Index:
- Escalating Conflict in Congo & Its Regional Implications
- Illegal Immigration Issue: India-US Relations
- NVS-02 Satellite Malfunction: ISRO's Navigation Mission
- U.K. to Introduce Laws Against AI-Generated Sexual Abuse Images
- U.K. to Introduce Laws Against AI-Generated Sexual Abuse Images
- Economic Survey 2024-25 Highlights
- Other News headline
1. Escalating Conflict in Congo & Its Regional Implications
Background
- M23 Rebels: Ethnic Tutsi-led insurgent group in the Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC).
- Named after March 23, 2009 Accord that ended a prior Tutsi revolt but was allegedly not upheld by the Congolese government.
- Resurgence in 2022 after accusing the DRC of failing to integrate Tutsis into governance.
Current Situation
- M23 captured Goma (capital of North Kivu province) on January 27, 2024 and its airport on January 28.
- Government forces and allied militia surrendered, leading to rebel control by January 30.
- Rebels pushing southward into South Kivu, facing resistance from the Congolese army and Burundian troops.
- UN reports suggest Rwandan troops have crossed into DRC, raising fears of a regional war.
M23 Rebels & Their Interests
- Advocates for Tutsi interests, particularly against Hutu militias like the Democratic Forces for the Liberation of Rwanda (FDLR).
- The FDLR was founded by Hutus who fled Rwanda after the 1994 genocide (which killed ~1 million Tutsis and moderate Hutus).
- M23 has controlled coltan mines in Rubaya, generating ~$800,000 per month (coltan is essential for smartphone production).
Rwanda’s Alleged Involvement
- DRC, UN, and Western powers (USA) accuse Rwanda of:
- Deploying troops & heavy weapons in support of M23.
- UN (2022) found “solid evidence” of Rwandan troops fighting alongside M23.
- Rwanda denies backing M23, instead accusing Congo of attacking Tutsis and siding with the FDLR.
Significance & Impact
- Humanitarian Crisis: Hundreds of thousands displaced due to M23 advances.
- Resource Conflict: Control over mineral-rich areas (coltan, crucial for tech industry).
- Regional Tensions: Potential for conflict to escalate between DRC, Rwanda, and Burundi.
- UN & International Concern: Risk of further instability in Central Africa.
Key Point
- Ethnic Conflict (Tutsis vs. Hutus, legacy of the Rwandan Genocide).
- Resource-driven War (Mineral wealth, particularly coltan).
- Geopolitical Implications (Regional security & international involvement).
- Humanitarian Impact (Displacement, civilian casualties).
2. Illegal Immigration Issue: India-US Relations
Background
- India’s Stand: India is ready to take back its citizens who entered the US illegally.
- US Immigration Policy: The Biden administration is increasing deportations, targeting 30,000 detainees at Guantanamo Bay.
India’s Diplomatic Approach
- Balanced Stance: India has assured cooperation but ensures that legal travel channels remain unaffected.
- High-Level Talks:
- PM Modi & Trump (Recent Call) – Discussed bilateral relations & upcoming Modi visit to the US.
- Meetings with US Leaders – Jaishankar (EAM), Ajit Doval (NSA), and Commerce Secretary met US counterparts to align immigration policies.
Why India is Cooperating?
- Low-Cost Gesture for New Delhi: Taking back illegal immigrants does not affect strategic or economic interests.
- US-India Visa Dynamics:
- Over 1 million US visas issued to Indians in 2024, reflecting high legal travel demand.
- Only 100 illegal Indian immigrants deported in 2024.
- India’s focus is on ensuring smooth H-1B visa
US Deportation Challenges
- Scale of the Problem:
- S. Immigration and Customs Enforcement (ICE) removed 217,484 non-citizens in FY 2024.
- Around 20,000 illegals from India are in Florida alone, but total Indian illegal immigrant population in the US is ~725,000.
- Trump aims to deport 2,500 people daily, requiring major enforcement efforts.
H-1B Visa & India’s Concerns
- H-1B Visa Importance:
- 72% of new H-1B visas issued in 2023 went to Indians.
- H-1B visa holders contribute to the US economy & tech sector.
- India’s Priority:
- Ensuring continued visa approvals for skilled professionals.
- Preventing large-scale deportations that could impact Indian tech workers.
Geopolitical & Strategic Implications
- Biden vs. Trump Policy Contrast:
- Biden: Balanced approach with selective deportations.
- Trump: Aggressive stance, preparing for mass deportations (potential MAGA influence).
- India’s Strategy:
- Maintain strong ties with both administrations.
Avoid economic fallout from visa restrictions.
3. NVS-02 Satellite Malfunction: ISRO's Navigation Mission
Context
- ISRO launched NVS-02 on January 29, 2024, as part of its 100th mission from Sriharikota.
- It is the second satellite in the NVS series, meant to replace IRNSS-1E in India’s Navigation with Indian Constellation (NavIC)
Issue & Malfunction
- Problem: ISRO failed to conduct orbit-raising operations due to a valve malfunction in the thruster system.
- Cause: Valves controlling oxidizer flow did not open, preventing orbit-raising maneuvers.
- Current Status:
- The satellite remains in an elliptical orbit instead of the intended Geostationary Orbit.
- ISRO is exploring alternative mission strategies to utilize the satellite.
Mission Details & Importance
- Launch Details: Successfully injected into Geosynchronous Transfer Orbit (GTO).
- Configuration:
- Equipped with L1, L5 & S-band navigation payloads.
- Has C-band ranging payload for precise tracking.
- Uses indigenous atomic clocks for high-precision timing.
- Planned Orbit:
- Meant to be placed at 75°E.
- Would enhance NavIC (Indian GPS alternative) for military & civilian applications.
Impact & Way Forward
- ISRO’s Response:
- Ground station communication remains intact.
- Power generation and other systems are functional.
- Alternative strategies for using the satellite in an elliptical orbit are being worked out.
- Significance:
- Strengthens India’s self-reliance in navigation.
- Enhances disaster management, defense, and real-time positioning applications.
- Challenges Ahead:
- Need for more robust testing of thruster mechanisms.
Potential delays in NavIC expansion due to malfunction.
4. U.K. to Introduce Laws Against AI-Generated Sexual Abuse Images
Context:
- The United Kingdom is set to become the first country to introduce laws against AI tools used for generating sexual abuse images.
- The government announced measures to criminalize the possession, creation, and distribution of AI-generated child sexual abuse material.
Key Provisions of the Law:
- Illegalization of AI-generated sexual abuse images
- Possessing, creating, or distributing AI tools designed to generate sexualized images of children will be punishable by up to five years in prison.
- Ban on AI ‘paedophile manuals’
- Manuals that instruct individuals on how to use AI for sexual exploitation will be punishable by up to three years in prison.
- Criminalization of online predators
- Those running websites that promote sharing child sexual abuse content or advice on grooming will face up to ten years in prison.
- Ban on AI models used for child abuse
- The law includes a ban on certain AI models facilitating child abuse.
Government’s Justification:
- Rapid Growth of Online Child Sexual Abuse Material
- AI is amplifying the problem by making it easier for perpetrators to groom children.
- Use of AI for Blackmailing
- Perpetrators manipulate images of children to blackmail them into further abuse.
- Call for Global Action
Other countries have yet to introduce similar laws, but the UK hopes they will follow suit.
5. Study Finds Microplastics in Delhi’s Groundwater
Context:
- A first-of-its-kind study commissioned by the Delhi government has detected microplastics in groundwater across the city.
- The study also found microplastics in the Yamuna’s water and soil samples from its banks.
Key Findings:
- Microplastics in Groundwater:
- Detected in samples from all 11 districts of Delhi.
- Likely due to leaching from the Yamuna River.
- Microplastics in Yamuna:
- Found in both water and soil samples from the riverbanks.
- Indicates contamination of groundwater due to river pollution.
- Water Treatment Limitations:
- Current water treatment systems cannot filter out microplastics, posing health risks.
- Delhi Government’s Response:
- Next phase of the study is underway; final report expected later this year.
The Energy and Resources Institute (TERI) conducting the study.
Health & Environmental Concerns:
- Human Health Risks
- Microplastics can be absorbed into the body, affecting organs and even the placenta of newborns (as per UNEP).
- They contain harmful chemicals that may cause genetic changes, brain development issues, and respiratory problems.
- Environmental Impact
- Pollutes groundwater, affecting drinking water quality.
- Can enter the food chain, leading to widespread ecological effects.
UNEP Report (2021) – ‘From Pollution to Solution’
- Warned about the dangers of chemicals in microplastics.
- Associated with serious health impacts, particularly in women.
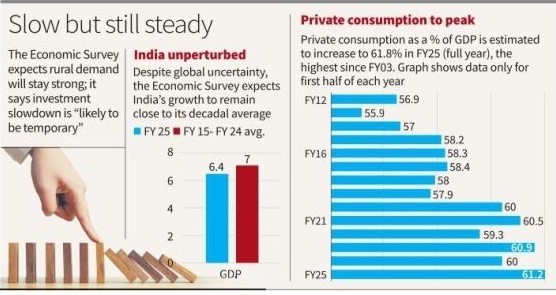
6. Economic Survey 2024-25 Highlights
Context:
- The Economic Survey 2024-25 was tabled in Parliament, assessing India’s economic performance and growth outlook.
Key Growth Projections:
- GDP Growth Forecast:
- Estimated growth of 4% in FY24.
- Growth expected to be in the range of 3% – 6.8% in FY25 & FY26.
Growth remains robust but faces strong external downsides.
Key Findings:
- Investment & Capital Formation:
- “Green shoots” observed in capital formation, signaling positive future investment trends.
- Private sector investment expected to rise gradually.
- Investment rate to increase from 31% of GDP to 35% over time.
- Private Consumption:
- Expected to peak at 61.8% of GDP in FY25, the highest since FY03.
- Urban demand remains uncertain, with mixed trends in Q3 of FY24.
- External Challenges & Risks:
- Global economic uncertainty and geopolitical risks pose challenges.
- Investment slowdown is likely temporary but needs monitoring.
- Deregulation & Trust Deficit:
- The survey emphasizes deregulation and trust-building measures to sustain economic momentum.
- Viksit Bharat (Developed India) 2047:
- 8% GDP growth required for the next two decades to achieve India’s developed country status.
- Indigenisation in the EV Sector:
- India must reduce dependence on China for raw materials and technology.
- Focus on domestic production and R&D to build a self-sufficient EV industry.