachment motion reflects concerns over judicial conduct in sensitive matters.
- Raises debates on judicial accountability vs. judicial independence.
- Constitutional Significance
- Reinforces that removal of judges is a legislative process, preventing potential executive or judicial interference.
- Highlights the complexity of removing judges under the Indian system.
5. Saudi Educator Wins $1M Global Teacher Prize for Charity & Prisoner Education
- Mansour Al-Mansour, a Saudi educator, won the $1 million Global Teacher Prize for his charity work and educating prisoners.
- The Global Teacher Prize is an international award recognizing outstanding contributions in education.
About the Global Teacher Prize
- Established by: Varkey Foundation in 2014.
- Awarded for: Exceptional commitment to education and innovative teaching practices.
- Prize Money: $1 million.
- Previous Winners Include:
- Ranjitsinh Disale (India, 2020) – Worked on girls’ education and developed QR-coded textbooks.
- Andria Zafirakou (UK, 2018) – Focused on art education for underprivileged students.
Significance of Mansour Al-Mansour’s Work
- Prisoner Rehabilitation:
- Uses education as a tool for reform.
- Helps prisoners gain skills for reintegration into society.
- Charity & Social Impact:
- Promotes inclusive education.
- Supports underprivileged communities through teaching initiatives.
- Recognition of Teachers in Social Change:
- Highlights role of education in reducing crime and enhancing human rights.
Encourages governments to invest in prison education programs.
6. HC Allows 25-Week Pregnancy Termination
Context:
- The Bombay High Court permitted a 35-year-old woman to medically terminate her 25-week pregnancy despite existing Medical Termination of Pregnancy (MTP) Rules, which allow termination only up to 24 weeks.
Key Highlights:
- Legal Aspects:
- The woman approached the High Court because her chosen private hospital refused termination beyond 24 weeks, citing legal restrictions.
- The court upheld her reproductive rights, stating autonomy over her body and health is fundamental.
- The HC granted relief under “utmost urgency” to facilitate termination.
- Medical Concerns:
- The fetus had skeletal dysplasia and other congenital conditions, leading to high post-natal morbidity.
- A panel of doctors confirmed multiple corrective surgeries would be required for survival.
- Challenges in MTP Act:
- The court observed a lacuna in the law preventing abortion beyond 24 weeks even in cases of severe fetal anomalies.
- There was no government hospital available to perform the procedure in time, necessitating court intervention.
- Significance:
- Highlights legal hurdles in reproductive rights despite medical urgencies.
- Raises concerns over strict MTP Rules limiting access to safe abortions.
May lead to policy discussions on extending the abortion limit for fetal abnormalities.
6. HC Allows 25-Week Pregnancy Termination
Context:
- The Bombay High Court permitted a 35-year-old woman to medically terminate her 25-week pregnancy despite existing Medical Termination of Pregnancy (MTP) Rules, which allow termination only up to 24 weeks.
Key Highlights:
- Legal Aspects:
- The woman approached the High Court because her chosen private hospital refused termination beyond 24 weeks, citing legal restrictions.
- The court upheld her reproductive rights, stating autonomy over her body and health is fundamental.
- The HC granted relief under “utmost urgency” to facilitate termination.
- Medical Concerns:
- The fetus had skeletal dysplasia and other congenital conditions, leading to high post-natal morbidity.
- A panel of doctors confirmed multiple corrective surgeries would be required for survival.
- Challenges in MTP Act:
- The court observed a lacuna in the law preventing abortion beyond 24 weeks even in cases of severe fetal anomalies.
- There was no government hospital available to perform the procedure in time, necessitating court intervention.
- Significance:
- Highlights legal hurdles in reproductive rights despite medical urgencies.
- Raises concerns over strict MTP Rules limiting access to safe abortions.
May lead to policy discussions on extending the abortion limit for fetal abnormalities.