1. Food Inflation and Retail Trends in India
Overview
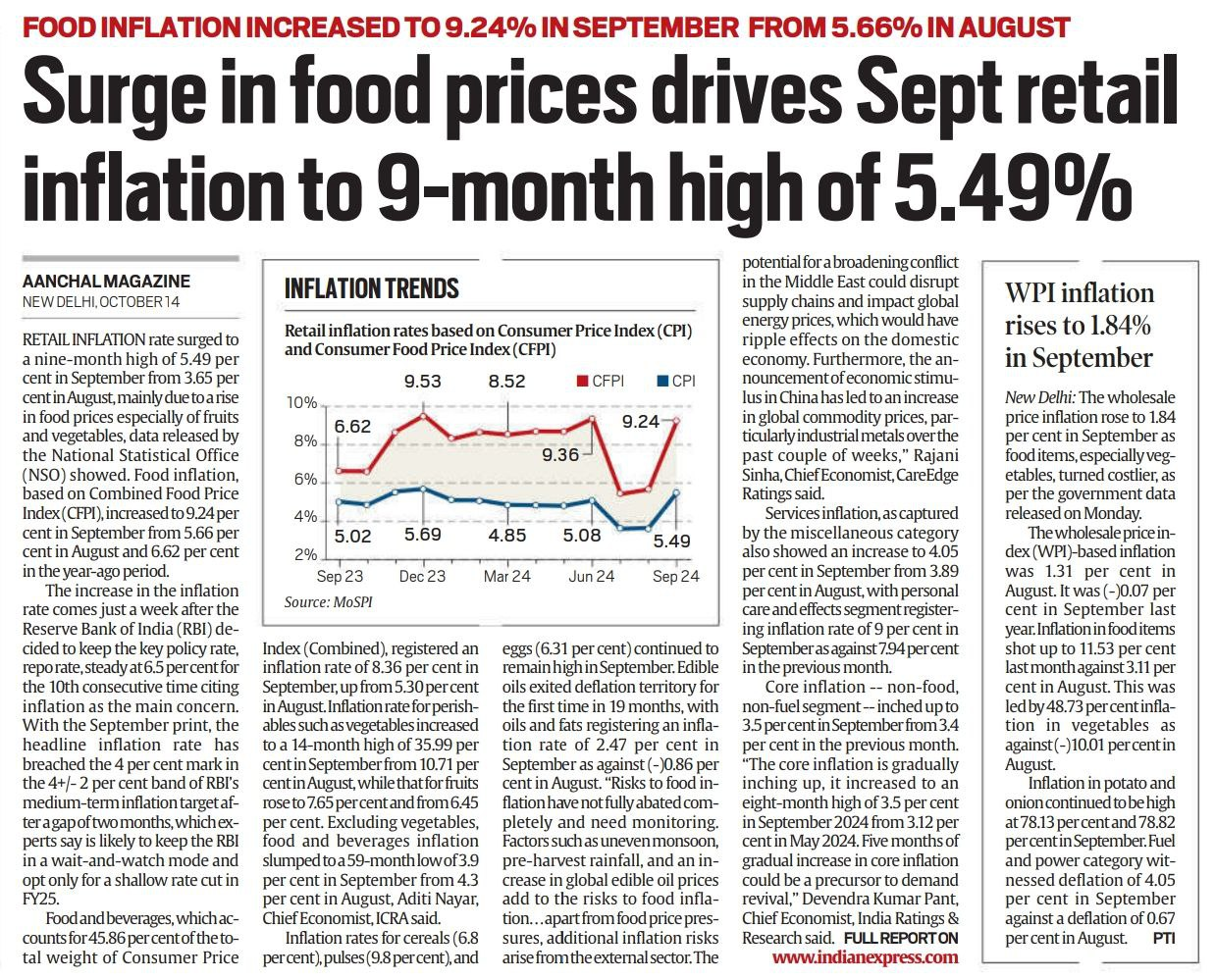
- Retail Inflation Rate: Increased to 49% in September 2024 from 3.65% in August, marking a nine-month high.
- Food Inflation: Rose to 24% in September from 5.66% in August and 6.62% in September 2023.
Key Factors Contributing to Inflation
- Surge in Food Prices: Significant increases in prices, especially for:
- Perishables: Vegetables saw inflation spike to 99% (14-month high) from 10.71% in August.
- Fruits: Inflation rose to 65% from 6.45%.
- Overall Food and Beverages Inflation: Increased to 36% in September from 5.30% in August.
- Core Inflation: Non-food, non-fuel segment rose slightly to 5% from 3.4% in August, indicating potential demand revival.
Specific Food Item Inflation
- Cereals: Inflation at 8%.
- Pulses: Inflation at 8%.
- Eggs: Inflation at 31%.
- Edible Oils: Shifted from deflation to 47% in September, indicating rising costs.
Economic Implications
- RBI Policy Response: The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) kept the repo rate steady at 5% for the tenth consecutive time, citing inflation concerns.
- Inflation Targeting: With inflation breaching the 4% mark, the RBI is likely to adopt a cautious approach in monetary policy, possibly delaying rate cuts.
External Influences
- Global Factors: Potential conflicts in the Middle East and China’s economic stimulus impacting global commodity prices could lead to further inflationary pressures.
- Weather Conditions: Uneven monsoon and pre-harvest rainfall are key domestic factors to monitor.
Wholesale Price Index (WPI) Trends
- WPI Inflation: Rose to 84% in September from 1.31% in August.
- Food Item Inflation (WPI): Increased to 53% in September from 3.11% in August, driven primarily by vegetables.
Specific Increases: Inflation in potatoes and onions at 78.13% and 78.82%, respectively.
2. NASA's Europa Clipper Mission
Overview
- Launch Date: October 14, 2024
- Mission Objective: Explore Jupiter’s moon Europa to investigate its potential for harboring life by analyzing ingredients necessary for life.
- Spacecraft: Europa Clipper, launched on a SpaceX Falcon Heavy rocket.
Mission Timeline
- Travel Duration: Approximately 5 years to reach Jupiter, expected arrival in 2030.
- Flybys: Planned 49 close flybys of Europa, enabling detailed study of its ice-covered ocean.
Key Features of Europa
- Icy Crust: Europa is believed to have a thick ice layer (15-24 km) over a global ocean that could be over 120 km deep.
- Potential for Life: The presence of a subsurface ocean makes Europa one of the most promising locations in the search for extraterrestrial life.
Scientific Goals
- Search for Ingredients: The mission will not look for life directly but will seek organic compounds and conditions suitable for life beneath the ice.
- Instruments: Clipper is equipped with nine scientific instruments designed to penetrate the ice and analyze the moon’s surface and subsurface.
Challenges and Precautions
- Radiation Exposure: The spacecraft will encounter significant radiation in Jupiter’s environment, equivalent to several million chest X-rays during its mission.
- Design Modifications: NASA had to address potential vulnerabilities in the spacecraft’s transistors due to this radiation.
Previous Missions and Context
- Historical Context: Prior missions, including the Pioneer and Voyager spacecraft, provided initial images of Europa. The Galileo spacecraft conducted detailed flybys in the 1990s.
- Future Missions: The European Space Agency’s JUICE (Jupiter Icy Moons Explorer) will arrive at Jupiter in 2025, complementing Clipper’s findings.
Broader Implications
- Habitability Insights: Discovering favorable conditions for life on Europa could imply similar possibilities on other ocean worlds, such as Saturn’s moon Enceladus.
Scientific Collaboration: This mission exemplifies international collaboration in space exploration, with a focus on understanding life beyond Earth.
3. Nobel Prize in Economic Sciences 2024
Overview
- Awarded To: Daron Acemoglu, Simon Johnson, and James A. Robinson for their studies on how institutions affect prosperity.
- Focus: The importance of societal institutions in determining economic success or failure of nations.
Key Concepts
- Inclusive vs. Extractive Institutions:
- Inclusive Institutions: Support democracy, rule of law, and protect property rights, leading to economic growth.
- Extractive Institutions: Concentrate power and resources, undermine growth, and create a system of exploitation.
Central Questions Addressed
- Why are some nations rich and others poor?
- What factors lead to the prosperity or failure of nations?
Historical Context
- The laureates explored the colonial history and its impact on present-day economic disparities.
- Found that the type of institutions established during colonization (inclusive vs. extractive) has long-term effects on prosperity.
India’s Case Study
- Historically, India had a robust industrial base pre-colonization, but institutional changes during British rule led to economic decline.
- Current institutions in India include:
- A democratic political system
- An independent judiciary
- Free media
Critiques and Counterarguments
- Arvind Subramanian’s Perspective: India and China present a challenge to the narrative:
- China has achieved economic growth without inclusive institutions.
- India has struggled despite having inclusive frameworks.
- The narrative is not absolute; both nations illustrate the complexity of institutional impacts over time.
Current Global Trends
- Acemoglu noted a global trend of weakening institutions and declining support for democracy.
- Emphasizes the need for better governance and accountability to restore faith in democratic systems.
Implications
- Understanding the role of institutions is critical for policymakers aiming to foster economic growth and improve governance.
Highlights the need for reforms that strengthen inclusive institutions to ensure sustainable development.