Index:
- Delimitation and Its Impact on South India
- Three-Language Policy & Its Challenges
- Internet Shutdowns in India – Issues & Concerns
- Wild and Safe: Human-Wildlife Conflict in Kerala
- Simultaneous Elections Bill – Legal and Practical Challenges
- Women Shifting from Unpaid Domestic Work – Govt. Survey (2024)
- Tribal Families Protest Over Sacred Groves in Similipal Tiger Reserve (STR), Odisha
- PM-KISAN Fund Transfer in Poll-Bound Bihar
- Internet Shutdowns in 2024: India’s Position
- PM Modi's Call to Fight Obesity
- Kota Cares Initiative
- India's Reputation in the Pharmaceutical Industry
1. Delimitation and Its Impact on South India
Context
- Tamil Nadu Chief Minister M.K. Stalin has called for an all-party meeting on March 5 to discuss the proposed delimitation exercise.
- Delimitation may reduce the number of Lok Sabha seats in Tamil Nadu.
Key Concerns
- Reduction in Lok Sabha seats:
- Tamil Nadu currently has 39 Lok Sabha seats.
- The delimitation exercise (2026) may reduce it to 31 seats.
- This is seen as a suppression of Tamil Nadu’s voice.
- Population control penalized:
- Southern states like Tamil Nadu have successfully controlled population through:
- Family planning
- Women’s education
- Healthcare advancements
- But the delimitation process may reduce their political representation in Parliament.
- Disproportionate representation:
- Northern states, with higher population growth, may gain more seats.
- This could shift political power from the South to the North.
Stalin’s Stand
- Calls delimitation a “Sword of Damocles” over southern states.
- Urges transcending political differences to oppose the exercise.
- Writes to various political parties to raise concerns.
Stresses that delimitation is not just a Tamil Nadu issue but affects all of South India.
2. Three-Language Policy & Its Challenges
Context
- Conflict between the Union Government and Tamil Nadu over the three-language formula in the New Education Policy (NEP) 2020.
- Tamil Nadu opposes it, calling it a ‘smokescreen’ for Hindi imposition and insists on continuing its two-language policy.
- Delay in Samagra Shiksha Abhiyan funds due to non-compliance with the policy.
Constitutional Provisions
- Official Language Act, 1963: Hindi is the official language of the Union, but English continues for official purposes.
- States’ Choice:
- States can adopt any one or more languages in use.
- Promotion of Hindi as a medium of expression is encouraged but not mandated.
What is the Three-Language Policy?
- Introduced in 1968 under the National Education Policy (NEP) of 1968.
- Mandated the teaching of Hindi in non-Hindi-speaking states.
- NEP 2020 retains it, allowing states flexibility in choosing languages, but requires students to learn at least two Indian languages.
Issues & Challenges
- Learning Outcomes:
- ASER 2022 report:
- 60% of students in Class V couldn’t read a Class I text.
- 25% of 14-18-year-olds could not read a Class I-level text in their regional language.
- 40% struggle with English comprehension.
- Poor foundational numeracy skills (subtraction, division, etc.).
- Implementation Barriers:
- Government schools lack resources to effectively teach three languages.
- Limited proficiency in third languages (e.g., Hindi in Tamil Nadu).
- Financial Burden:
- Education expenditure (2020):
- Centre & States together spent 4-4.5% of GDP (against 6% target in NEP 2020).
- States bear 85% of the cost.
- Sociopolitical Opposition:
- Tamil Nadu follows a two-language policy (English & Tamil).
- Concern over Hindi imposition on non-Hindi-speaking states.
- Linguistic diversity vs. Uniformity debate.
The Way Forward
- Focus on foundational learning rather than just adding more languages.
- Strengthening regional languages & English in government schools.
- Providing autonomy to states in language policy decisions.
- Balancing cultural diversity while ensuring employability and competitiveness.
Key Data Points
- 2011 Census:
- 26% Indians bilingual, 7% trilingual.
- Urban areas: 44% bilingual, 15% trilingual.
- Rural areas: 22% bilingual, 5% trilingual.
3. Internet Shutdowns in India – Issues & Concerns
Context
- India leads globally in government-ordered Internet shutdowns (Software Freedom Law Center, Access Now reports).
- 84 shutdowns in 2024:
- 41 imposed during protests.
- 23 imposed for communal clashes.
- 5 shutdowns imposed during exams to prevent cheating.
Concerns & Challenges
- Impact on Fundamental Rights:
- Supreme Court ruling (Anuradha Bhasin vs Union of India): Shutdowns must meet tests of necessity & proportionality.
- Violates freedom of speech and expression (Article 19).
- Economic & Social Consequences:
- Disrupts livelihoods, medical care, and education.
- Erodes trust in digital governance.
- Hinders business operations, financial transactions.
- Lack of Transparency & Accountability:
- Many shutdowns lack valid government orders on official websites.
- Telecommunications (Temporary Suspension of Services) Rules, 2024 require detailed reasons, but compliance is poor.
- Overuse of Shutdowns:
- Used excessively rather than as a last resort.
- India had 296 shutdowns in 2023, affecting millions.
Alternative methods like misinformation countermeasures, controlled restrictions on social media should be explored.
4. Wild and Safe: Human-Wildlife Conflict in Kerala
Context
- Rising human-wildlife conflict in Kerala, covering nearly 29% forested land.
- Recent fatalities due to wild animal attacks in deep forests, forest-fringed areas, and villages.
- Climate factors: Dry spells & extreme summers worsening conflicts.
- Criticism of the Kerala government for poor wildlife management.
- Call for culling wildlife by some groups, but Forest Department data shows declining wildlife populations (e.g., elephant population declined by 7%).
- Snakebites responsible for 75% of wildlife-related deaths, reduced from 113 (2012) to 34 (2023).
- Overall decrease in human-wildlife fatalities (146 in 2018 to 57 in 2023).
Anthropogenic Causes
- Habitat fragmentation due to human activities, esp. in elephant corridors (Aralam Farm, Kannur & Chinnakanal, Idukki).
- Unregulated tourism, cattle grazing, encroachments, food waste dumping worsening human-wildlife encounters.
- Invasive species (Senna spectabilis) replacing natural vegetation.
Government Initiatives
- Declared human-wildlife conflict a state-specific disaster (2023) → Disaster Management Authority involved.
- Participatory forest & wildlife management approach adopted.
- Forest Department measures:
- Restored 5,031 hectares of natural forest.
- Built ponds, check dams to support wildlife.
- Challenges in restoring industrial plantations (eucalyptus, acacia).
- Conflict Mitigation Efforts:
- Solar fencing effective.
- ₹52-crore elephant-proof wall at Aralam incomplete.
Multi-agency approach involving Disaster Management, Revenue, Local Self-Government, Tribal Welfare, Agriculture, Health, & Forest Departments.
5. Simultaneous Elections Bill – Legal and Practical Challenges
Context
- Former Chief Justice of India (CJI) U.U. Lalit stated that the Simultaneous Elections Bill may not survive a legal challenge.
- Parliamentary Joint Committee reviewing the bill (128th Constitutional Amendment Bill, 2024).
Key Legal Concerns
- Violation of the Basic Structure of Constitution:
- Curtailing the tenure of State Assemblies to synchronize elections is unconstitutional.
- Cited the Kesavananda Bharati judgment, which limits Parliament’s power to amend the Constitution’s basic structure.
- Staggered Approach & Legal Ambiguities:
- Assemblies formed before and after the first synchronized election will face term mismatches.
- Bill includes provisions to fix an “appointed date” for elections, which may create legal inconsistencies.
- State Legislatures’ Autonomy:
- State Assemblies and Parliament stand on equal constitutional footing.
- Forcing them to synchronize elections makes State Assemblies subservient to Parliament.
Practical Concerns
- High Costs vs. Cost Optimization:
- Pro: Single election cycle reduces repeated expenditures on elections.
- Con: Assembly elections currently funded by States, whereas Lok Sabha elections funded by Centre.
- Instances like Delhi and Haryana’s Assembly elections costing more than Lok Sabha elections raise concerns.
- Administrative & Security Challenges:
- Logistical difficulties in deploying security forces across the country.
- Extended deployment strains administration and security personnel.
- Political & Democratic Challenges:
- Concerns over single-party dominance due to consolidated election cycles.
Opposition demands a detailed study and debate before implementing changes.
6. Women Shifting from Unpaid Domestic Work – Govt. Survey (2024)
Key Findings of the Survey
- Increase in Women’s Workforce Participation:
- Women in 15-59 age group engaged in employment-related activities rose to 25% in 2024 from 21.8% in 2019.
- Men’s participation increased to 75% from 70.9%.
- Reduction in Unpaid Domestic Work:
- Women spent 305 minutes per day in unpaid domestic services in 2024, compared to 315 minutes in 2019.
- Men spent 88 minutes daily on such activities.
- Caregiving Responsibilities:
- 41% of women in the 15-59 age group participated in household caregiving vs. 21.4% of men.
- Women spent 137 minutes daily on caregiving vs. 75 minutes by men.
Leisure and Other Activities
- Individuals spent time on culture, leisure, and mass media:
- Men: 177 minutes/day, Women: 164 minutes/day.
- Children (6-14 years) spent 413 minutes daily in learning.
Self-Care and Maintenance
- Self-care and maintenance activities took 708 minutes per day on average.
- 8% of the population engaged in household production (e.g., growing food for self-use), spending 116 minutes daily.
Survey Coverage
- 1,39,487 households surveyed:
- 83,247 in rural areas
- 56,240 in urban areas
Total respondents: 4,54,192 individuals (2,85,389 rural & 1,68,803 urban).
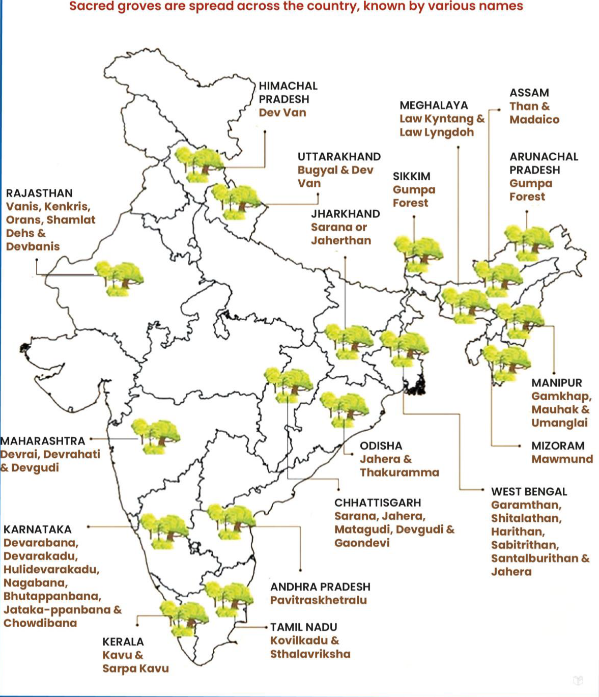
7. Tribal Families Protest Over Sacred Groves in Similipal Tiger Reserve (STR), Odisha
Issue
- Tribal families of the Munda community, former residents of Jamunagarh village in Similipal Tiger Reserve (STR), Odisha, have alleged denial of rights to perform rituals in sacred groves.
- Their traditional worship spaces have been fenced off following the translocation of Zeenat, a tigress from Maharashtra.
Background
- Zeenat, a three-year-old tigress, was translocated from Tadoba-Andhari Tiger Reserve (Maharashtra) to STR on November 14 to improve the genetic diversity of the tiger population.
Authorities have restricted access to sacred lands and burial grounds, preventing tribals from performing their age-old worship practices.
Key Concerns of Tribals
- Loss of Cultural Heritage
- Tribals worship nature and conduct traditional rites in sacred groves.
- They believe separation from homeland, deities, and ancestors has caused distress among their community.
- Eviction and Displacement
- Residents of Jamunagarh were relocated in two phases (2015 & 2022).
- Despite relocation, they continued visiting their sacred groves for rituals, which are now forbidden by STR authorities.
- Official Restrictions
- Authorities cite the “tiger supplementation programme” as the reason for restricting access.
- The Deputy Director of South Wildlife Division denied them permission to return to perform sacred rites.
Tribal Protest
- Demonstration held in Bhubaneswar by displaced tribals to raise their grievances.
Memorandum submitted to the Principal Chief Conservator of Forests demanding restoration of access to sacred sites.
8. PM-KISAN Fund Transfer in Poll-Bound Bihar
Context
- Prime Minister Narendra Modi initiated a fund transfer under the PM Kisan Samman Nidhi (PM-KISAN) scheme from Bhagalpur, Bihar, ahead of the state Assembly elections.
Key Highlights
- ₹22,000 crore transferred to 9.8 crore farmers across India.
- More than 75 lakh farmers in Bihar
- Each farmer received ₹2,000 under the 19th installment of the scheme.
About PM-KISAN Scheme
- Launched in 2019, it provides ₹6,000 annually to small and marginal farmers in three equal tranches of ₹2,000.
- Beneficiaries: Farmers with up to 2 hectares of land.
Political Significance
- Bihar is election-bound later this year.
- PM Modi was accompanied by Bihar CM Nitish Kumar and Union Agriculture Minister Shivraj Singh Chouhan.
- Opposition RJD criticized the visit, calling it an election-year move.
Importance
- Financial support to farmers, especially in rural Bihar.
- Electoral impact as PM-KISAN is a key welfare scheme.
- Criticism from opposition about political intent behind fund distribution.
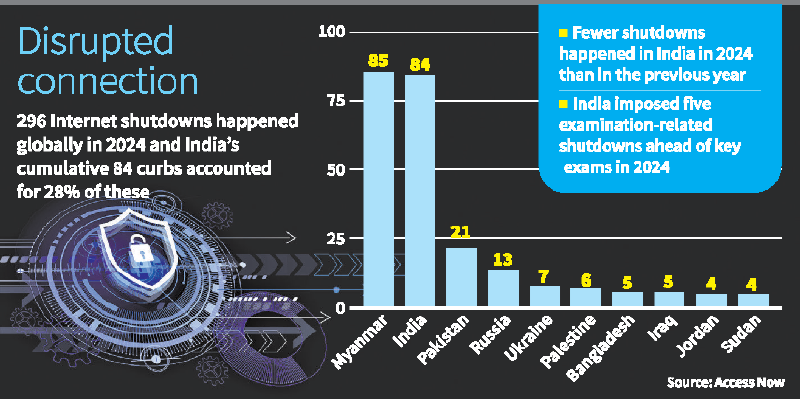
9. Internet Shutdowns in 2024: India’s Position
Context
- A report by Access Now highlights global internet shutdown trends in 2024.
- India had the highest government-imposed shutdowns globally, despite Myanmar having the most overall disruptions.
Key Findings
- 296 internet shutdowns globally in 2024 (highest ever).
- India accounted for 84 shutdowns (28% of global shutdowns).
Myanmar topped with 85 shutdowns, 11 of which were imposed by insurgent groups.
India-Specific Data
- Shutdowns occurred in 16 states and Union Territories.
- Top states/UTs with shutdowns:
- Manipur (21)
- Haryana (12)
- Jammu & Kashmir (12)
- Reasons for shutdowns:
- 41 related to protests
- 23 due to communal violence
- 5 ahead of key examinations
Examination-Related Shutdowns
- India imposed 5 shutdowns before major exams.
- Jharkhand (Sept 22, 2024): Internet was suspended for 5 hours during a government exam.
- Assam & Rajasthan: Shutdowns were imposed during recruitment exams.
Global Comparison
- Pakistan (21), Russia (13), Ukraine (7) also imposed internet restrictions.
- China & Thailand had limited shutdowns in Myanmar.
Concerns Raised
- Internet blackouts violate digital rights and affect communication and businesses.
- Exam-related shutdowns are seen as disproportionate responses to cheating concerns.
10. PM Modi's Call to Fight Obesity
Context
- Prime Minister Narendra Modi emphasized the need to reduce obesity and cut edible oil consumption by 10%.
- Highlighted in the 119th episode of Mann Ki Baat.
Key Points
- Obesity cases have doubled in the past few years.
- 1 in 8 Indians is affected by obesity.
- Children are particularly vulnerable to obesity-related health risks.
Call to Action
- Reduce oil consumption by 10% per month to improve public health.
- Simple dietary changes can bring significant health benefits.
- Encouraged public participation in creating awareness.
Celebrity Involvement
- PM Modi nominated prominent figures to spread awareness:
- Industrialists: Anand Mahindra, Nandan Nilekani
- Actors: Mohanlal, R. Madhavan, Dinesh Lal Yadav (Nirahua)
- Athletes: Shooter Manu Bhaker, weightlifter Mirabai Chanu
- Authors: Sudha Murty
- Singer: Shreya Ghoshal
- Urged them to nominate 10 more people to create a chain of awareness.
Other Health Initiatives
TB-Free India by 2025: Urged citizens to join the “Nikshay Mitra” programme to support tuberculosis patients.
11. Kota Cares Initiative
Context
- Kota, Rajasthan, is a major coaching hub with 25 lakh students preparing for competitive exams annually.
- Rising stress and suicide cases among students prompted the launch of “Kota Cares” initiative in December 2024.
Key Objectives
- Improve student welfare, mental health support, and safety protocols.
- Bring together district administration, coaching institutes, hostels, and local communities.
Major Reforms & Measures
- Student Housing & Safety
- Caution deposits eliminated across 4,000 hostels.
- Hostel maintenance capped at ₹2,000 annually.
- Transparent payment systems with mandatory receipts.
- Strict guidelines for room changes, vacations, and payments.
- Special provisions for women’s hostels, including women wardens.
- Mental Health & Well-Being
- Kota Cares helpdesks at railway stations and bus stands.
- City-wide student support network.
- Free access to Chambal riverfront for relaxation.
- Dedicated relaxation areas in hostels.
- Mid-term psychological evaluations for students.
- Prevention of Suicides & Emergency Response
- Installation of modern safety systems: CCTV, biometric entry, and certified anti-hanging devices in hostels.
- No-objection fire safety certificates.
- Emergency medical services available 24/7.
- Mandatory training for hostel staff & gatekeepers.
Monitoring & Feedback
- District administration set up a mechanism to track progress and gather student feedback.
12. India's Reputation in the Pharmaceutical Industry
Context
- India’s pharmaceutical industry, known as the “pharmacy of the global South”, faces a reputation crisis due to multiple safety concerns.
Key Incidents
- Cough Syrup Controversy
- India-made cough syrups contained toxic levels of diethylene glycol and ethylene glycol.
- Caused deaths of:
- 66 children in Gambia (2022)
- 65 children in Uzbekistan (2022)
- 12 children in Cameroon (2023)
- Contaminated Eye Drops in the U.S. (2023)
- Drug-resistant bacteria in India-made eye drops killed 3 and blinded 8 people.
- Illegal Opioid Export by Aveo Pharmaceuticals
- A Maharashtra-based company manufactured and exported unapproved opioid drugs (tapentadol + carisoprodol) to West Africa.
- BBC investigation revealed criminal drug trade despite regulatory bans.
Regulatory Issues
- Only Central Drugs Standard Control Organization (CDSCO) can approve new fixed-dose combinations (FDCs).
- State drug authorities bypass this approval, leading to illegal manufacturing.
- India initially denied WHO reports on toxic cough syrups but later took strict action against Aveo Pharmaceuticals.
Actions Taken
- Seizure of 13 million illegal drugs & 26 batches of active ingredients.
Manufacturing license revoked, exports banned, and show cause notice issued.