Index:
- Kumbh Mela: Origin, History, and Appeal
- Law by Reflex: Good Implementation, Not Stringency, Will Deter Sexual Crimes
- India-U.S. Joint Sonobuoy Production Line
- Declining Fertility Levels and Kerala's Rising Maternal Mortality Ratio (MMR)
- ISRO's SPaDeX Docking Trial Success
- Naxalism to Be Wiped Out by 2026: Key Statements by Amit Shah
- Other news Headlines
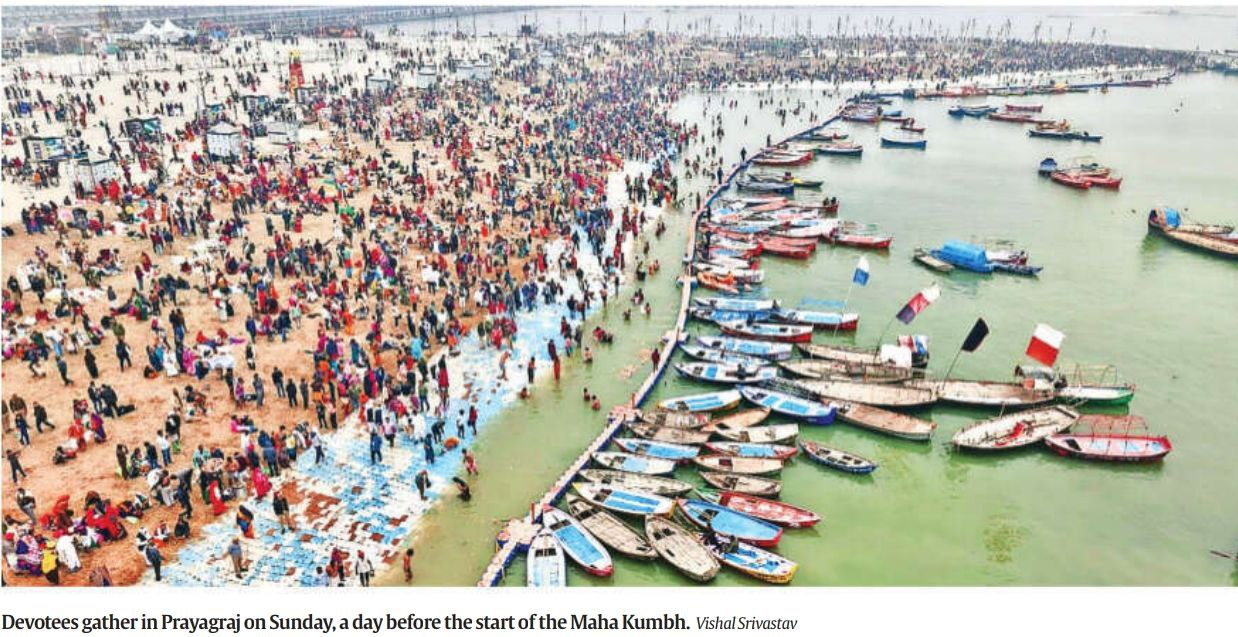
1. Kumbh Mela: Origin, History, and Appeal
What is Kumbh Mela?
- Definition: A large Hindu religious gathering where devotees take a dip in sacred rivers.
- Significance: It is the largest religious congregation on Earth, held periodically in four cities: Haridwar, Prayagraj, Nashik, and Ujjain.
- Types:
- Purna Kumbh Mela: Every 12 years.
- Ardh Kumbh Mela: Every 6 years.
- Maha Kumbh Mela: Every 12 cycles (144 years).
Mythological Origins
- Sanskrit word ‘Kumbh’ means pot.
- Associated with the Samudra Manthan (churning of the ocean) by gods and demons to retrieve the pot of amrit (nectar of immortality).
- Drops of amrit spilled at:
- Haridwar
- Prayagraj
- Nashik
- Ujjain
- These locations became the venues of Kumbh Mela.
Astrological Significance
- Based on planetary positions:
- Jupiter in Taurus and Sun in Capricorn → Haridwar.
- Jupiter in Aquarius and Sun in Aries → Prayagraj.
- Jupiter and Sun in Leo → Nashik.
- Jupiter in Scorpio and Sun in Capricorn → Ujjain.
Historical Evolution
- Origin traced to ancient texts like:
- Puranas: Mentions the significance of river baths.
- Rigveda: Refers to sacred rivers.
- Institutionalized by Adi Shankaracharya in the 8th century CE.
- First historical mention: Mughal period.
- Took the form of a regular festival in the 12th century.
Key Rituals
- Snan (Bathing): Ritual bath to cleanse sins and attain moksha.
- Satsang: Spiritual discourses by saints and scholars.
- Pujas and Offerings: To the Ganga and other deities.
Why is it Important?
- Religious Significance: Cleansing of sins, spiritual growth, and attaining liberation.
- Social Impact: Promotes unity and offers an opportunity for saints to spread teachings.
- Economic Boost: Generates revenue for local communities and tourism.
Debate Over Antiquity
- No direct textual evidence of Kumbh in ancient scriptures.
- Likely evolved from Hindu practices of river worship and congregations.
Modern-day Relevance
- Attracts millions of devotees globally.
- Declared an Intangible Cultural Heritage by UNESCO.
Serves as a platform for cultural, religious, and social dialogue.
2. Law by Reflex: Good Implementation, Not Stringency, Will Deter Sexual Crimes
Key Issues Highlighted
- Legislative Response: Governments often enact stricter laws as a reaction to political or public outcry over specific crimes.
- Recent Example: Tamil Nadu Assembly amended laws on sexual crimes after a rape case at Anna University.
- Concerns:
- Changes lack empirical evidence supporting stricter laws as a deterrent.
- Reflects political messaging rather than substantive reforms.
Amendments Introduced
- Enhanced Punishments:
- Stricter penalties under procedural and penal laws.
- Extension of bail-denying provisions.
- Death penalty for acid attacks causing vegetative states.
- Protection Orders: Binding orders to prevent perpetrators from contacting survivors.
- New Definition of Harassment: Includes digital, electronic, and non-verbal means, which could be prone to misuse.
Key Arguments
- Increased Stringency vs. Implementation:
- Stricter laws may not necessarily reduce sexual crimes.
- Focus should be on:
- Impartial investigation.
- Strengthening conviction processes.
- Addressing systemic failures.
- Potential Misuse: Overbroad definitions could lead to misuse and unintended consequences.
- Public Safety and Workplaces: Making spaces safer for women is more effective than punitive measures alone.
Suggestions for Improvement
- Effective Implementation:
- Enforce existing laws efficiently.
- Address delays in investigation and trial processes.
- Systemic Reforms:
- Improve workplace safety.
- Promote gender sensitization.
- Empirical Evidence: Base policy changes on data and research, not political compulsions.
3. India-U.S. Joint Sonobuoy Production Line
Key Highlights
- Sonobuoys: Devices used to detect submarines
- Production Plan: Final assembly to take place in India; operational production line expected by 2027.
- Partnership: Joint collaboration between:
- S. company Ultra Maritime.
- India’s Bharat Dynamics Ltd. (BDL), a defense public sector undertaking.
- Framework: In line with “Make in India”
Significance of the Initiative
- Strengthening Defense Capabilities:
- Enhances underwater warfare technologies for the Indian Navy.
- Sonobuoys compatible with:
- P-8 aircraft.
- MH-60R helicopters.
- MQ-9B Sea Guardian drones.
- Strategic Collaboration:
- Part of the India-U.S. Initiative on Critical and Emerging Technologies (ICET) launched in
- Promotes joint production and technology sharing.
- Regional Importance:
- Complements India’s military platforms already procured from the U.S.
- Aligns with the operational frameworks of other Quad members (Australia, Japan).
Technological Features
- Acoustic Performance: Optimized for Indian Ocean conditions.
- Interoperability: Sonobuoys interchangeable with systems used by the U.S. Navy and allied nations.
Advanced Capabilities: Wide-area search, multi-static active sonar.
4. Declining Fertility Levels and Kerala's Rising Maternal Mortality Ratio (MMR)
Key Highlights
- Kerala’s MMR:
- Lowest in India at 19 per 1 lakh live births (2018-20, Sample Registration System).
- Actual estimates from Kerala’s Health Department: 29 per 1 lakh live births.
- Recent Trend:
- Despite near 100% institutional deliveries, Kerala’s MMR is rising.
- The rise is attributed to declining birth rates, not an increase in maternal deaths.
Factors Driving the Trend
- Declining Fertility Rates:
- Births dropped from an average of 5-5.5 lakh annually (1980s) to 93 lakh in 2023.
- Replacement level fertility of 1 was achieved in 1987-88, marking Kerala’s early demographic transition.
- Changing Demographics:
- Societal attitudes towards marriage and childbirth.
- Increased immigration and urbanization.
Implications
- Numerical Impact on MMR:
- Fewer births reduce the denominator, artificially inflating MMR figures.
- Kerala’s projected MMR for 2024-25: 32 per 1 lakh live births.
- Irreversible Trends:
- Fertility decline is challenging to reverse once demographic transition occurs.
- Potential long-term effects on Kerala’s social and economic fabric.
Policy Challenges
- Sustainable Development Goals (SDG):
- Kerala aimed to achieve an MMR of 20 by 2030, but the target seems unlikely.
- Health System Adjustments:
- Address non-medical and demographic challenges.
Promote policies encouraging childbirth and family planning.
5. ISRO's SPaDeX Docking Trial Success
Key Highlights
- SPaDeX Mission:
- Objective: Develop and demonstrate spacecraft rendezvous, docking, and undocking
- Satellites involved: SDX01 (Chaser) and SDX02 (Target).
- Launch vehicle: PSLV C60, launched on December 30, 2023 from Satish Dhawan Space Centre, Sriharikota.
- Milestone Achieved:
- Successfully brought the satellites within 3 meters during the trial.
- Satellites were later moved back to a safe distance for further analysis.
Challenges Overcome
- Unexpected Drift:
- January 7: Docking experiment postponed due to higher-than-expected drift between satellites.
- Drift was corrected, enabling a successful trial on January 13.
- Step-by-Step Progress:
- Satellites were first brought within 15 meters before closing the gap to 3 meters.
Significance of the SPaDeX Mission
- Technological Advancement: Demonstrates India’s capability in satellite rendezvous and docking, critical for advanced space missions.
- Future Mission Applications:
- Human Spaceflight: Enabling docking for crewed lunar missions.
- Sample Return Missions: Retrieving materials from the moon or other celestial bodies.
- Indian Space Station: Docking and undocking for construction and operations.
Global Context
- India’s Position: If docking is successfully executed, India will join S., Russia, and China as the fourth country to master this technology.
Strategic Importance: Enhances India’s standing in global space exploration and contributes to future international collaborations.
6. Naxalism to Be Wiped Out by 2026: Key Statements by Amit Shah
Key Announcement
- Union Home Minister Amit Shah declared that Naxalism will be completely eradicated in India by March 31, 2026.
- Context: The statement was made at the Maharashtra BJP state executive meeting in Shirdi.
Achievements Under BJP (2014–2024)
- Abrogation of Article 370: Revoking Jammu & Kashmir’s special status.
- Reining in terrorism: Strengthening internal security.
- Ram Temple Construction: Ayodhya project nearing completion.
- Naxal Surrenders:
- As per Nitin Gadkari, nearly 5,000 Naxals surrendered in Gadchiroli.
- Gadchiroli district, once a Naxal stronghold, is now progressing with steel projects and rapid development.
Political Goals for Maharashtra
- Strengthening BJP:
- Aimed to make Maharashtra BJP “unconquerable.”
- Focused on local body elections to defeat Opposition parties.
- Criticism of Opposition:
- Accused Uddhav Thackeray of betraying Hindutva principles by aligning with Congress and NCP.
- Targeted Sharad Pawar’s political influence since 1978.
Significance of Maharashtra’s Political Landscape
- BJP’s Historic Victory:
- A major blow to the Opposition’s INDIA bloc.
- Asserted that Devendra Fadnavis will lead reforms to make Maharashtra:
- Drought-free.
- A hub of mega projects like Samruddhi Mahamarg, Metro, and FDI
- Economic Transformation: Gadchiroli, a former Naxal area, is emerging as a revenue-generating district.
Naxalism Eradication Plan
- Surrender and Rehabilitation:
- Encouraging Naxals to surrender and reintegrate into society.
- Development in Affected Areas:
- Infrastructure projects (e.g., steel plants in Gadchiroli).
- Focus on economic and social transformation.
- Enhanced Security Measures:
Proactive steps to eliminate Naxal activities in remaining strongholds.