Index:
- Cancer-related Mortalities in India
- Impact of Coal-Fired Power Plants on Agriculture in India
- Indian Peacekeepers and UN Missions
- Indian Peacekeepers and UN Missions
- Indian Peacekeepers and UN Missions
- Delayed Justice and Legal System in India
- Farmers’ Share in Rabi Crop Consumer Prices (RBI Survey)
- NASA’s New Space Telescope – SPHEREx
- Other news headlines
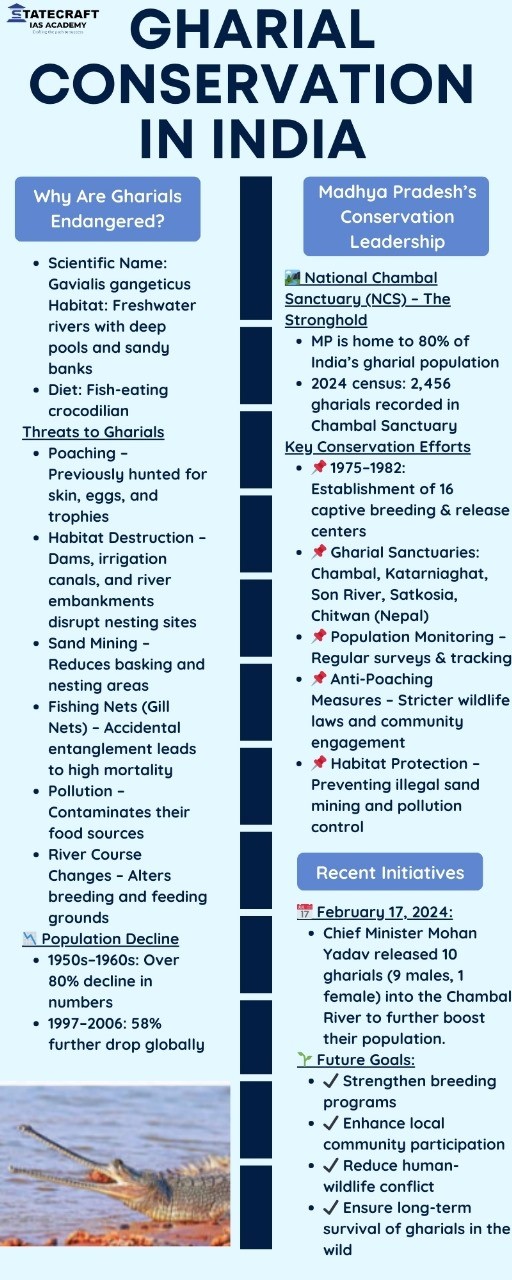
- GHARIAL CONSERVATION IN INDIA -Infographics
1. Cancer-related Mortalities in India
Context
- Approximately 3 out of every 5 individuals in India die following a cancer diagnosis.
- Cancer-related mortality increased faster among women (1.2%-4.4% annual percentage change) compared to men (1.2%-2.4%) over the past decade.
- The trend is expected to continue rising.
Source of Data
- Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR)
- Global Cancer Observatory (GLOBOCAN, 2022 estimates) – an online database providing global cancer statistics and mortality estimates for 185 countries.
Prevalence & Risk Factors
- Five most common cancers in India account for 44% of the country’s total cancer burden.
- Age-wise risk:
- Lowest risk of cancer-related mortality in childhood and reproductive age group (0.08%-1.3%).
- Higher risk in middle-aged and geriatric population.
- India is expected to witness the highest cancer burden ever in the near future, worsened by an impending cancer epidemic.
Gender Disparities
- Women show higher crude incidence and crude mortality rates than men.
- Based on 2022 population estimates:
- Females: 0.676 billion
- Males: 0.731 billion
Crude rates = Number of new cancers or deaths divided by the population at risk.
2. Impact of Coal-Fired Power Plants on Agriculture in India
Context
- Coal-fired power plants are significantly reducing rice and wheat yield in India, causing up to 10% crop loss in several states.
- Primary cause: Nitrogen oxides (NOx) emissions, which are phytotoxic, meaning they stress plants and interfere with crucial cellular functions.
Pollution and Agricultural Impact
- Coal plant emissions include carbon dioxide, nitrogen oxides, sulfur oxides, soot, particulate matter, and trace gases.
- NOx emissions from coal-fired plants have been linked to:
- Smog formation
- Soil acidification
- Crop damage and reduced productivity
Methodology of Study
- Researchers used high-resolution satellite imaging to track NOx pollution from coal plants.
- Used near-infrared reflectance of vegetation (NIR) to measure plant health.
- Findings showed regions downwind of coal plants had the highest NOx concentrations and suffered the most agricultural damage.
State-wise Crop Impact
- West Bengal, Punjab, Uttar Pradesh, and Madhya Pradesh were significantly affected.
- Yield reductions due to NOx pollution:
- Madhya Pradesh: Rice yield could increase by 5.1% if NOx emissions were reduced by 50%.
- West Bengal: Yield increase of 5-7% expected with coal pollution control measures.
Economic Impact
- Crop damage results in significant economic losses:
- Wheat loss due to NOx emissions was linked to 5% yield reduction.
- Estimated financial loss: ₹7,000 crore annually.
Coal Dependency & Food Security
- India’s dependence on coal is a major challenge for agricultural productivity.
- Global Hunger Index (2024): India ranked 108 out of 127 countries, indicating food security concerns.
- The study calls for policy measures to balance coal use and agricultural protection.
Policy Recommendations
- Stricter pollution control measures on coal-fired power plants.
- Installation of NOx control equipment to limit emissions.
Policy interventions that balance energy needs with food security.
3. Indian Peacekeepers and UN Missions
Context
- Indian peacekeepers serve with commitment in various UN peacekeeping missions
- India is among the top troop-contributing nations to the UN.
- As of October 2024, India had 5,466 personnel in UN peacekeeping missions, including 5,046 military personnel, making it the fourth-largest contributor after Nepal, Rwanda, and Bangladesh.
Peacekeeping in the Democratic Republic of the Congo
- The UN mission in the DRC faces restrictions in areas controlled by M23 rebels.
- The M23 rebels are supported by Rwandan forces, creating instability and humanitarian concerns.
- Indian peacekeepers are deployed in M23-controlled regions, ensuring security while facing movement and supply restrictions.
Reforms in UN Peacekeeping
- The Under-Secretary-General for UN Peace Operations, Jean-Pierre Lacroix, emphasized the need for reforms in international governance and the UN Security Council.
- He called for member states to play a role in peacekeeping reforms.
India’s Role & Women in Peacekeeping
- India hosted a conference on ‘Women in Peacekeeping – A Global South Perspective’ on February 24-25, 2024.
- The conference included women peacekeepers from India and 35 other countries.
Ceasefire & Monitoring in Ukraine
When asked about a third-party UN monitoring mechanism for a Ukraine ceasefire, Lacroix called it highly hypothetical at this stage.
4. Tunnel Disasters & Risk Assessment
Context
- Recent tunnel collapses in India highlight the importance of scientific risk assessment before tunnel construction.
- Two major incidents:
- Silkyara Tunnel Collapse (Uttarakhand, Nov 2023) – 41 workers trapped, rescued in 16 days.
- Srisailam Left Bank Canal Tunnel Collapse (Telangana, Feb 2025) – 8 workers trapped due to water seepage.
- Causes of Tunnel Collapses
- Water seepage leading to roof collapse (Srisailam case).
- Structural deformities in rock formations (Silkyara case).
- Undetected aquifers (underground water channels) causing sudden flooding.
- Lack of pre-construction geological studies to assess subsurface risks.
- Challenges in Rescue Operations
- Continuous water flow making rescue difficult (Srisailam).
- Complex excavation methods required, including horizontal and vertical drilling (Silkyara).
- Safety hazards in manual excavation (e.g., use of ‘rat-hole’ miners in Silkyara).
- Lessons & Recommendations
- Comprehensive geological surveys must be conducted before tunnel projects.
- Real-time monitoring for early warning of water seepage or structural instability.
- Emergency rescue preparedness including rapid deployment of expert teams.
- Stronger regulatory oversight on tunneling in water-prone regions.
Use of advanced tunneling technologies to minimize risks.
5. Use of Cash in Agricultural Transactions in India
Context:
- Over 70% of Indian farmers still use cash to sell their produce.
- Digital payments have increased but remain limited in agriculture-related transactions.
Survey Data from RBI Report:
- Title: Dynamics of Agriculture Supply Chain: Insights from Pan India Survey during Rabi Marketing Season
- Conducted by Rajib Das, Rishabh Kumar, Manika Sethi, Love Kumar Shandilya, and Alice Sebastian.
Cash vs. Digital Payments in Agricultural Transactions:
- 2019: 88% farmers used cash.
- 2022: Declined to 79%.
- 2024: Further declined to 72%.
- Use of electronic payments increased from 8% (2019) → 18% (2024).
- Traders and retailers are using more digital payments compared to farmers.
Farmers’ Source of Market Price Information (2024):
- 55% rely on traders.
- 10% use online platforms (websites, apps).
- Many farmers remain disconnected from digital practices.
Reasons for Crop Damage (2023-24 Rabi Season):
- Weather factors (drought, unseasonal rain) – 37%.
- Climate change impact – 30%.
- Other factors: Pests, diseases, poor irrigation.
Factors Influencing Farmers’ Crop-Sowing Decisions:
- Weather forecasts.
- Contract farming & advisory.
- Govt procurement & price stability.
- Availability of irrigation, inputs, & credit.
Share of Farmers in Final Retail Price (2024):
- Higher for non-perishable crops (wheat, paddy).
- Lower for perishables (fruits, vegetables).
6. Delayed Justice and Legal System in India
Key Theme:
- Justice Delayed is Justice Denied – The case of Sajjan Kumar highlights issues of delayed justice and political influence in legal proceedings.
Case Study: 1984 Anti-Sikh Riots & Sajjan Kumar’s Conviction
- Crime: Led a mob that killed a 50-year-old man and his 18-year-old son during the 1984 anti-Sikh riots in Delhi.
- Verdict: Life imprisonment in 2024, 40 years after the crime.
- Previous Conviction (2021): Delhi HC sentenced him to life imprisonment for overseeing the killing of five people in Raj Nagar.
Issues in the Justice System:
- Delayed Investigations:
- Initial failure of police to conduct genuine probes.
- Omnibus FIRs clubbing multiple incidents, preventing individual accountability.
- Witness intimidation and suppression of key evidence.
- Political Influence:
- Powerful individuals evading justice through political protection.
- Cover-ups and discouragement of complaints.
- Judicial Commissions and Reopened Cases:
- Justice Ranganath Misra Commission
- Justice Nanavati Commission
- Jain-Aggarwal Committee
- Affidavits before these panels exposed contradictions, but defence lawyers exploited delays.
- Challenges in Prosecution of Mob Violence:
- Lack of credible witnesses due to fear and intimidation.
- Delayed legal action weakens evidence and conviction rates.
Lessons for Governance & Law:
- Strengthening Judicial Processes:
- Need for fast-track courts for mass violence cases.
- Independent investigations free from political influence.
- Witness Protection Mechanisms:
- Stronger laws to safeguard witnesses and whistleblowers.
- Effective protection programs to encourage testimonies.
- Police Reforms:
- Accountability in law enforcement to ensure fair investigation.
Removal of political interference in police actions.
7. Farmers’ Share in Rabi Crop Consumer Prices (RBI Survey)
Key Findings of RBI Survey (May–July 2024):
- Farmers receive 40-67% of consumer prices for major rabi crops.
- Higher share for non-perishable crops (wheat, lentils, mustard).
- Lower share for fruits & vegetables due to perishability & intermediaries.
Farmers’ Share in Consumer Prices:
- Wheat: 67% (Govt procurement stabilizes price).
- Rice: 52% (Public procurement at MSP).
- Lentils: 66% (Smallholder farmers, high import dependence).
- Gram (Chana): 60% (Pulses require price incentives).
- Rapeseed & Mustard: 52% (Slight decline from 55% in 2021).
- Fruits & Vegetables: 40-63% (Lower due to perishability & intermediaries).
Challenges in the Supply Chain:
- Higher markups by traders & retailers reduce farmers’ earnings.
- Unorganised logistics in fruits & vegetables affect price transmission.
- Perishable nature of produce increases dependency on climatic conditions & demand-supply fluctuations.
Structural Issues in Agricultural Markets:
- Middlemen dominate supply chains, reducing farmers’ income.
- Seasonal production & short shelf life lead to price instability.
- Lack of diversification due to dependence on traditional crops.
Way Forward (Policy Interventions Needed):
- Strengthen direct farmer-to-consumer linkages (APMC reforms, eNAM).
- Encourage food processing & storage infrastructure for perishables.
- Improve logistics & market access for small farmers.
Enhance MSP implementation & procurement efficiency.
8. NASA’s New Space Telescope – SPHEREx
Introduction
- NASA to launch SPHEREx (Spectro-Photometer for the History of the Universe, Epoch of Reionization, and Ices Explorer) for a two-year mission.
- Aim: Understanding universe formation, galaxy evolution, and biogenic molecules in the Milky Way.
Key Objectives of SPHEREx
- Mapping the Universe in Infrared
- First mission to map the sky in 102 infrared colors every six months.
- Infrared mapping reveals distant galaxies, star births, and cosmic dust.
- Measuring Cosmic Inflation
- Studies the rapid expansion of the universe (14 billion years ago).
- Uses spectroscopic imaging to create 3D maps of 450 million galaxies.
- Search for Life – Biogenic Molecules
- Identifies water, carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen in the Milky Way.
- Studies how life-forming molecules traveled to Earth.
Significance of SPHEREx
- Complements James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) but with a broader sky view.
Helps understand cosmic structure, early universe physics, and life formation.