1. RBI Report on Currency and Finance 2023-24
CONTEXT: RBI released its report on currency and finances showing the impact and challenges of digitalisation. India is leveraging digital infrastructure, fintech ecosystem, and conducive policies to become a leading digital economy.
Key Points:
- Benefits: Improved accessibility, convenience, financial inclusion, and boost to external trade.
- Challenges: Impulsive spending, herd behaviour, data breaches, cyber security risks, Data Breaches: Project Nexus and potential impact on monetary policy.
Implications:
- Financial Stability: Digitalisation can create a more complex and interconnected financial system, increasing systemic risks.
- Monetary Policy: Digitalisation can impact inflation, output, and monetary policy transmission. Central banks need to adapt their models accordingly.
- Consumer Protection: Increased focus on data privacy, cyber security, and financial literacy is essential.
- Financial Inclusion: Digital platforms have the potential to expand financial services to underserved populations.
- Economic Growth: Digitalisation can drive economic growth and create new job opportunities.
- Governance: Efficient delivery of public services through digital platforms.
- Global Leadership: India has the potential to emerge as a global leader in digital finance.
Digital Revolution in India Government Services · Aadhaar: Unique identification for every citizen, enabling efficient service delivery. · Digital India: Government’s flagship program for digital infrastructure and governance. Financial Services · UPI: Revolutionized payments, making transactions seamless and cashless. · Fintech: Rise of financial technology companies offering innovative solutions. E-commerce and Retail · Online Shopping: Booming e-commerce industry, offering a vast range of products. · Digital Payments: Cashless transactions becoming the norm in retail. Healthcare · Telemedicine: Remote healthcare services, bridging the gap between patients and doctors. · Digital Health Records: Electronic health records for efficient patient management. Education · Online Learning: MOOCs and online platforms democratizing education access. · Edtech: Innovative educational technology solutions transforming classrooms. Agriculture · Digital Agriculture: Technology-driven farming practices for increased productivity. · Agri-tech Startups: Innovative solutions for challenges faced by farmers. Other Sectors · Transportation: Ride-sharing, electric vehicles, and smart cities transforming mobility. · Media and Entertainment: Digital content consumption soaring, new platforms emerging. |
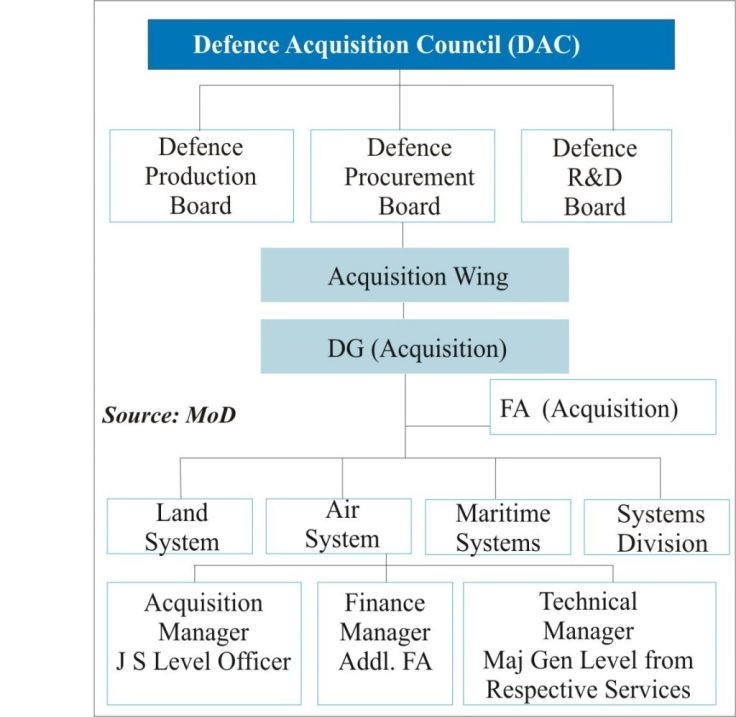
2. Defence Acquisition Council (DAC)
CONTEXT: DAC approves amendment to MQ-9B UAV (AoN) deal with US
Formation: | Established in 2001 following the recommendations of the Group of Ministers on ‘Reforming the National Security System’ post-Kargil War.
|
Purpose | The highest decision-making body in the Ministry of Defence for new policies and capital acquisitions for the three services (Army, Navy, Air Force) and the Indian Coast Guard.
|
Chairperson | Defence Minister of India. |
Members:
| · Minister of State for Defence · Chief of Army Staff · Chief of Air Staff · Chief of Naval Staff · Defence Secretary · Secretary Defence Production · Secretary Defence R&D · Chief of Integrated Defence Staff · Director General Acquisition · Chief of Integrated Staff Committees HQ IDS
|
Functions:
| 1. Approval of AoN (Acceptance of Necessity): For Capital Acquisition Proposals. 2. Categorization of Acquisition Proposals: · ‘Buy’ (outright purchase) · ‘Buy and Make’ (purchase followed by licensed production/indigenous development) · ‘Make’ (indigenous production and R&D) 3. Approval of Long-Term Integrated Perspective Plan (LTPP): 15-year plan for Defence Forces. 4. Monitoring Progress: Overseeing major projects based on feedback from the Defence Procurement Board.
|
Recent Approvals:
| · Procurement of weapons and equipment worth ₹22,800 crore focusing on indigenous design and manufacturing. · Approval for 24 Capital Acquisition Proposals worth ₹84,328 crore, with 97.4% from indigenous sources. |
Significance | · Enhances India’s defence capabilities. · Promotes ‘Make in India’ initiative. · Reduces dependency on foreign equipment.
|
2. Defence Acquisition Council (DAC)
CONTEXT: DAC approves amendment to MQ-9B UAV (AoN) deal with US
Formation: | Established in 2001 following the recommendations of the Group of Ministers on ‘Reforming the National Security System’ post-Kargil War.
|
Purpose | The highest decision-making body in the Ministry of Defence for new policies and capital acquisitions for the three services (Army, Navy, Air Force) and the Indian Coast Guard.
|
Chairperson | Defence Minister of India. |
Members:
| · Minister of State for Defence · Chief of Army Staff · Chief of Air Staff · Chief of Naval Staff · Defence Secretary · Secretary Defence Production · Secretary Defence R&D · Chief of Integrated Defence Staff · Director General Acquisition · Chief of Integrated Staff Committees HQ IDS
|
Functions:
| 1. Approval of AoN (Acceptance of Necessity): For Capital Acquisition Proposals. 2. Categorization of Acquisition Proposals: · ‘Buy’ (outright purchase) · ‘Buy and Make’ (purchase followed by licensed production/indigenous development) · ‘Make’ (indigenous production and R&D) 3. Approval of Long-Term Integrated Perspective Plan (LTPP): 15-year plan for Defence Forces. 4. Monitoring Progress: Overseeing major projects based on feedback from the Defence Procurement Board.
|
Recent Approvals:
| · Procurement of weapons and equipment worth ₹22,800 crore focusing on indigenous design and manufacturing. · Approval for 24 Capital Acquisition Proposals worth ₹84,328 crore, with 97.4% from indigenous sources. |
Significance | · Enhances India’s defence capabilities. · Promotes ‘Make in India’ initiative. · Reduces dependency on foreign equipment.
|
3. Quad Meeting: IPMDA And Key Takeaways
Quadrilateral Security Dialogue (Quad)
- Members: India, US, Australia, Japan
- Focus: Indo-Pacific region, maritime security, and democratic values
Key Decisions and Announcements
- Expansion of IPMDA: The Indo-Pacific Partnership for Maritime Domain Awareness (IPMDA) will be expanded to the Indian Ocean Region.
- Aim: Enhance maritime security and safety.
- Freedom of Navigation: Reaffirmed commitment to freedom of navigation and overflight, and unimpeded commerce.
- Implication: Counterbalancing China’s maritime assertiveness.
- Global Issues: Addressed conflicts in Ukraine, Gaza, and Myanmar.
- Called for immediate cessation of violence in all three regions.
- Expressed support for Ukraine’s sovereignty and territorial integrity.
- Condemned Hamas attacks on Israel but highlighted the humanitarian crisis in Gaza.
Urged Myanmar military to cease violence and allow humanitarian aid.
Significance if IPMDA
Aspect Importance
| Importance |
Security | Enhances maritime security (piracy, illegal fishing etc.)
|
Trade | Safeguards trade routes (vital for global economy)
|
Environment | Protects marine environment (pollution, resource management)
|
Cooperation | Strengthens regional cooperation (trust, information sharing)
|